B3.1.3- the eye
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
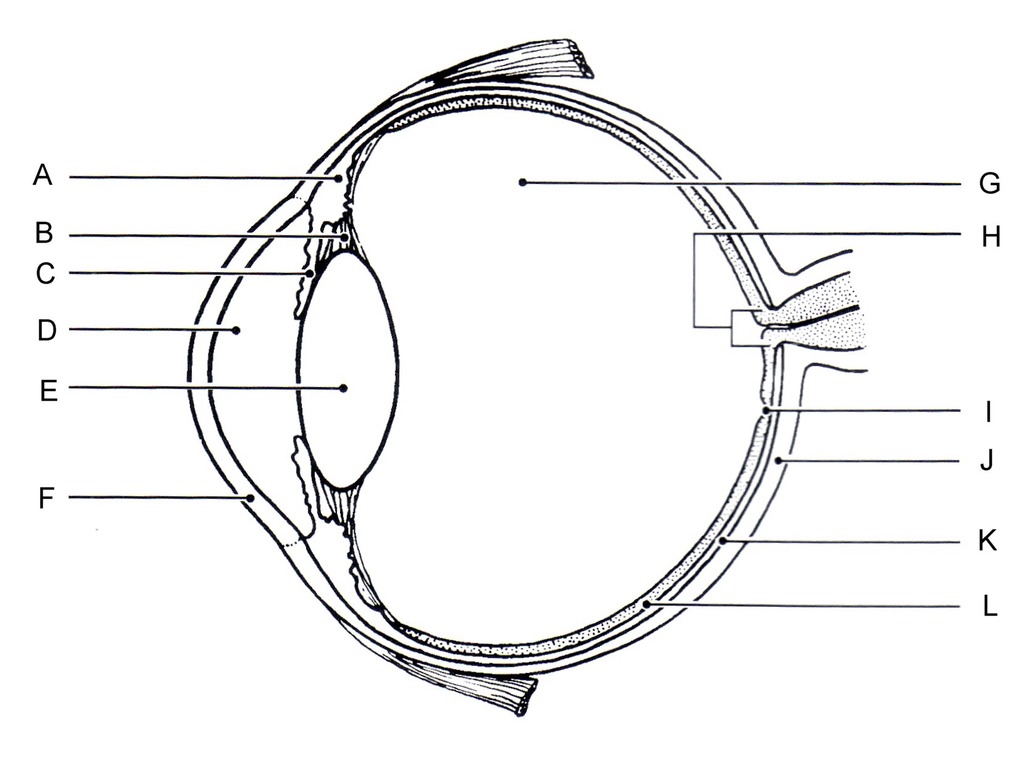
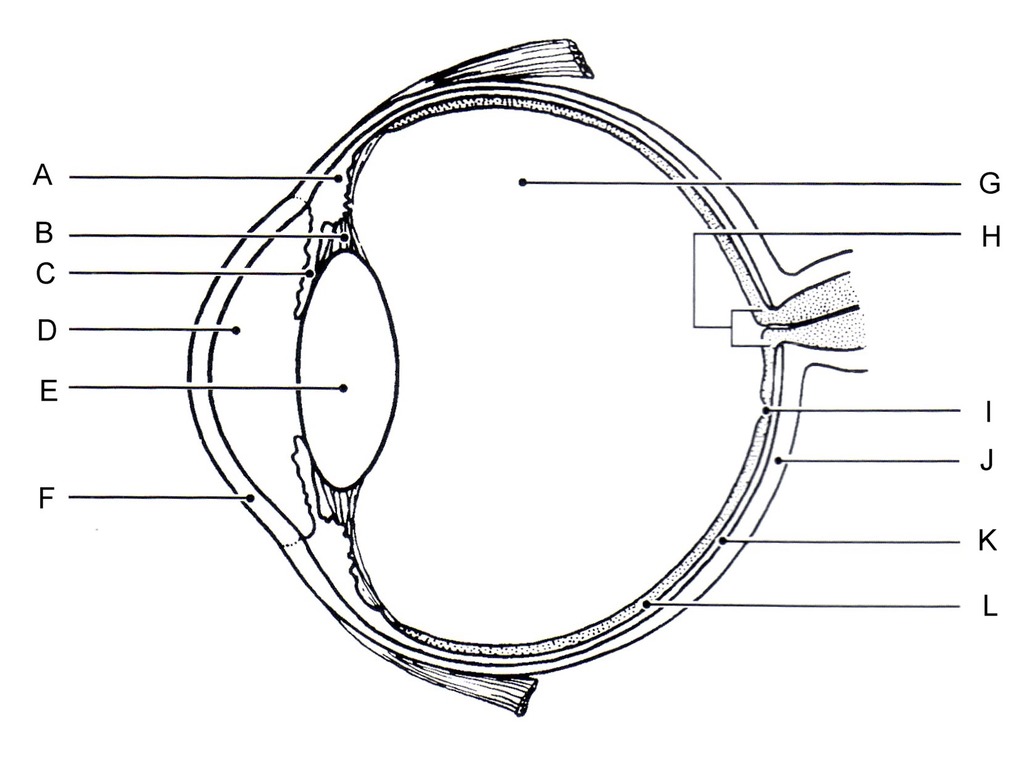
what are the features that make up the eye- A,B,C,D,E,F,H,L 7
E. lens- focuses light onto retina
B. suspensory ligaments- connects ciliary muscle to lens
A. ciliary muscle- alters shape of lens
C. iris- alters pupil size by contracting or relaxing
D. pupil- allows light to enter eye
H. optic nerve
F. cornea- protects eye
L. retina- light receptor
what is the process of you creating an image to your eyes 3
light comes through pupil
it then goes into the retina and produces a nerve impulse
this goes down the optic nerve to the brain where it produces a visual image.
what happens when your ciliary muscle CONTRACTS
your lens becomes fatter and MORE convex.
what happens when the ciliary muscle RELAXES
your lens becomes thinner and LESS convex
when your at a short sight where does the light go
in front of the retina
what do you need when you are short sighted and how does it help
a CONCAVE lens and it bends light outwards
when your sight is long where does the light go
behind the retina
what do you need when you are long sighted and how does it help
you need a convex lens which bends light inwards
what are the retinas 2 type of photoreceptors cells
Rod cells and Cone cells
what do Rod cells do
they respond to light and allow you to see in low light levels. they are NOT responsive to different colours
what do cone cells do
they respond to different colours. different Cone cells respond to red, blue, and green light