AP Macro Unit 4 - Financial Sector
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:30 PM on 4/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
1
New cards
Income
* Money earned from working
2
New cards
Wealth
* Value of accumulated assets
3
New cards
Assets
* Something you own that has value that can be converted into cash (liquified)
* Examples: cars, homes
* Examples: cars, homes
4
New cards
Liabilities
* A financial obligation that has to be paid back
* Examples: loans
* Examples: loans
5
New cards
Budget deficit
* Government spends more money in one year than it receives in tax revenue
6
New cards
Budget surplus
* Government receives more money in one year in tax revenue than its spends
7
New cards
National Debt
* Sum of all the budget deficits and budget surpluses added together
8
New cards
Liquidity
* The ease with which an asset can be accessed and converted into cash
* Cash is the most liquid asset
* Cash is the most liquid asset
9
New cards
Rate of Return
* Net gain or loss of an investment over a specific time period
10
New cards
Risk
* Chance that an outcome or an investment’s actual gains differ from the expected outcome
11
New cards
Bond
* An interest-bearing asset often issued by businesses or the government
* Also referred to as “securities”
* Sold by a firm with the expectation to be paid back with interest
* Also referred to as “securities”
* Sold by a firm with the expectation to be paid back with interest
12
New cards
Debt Financing
* Occurs when a company raises money by selling debt instruments to investors
* Opposite of Equity Financing
* The BORROWING of money to fund the company
* Opposite of Equity Financing
* The BORROWING of money to fund the company
13
New cards
Stock
* A security that gives you ownership in a company
* Sold on the Stock Market
* Prices are determined by company growth expectations
* Sold on the Stock Market
* Prices are determined by company growth expectations
14
New cards
Equity Financing
* Process of raising capital through the sell of shares
* Done to avoid debt
* Gives external control over management and profits of the firm
* Opposite of Debt Financing
* The SELLING of equity in the company
* Done to avoid debt
* Gives external control over management and profits of the firm
* Opposite of Debt Financing
* The SELLING of equity in the company
15
New cards
Loans
* The process of borrowing money and repaying it back with interest
* Agreement between a borrower and lender
* Can be an asset or a liability
* Types of loans:
* Credit cards
* Agreement between a borrower and lender
* Can be an asset or a liability
* Types of loans:
* Credit cards
16
New cards
Bank Deposits
* The money in your bank account
* AKA Demand Deposits
* Debit card
* AKA Demand Deposits
* Debit card
17
New cards
Bond Prices and Interest Rate have a(n) _______ relationship
* Inverse
* Why?
* Most bonds pay a fixed rate of interest so as interest rates fall in the economy, the bonds are more desirable and their prices rise
* Consumers are less interested in fixed-rate interest rates with a bond when interest rates in the economy are increasing, because they’ll get less in return than they can right now, so they demand less and the prices decrease
* Why?
* Most bonds pay a fixed rate of interest so as interest rates fall in the economy, the bonds are more desirable and their prices rise
* Consumers are less interested in fixed-rate interest rates with a bond when interest rates in the economy are increasing, because they’ll get less in return than they can right now, so they demand less and the prices decrease
18
New cards
Bonds
* IOUs issued by the government, or firms, with a fixed repayment date
* On that day, you get your money back plus the fixed interest rate agreed upon before hand
* Used to control the money supply
* Increase - buy bonds back from banks, giving money
* Decrease - sell bonds to banks, taking money
* On that day, you get your money back plus the fixed interest rate agreed upon before hand
* Used to control the money supply
* Increase - buy bonds back from banks, giving money
* Decrease - sell bonds to banks, taking money
19
New cards
Interest Rates
* Reward for saving money (deposit)
* Price for borrowing money (loan)
* Price for borrowing money (loan)
20
New cards
Nominal Interest Rates
* Interest rates that are not adjusted for the impact of inflation
* What is advertised by banks, investments, and debt issuers as the interest rate
* Always higher than real interest rates because it doesn’t take into account the continual loss of value in money
* What is advertised by banks, investments, and debt issuers as the interest rate
* Always higher than real interest rates because it doesn’t take into account the continual loss of value in money
21
New cards
Nominal Interest Rate Equation
* Real Interest Rate + Expected Inflation Rate
22
New cards
Real Interest Rates
* Interest rates that have been adjusted for the impact of inflation
* Investors can use this to estimate actual returns later on for when the value of money has changed
* Investors can use this to estimate actual returns later on for when the value of money has changed
23
New cards
Real Interest Rate Equation
