Cancer Associated Venous Thromboembolic disease
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Patient risk factors for CAT:
· Advanced age
· Obesity
· Hospitalization
· Poor performance status
· History of VTE
· Platelets >350
· Leukocytes >11
Elevated inflammatory markers (d-dimer, TF, CRP)
Cancer Risk factors for CAT:
· Pancreas
· Brain
· Lung
· Ovarian
· GI/gastric
· Kidney
· Lymphoma
· Myeloma
· Metastatic cancer
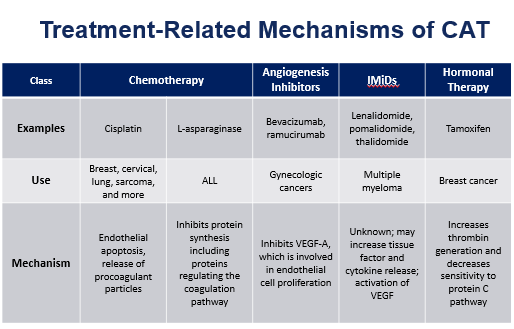
Treatment risk factors for CAT:
· Hospitalization
· Chemotherapy (
· Angiogenesis inhibitors
· Immunomodulators
· Hormonal therapy
· Immunotherapy
· Surgery
· Radiation therapy
· Central venous catheters
What is DVT?
§ Clot in a deep vein, such as the leg or arm
§ Symptoms:
· Redness
· Swelling
· Pain
· typically, unilateral
What is a PE?
§ Occurs when DVT breaks from a vein wall, travels to the lungs, and blocks blood supply.
§ Symptoms:
· Dyspnea
· Cough
· shortness of breath
What is Catheter associated VTE?
§ Occurs due to endothelial irritation and coagulation from central venous catheter or peripheral line.
§ May occur in upper extremity.
§ VTE is a common cause of death and complication in patients with cancer.
What is the pathophysiology of CAT?
§ Pro-coagulation factors:
· Tissue factor leads to thrombin and fibrin formation.
§ Fibrinolytic activities:
· Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 ( PAI-1)
§ Platelet activation:
· ADP, thromboxane A2 (TxA20, CD40L
§ Endothelial damage:
· Cytokine release from cancer cells of WBCs
What are the NCCN Guidelines for treatment of CAT?
§ In the absence of contraindications, DOACs, LMWH, and warfarin can be considered for treatment of cancer associated VTE:
· DOACs preferred for patients without gastric or gastroesophageal lesions:
o Apixaban (category 1)
o Edoxaban (category 1)
o Rivaroxaban
§ LMWH preferred for patients with gastric or gastroesophageal lesions:
· Dalteparin (category 1)
· Enoxaparin
§ Alternative Agents :
· Warfarin
· Dabigatran
· Fondaparinux
· UFH
§ Duration of treatment:
· At least 6 months if provoked.
· Indefinite if active cancer, persistent thrombophilic state, or unprovoked
What are some considerations of DOAC use?
§ Patients with gastric or gastroesophageal lesions:
· Major bleed risk, including the risk of GI bleed limits the use of DOACs
Hokusai VTE (2018):
§ Compared Edoxaban to Dalteparin
§ Edoxaban 60 mg po daily following LMWH > 5 days for at least 6 months.
§ Dalteparin 200 IU/kg SC Q24Hrs x30 days , followed by 150 IU/kg SC Q24Hrs for at least 6 months.
§ Results:
· Edoxaban is non-inferior for treatment of CAT but has increased bleeding risk.
Select-D (2018):
§ Compared Rivaroxaban to Dalteparin
§ Excluded patients with primary esophageal or gastro-esophageal cancer ( due to interim safety analysis-concerns for bleeding).
§ Rivaroxaban:
· Initial dose: 15 mg po bid x 21 days.
· Maintenance dose: 20 mg po daily for at least 6 months.
§ Dalteparin: 200 IU/kg SC Q24Hrs x30 days, followed by 150 IU/kg SC Q24Hrs for at least 6 months.
§ Failed to meet power to compare efficacy and safety.
§ Results:
· Rivaroxaban decreased the risk of VTE recurrence but increased the risk of bleeding.
CARAVAGGIO (2020):
§ Compared Apixaban to Dalteparin.
§ Apixaban:
· Initial dose: 10 mg po bid x7 days.
· Maintenance dose: 5 mg po bid or at least 6 months.
§ Results:
· Apixaban is non-inferior to dalteparin for treatment of CAT.
· Reduced risk of recurrent VTE.
· No increased risk of major bleeding.
Medications for the treatment of CAT:
§ Edoxaban (Savaysa):
· Dose: 60 mg po daily ; if <60 kg: 30 mg.
· Renal Function: Avoid if CrCl > 95 ; CrCl 15-50: 30 mg ; CrCl < 15: Avoid.
· Use A Parenteral Overlap for 5 days before starting Edoxaban.
§ Rivaroxaban (Xarelto):
· Dose: 15 mg po bid x21 days , then 20 mg po daily with food.
· Renal Function: Avoid if CrCl <30.
· No parenteral overlap
§ Apixaban (Eliquis):
· Dose: 10 mg po bid x7 days, then 5mg po bid.
· Renal Function: can be used in all types of renal function.
· No parenteral overlap.
What are some absolute contraindications to anticoagulation therapy?
· Active bleeding (major)
· Indwelling neuraxial catheters
· Neuraxial anesthesia/lumbar puncture
· Interventional spine and pain
What are the relative contraindications to anticoagulation therapy?
· Clinically significant measurable bleeding
· Thrombocytopenia (platelets <30-50)
· Underlying coagulopathy
· Severe platelet dysfunction
· Recent surgery at high risk for bleeding
· High fall risk
· Primary and metastatic brain tumors
· Long term antiplatelet therapy
NCCN Inpatient VTE/PE Prophylaxis guidelines:
· Recommended for patients with confirmed or suspected cancer diagnosis.
· UFH or LMWH (has a short half-life).
ASCO inpatient VTE/PE Prophylaxis guidelines:
· Recommended for patients with active cancer and acute medical illness or reduced mobility.
· Not recommended for patients with minor procedures or chemotherapy infusions.
ASH inpatient VTE/PE prophylaxis guidelines:
· Recommended for acutely ill hospitalized medical patients.
· UFH, LMWH, or fondaparinux preferred over DOACs.
Outpatient VTE/PE Prophylaxis:
§ Khorana Score
§ Intermediate to high-risk score >2:
· Consider anticoagulant prophylaxis for up to 6 months or longer.
· Low risk VTE: < 2:
o No routine prophylaxis.
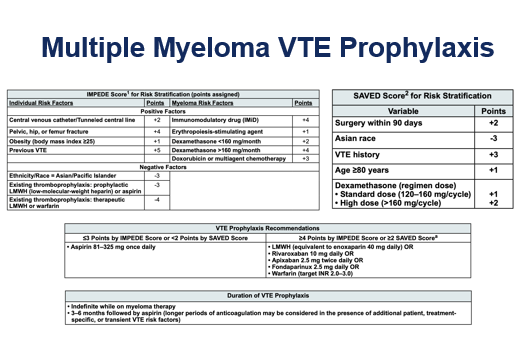
Multiple Myeloma:
§ Increased risk of VTE due to pathophysiology.
§ Highest risk of VTE is within 6 months of diagnosis.
§ Increased risk