* Nominal Interest Rate - Inflation
24
New cards
Discount Rate
* The interest rate at which the Federal Reserve lends money to banks
* The interest rate banks are charged to borrow money from the FED
* If it increases, lending becomes more expensive and the money supply decreases
* If it decreases, lending becomes less expensive and the money supply increases
* The interest rate banks are charged to borrow money from the FED
* If it increases, lending becomes more expensive and the money supply decreases
* If it decreases, lending becomes less expensive and the money supply increases
25
New cards
Fiat Money
* Something that serves as money or currency and has no other uses
* Examples:
* Paper money
* Coins
* Examples:
* Paper money
* Coins
26
New cards
Commodity Money
* Something that performs the function of money and has alternative, non-monetary use
* Examples:
* Gold
* Silver
* Other precious metals
* Oil
* Tobacco
* Examples:
* Gold
* Silver
* Other precious metals
* Oil
* Tobacco
27
New cards
Time Value of Money Equations (Present and Future)
\

28
New cards
Functions of Money
* Medium of Exchange
* Used to buy goods and services without complications of bartering
* Unit of Account
* Used to measure the value of goods and services
* Store of Value
* Used to preserve or save purchasing power for future consumption
* Used to buy goods and services without complications of bartering
* Unit of Account
* Used to measure the value of goods and services
* Store of Value
* Used to preserve or save purchasing power for future consumption
29
New cards
Money Supply
* Constant - vertical supply curve
30
New cards
Money Supply Equation
* M1 + M2
31
New cards
M1
* Coins, paper currency, and checkable deposits, including checking accounts and debit accounts
* High liquidity
* Acts as a Medium of Exchange
* High liquidity
* Acts as a Medium of Exchange
32
New cards
M1 Equation
cash + coins + checking deposits + traveller’s checks
33
New cards
M2
* Measure of the money supply that includes all elements of M1 as well as “near money” (savings deposits, money market securities, mutual funds, and other time deposits)
* Medium liquidity
* Acts as a Store of Value
* Medium liquidity
* Acts as a Store of Value
34
New cards
M2 Equation
M1 + savings deposits + small time deposits + money market deposits + money market mutual funds
35
New cards
Monetary Base (M0 or MB)
* Refers to the money in circulation or in bank reserves
* The physical paper and coin currency used in the economy and bank deposits
* NOT included in the money supply
* The physical paper and coin currency used in the economy and bank deposits
* NOT included in the money supply
36
New cards
Monetary Base Equation
Currency in circulation + Bank reserves
37
New cards
Fractional Reserve Banking
* Practice by which a bank accepts deposits and is required to hold only a fraction of its deposits in cash reserves
38
New cards
Reserve Ratio/Reserve Requirement
* Set by the Federal Reserve
* Amount (in percentage) of demand deposits the bank has to hold in reserve
* If it decreases, there is more money available to loan out, and the money supply increases
* If it increases, there is less money available to loan out, and the money supply decreases
* Amount (in percentage) of demand deposits the bank has to hold in reserve
* If it decreases, there is more money available to loan out, and the money supply increases
* If it increases, there is less money available to loan out, and the money supply decreases
39
New cards
Demand Deposits
* A deposit of money left in a bank that can be withdrawn without prior notice by the account holder
40
New cards
Excess Reserves
* The remainder of every demand deposit after required reserves are held
* Turned into new loans - what is multiplied through the economy to “make new money”
* Turned into new loans - what is multiplied through the economy to “make new money”
41
New cards
Money Multiplier
* Amount of money banks generate with each dollar of excess reserves
* Take the new loans and multiply that amount by this number to find the amount of money generated by banks
* Take the new loans and multiply that amount by this number to find the amount of money generated by banks
42
New cards
Money Multiplier Equation
* 1 / (reserve ratio)
43
New cards
Bank Balance Sheets
* Visual records of fractional reserve banking within a bank
* Shows the assets and liabilities of a bank
* Assets and liabilities must equal each other
* Shows the assets and liabilities of a bank
* Assets and liabilities must equal each other
44
New cards
Liabilities (Banking Industry)
* Financial obligations a bank must pay to a customer, and must be repaid when requested
* Examples:
* Demand Deposits
* Account investments
* Equity
* Examples:
* Demand Deposits
* Account investments
* Equity
45
New cards
Assets (Banking Industry)
* Possessions that are owned or credited to a bank that can be collected or liquified into cash
* Examples:
* Required reserves
* Excess reserves
* Outstanding loans
* Securities
* Examples:
* Required reserves
* Excess reserves
* Outstanding loans
* Securities
46
New cards
There is a(n) _______ relationship between nominal interest rates and the quantity of money demanded
* Inverse
* Why?
* The opportunity cost to hold wealth in the form of money instead of the form of other assets is nominal interest rate
* When interest rates are low, the opportunity cost is lower, so people opt to hold wealth in money because they will have more chance to gain more in other investments than depositing their money in banks
* Why?
* The opportunity cost to hold wealth in the form of money instead of the form of other assets is nominal interest rate
* When interest rates are low, the opportunity cost is lower, so people opt to hold wealth in money because they will have more chance to gain more in other investments than depositing their money in banks
47
New cards
Demand for Money
* People demand money in transaction demand (to buy stuff) and asset demand (liquid asset vs non-liquid asset)
48
New cards
Shifters for the Demand of Money curve
* Price Level
* Real GDP
* Transaction costs
* Real GDP
* Transaction costs
49
New cards
When RGDP increases, the demand for money…
increases
50
New cards
Supply of Money
* Vertical line on the Demand for Money graph
* Unrelated to the interest rate - set by the FED
* Unrelated to the interest rate - set by the FED
51
New cards
Shifters for the Supply of Money curve
* Reserve Requirement
* Discount Rate
* Open Market Operations
* Discount Rate
* Open Market Operations
52
New cards
Money Market Equilibrium
* Quantity of money demanded is equal to quantity of money supplied
53
New cards
Open Market Operations (securities)
* The FED buys or sells bonds
* When the FED buys bonds, money is injected into the economy and the money supply increases
* When the FED sells bonds, money is taken out of the economy and the money supply decreases
* When the FED buys bonds, money is injected into the economy and the money supply increases
* When the FED sells bonds, money is taken out of the economy and the money supply decreases
54
New cards
Shifters for the Demand for Money curve
* PL (Inflation)
* Inflation increases, demand for money increases
* Income
* Income increases, demand for money increases
* Technology
* Products like ApplePay and GooglePay have decreased demand for money
* Inflation increases, demand for money increases
* Income
* Income increases, demand for money increases
* Technology
* Products like ApplePay and GooglePay have decreased demand for money
55
New cards
Demand for Money curve
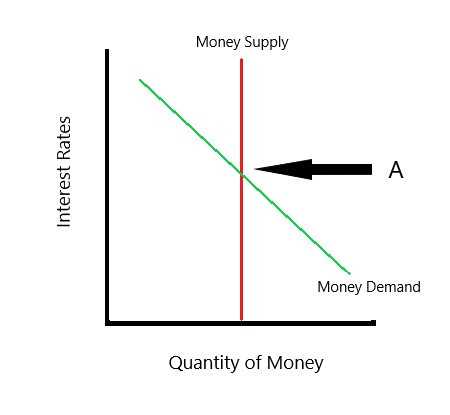
56
New cards
Interest on Reserves (IOR)
* The FED pays interest on reserves, encouraging banks to keep more deposits in reserve and loan less out
* Decreasing will increase the money supply
* Increasing will decrease the money supply
* Decreasing will increase the money supply
* Increasing will decrease the money supply
57
New cards
Investment Demand
* The desired quantity of investment spending by firms across the economy on physical capital and other resources for the purpose of future productivity/profitability
58
New cards
There is a(n) _______ relationship between nominal interest rates and the quantity of investment demanded
* Inverse
* When interest rates fall, investment increases
* When interest rates rise, investment decreases
* When interest rates fall, investment increases
* When interest rates rise, investment decreases
59
New cards
Expansionary Monetary Policy
* AKA Easy Monetary Policy
* Increase money supply
* Increase RGDP output
* Increase money supply
* Increase RGDP output
60
New cards
Contractionary Monetary Policy
* AKA Tight Monetary Policy
* Decrease money supply
* Decrease RGDP output
* Decrease money supply
* Decrease RGDP output
61
New cards
Tools of Monetary Policy
* Discount Rate
* Reserve Ratio
* Open-Market Operations
* Federal Funds Rate
* Reserve Ratio
* Open-Market Operations
* Federal Funds Rate
62
New cards
Discount Rate
* The interest rate the Federal Reserve charges commercial banks to borrow money directly from the Treasury
63
New cards
Low discount rate causes…
… banks to borrow more because it’s cheaper, increasing the money supply
64
New cards
High discount rate causes…
… banks borrow less because it’s more expensive, decreasing the money supply
65
New cards
Reserve Ratio
* AKA Reserve Requirement
* Portion or percentage of all new demand deposits that banks must hold in reserve and cannot lend
* Portion or percentage of all new demand deposits that banks must hold in reserve and cannot lend
66
New cards
High Reserve Ratio causes…
… less money to be leant out, decreasing the money supply
67
New cards
Low Reserve Ratio causes…
… more money to be leant out, increasing the money supply
68
New cards
Open Market Operations
* Most popular tool used by the Federal Reserve
* Involves the buying and selling of treasury bonds
* Involves the buying and selling of treasury bonds
69
New cards
When the Federal Reserve buys bonds…
… it gives money to banks, increasing the money supply
70
New cards
When the Federal Reserve sells bonds…
… it takes money from the banks, decreasing the money supply
71
New cards
Federal Funds Rate
* The interest rate that commercial banks and depository institutions borrow money directly from each other
72
New cards
High Federal Funds Rate causes…
… borrowing money to be more expensive, so banks borrow less and decrease the money supply
73
New cards
Low Federal Funds Rate causes…
… borrowing money to be less expensive, so banks borrow more and increase the money supply
74
New cards
Low Nominal Interest Rate causes…
… an increase in Quantity of Investment Demanded, which will increase Aggregate Demand
75
New cards
High Nominal Interest Rate causes…
… a decrease in Quantity of Investment Demanded, which will decrease Aggregate Demand
76
New cards
Loanable Funds Market
* The interaction of borrowers and savers in the economy
* Borrowers demand loanable funds
* Savers supply loanable funds
* Borrowers demand loanable funds
* Savers supply loanable funds
77
New cards
Loanable Funds Market Equilibrium
* Real Interest Rate is adjusted so that the amount of borrowing is equal to the amount of saving
78
New cards
Demand of Loanable Funds
* The quantity of credit wanted and needed at every real interest rate by borrowers in an economy
79
New cards
When interest rates ____, the demand for loanable funds _______
When interest rates *rise*, the demand for loanable funds *decrease*
80
New cards
Shifters for Demand of Loanable Funds
* FADE
* Foreign Demand for Domestic Currency
* All Borrowing, Lending, and Credit
* Deficit Spending
* Expectations for the Future
* Foreign Demand for Domestic Currency
* All Borrowing, Lending, and Credit
* Deficit Spending
* Expectations for the Future
81
New cards
Foreign Demand for Domestic Currency
* Foreign investors want more of a country’s money to make purchases of that country’s goods and services, so the demand for the country’s currency increases
* When the demand for a country’s currency increases, the demand for loanable funds decreases
* When the demand for a country’s currency increases, the demand for loanable funds decreases
82
New cards
All Borrowing, Lending, and Credit
* Increase in loans, credit, and borrowing by consumers and firms leads to an increase in demand for loanable funds
83
New cards
Deficit Spending
* When the government spends more money than is being brought in with tax revenue
* If the government spends more, there is an increase in demand for loanable funds to cover costs not covered by tax revenue
* If the government spends more, there is an increase in demand for loanable funds to cover costs not covered by tax revenue
84
New cards
Crowding Out
* Government borrowing drives up the interest rate on loanable funds and decreases private investment
* The amount of private investing decreases because less people want to take out loans with an increased interest rate, but the overall quantity of loanable funds increases because of government borrowing
* The amount of private investing decreases because less people want to take out loans with an increased interest rate, but the overall quantity of loanable funds increases because of government borrowing
85
New cards
Expectations for the Future
* If there are predictions for future growth, there will be an increase in demand for loanable funds
* Businesses are willing to take out loans to improve and invest in their business
* Consumers are confident in the economy and feel comfortable taking out loans
* Concerns about the economy will lead to a decrease in demand for loanable funds
* Businesses are willing to take out loans to improve and invest in their business
* Consumers are confident in the economy and feel comfortable taking out loans
* Concerns about the economy will lead to a decrease in demand for loanable funds
86
New cards
Supply of Loanable Funds
* The quantity of credit provided at every real interest rates by banks and other lenders in an economy
87
New cards
When interest rates __, the supply of loanable funds ______
When interest rates *rise*, the supply of loanable funds *increase*
88
New cards
Determinants for the Supply of Loanable Funds
* SELF
* Savings Rate
* Expectations for the Future
* Lending at the Discount Window
* Foreign Purchases of Domestic Assets
* Savings Rate
* Expectations for the Future
* Lending at the Discount Window
* Foreign Purchases of Domestic Assets
89
New cards
Savings Rate
* When consumers put more money into savings, demand deposits increase, increasing the reserves banks can loan out, increasing the supply of loanable funds
90
New cards
Expectations for the Future
* When the economy contracts, consumers will put more money into banks, giving banks more reserves to loan out, increasing the supply of loanable funds
91
New cards
Lending at the Discount Window
* When the discount rate is lowered by the Fed, banks are more willing to borrow funds, increasing the supply of loanable funds
92
New cards
Foreign Purchases of Domestic Assets
* A foreign investor decides to buy domestic assets, such as bonds, and puts more money in the banking system and increases the supply of loanable funds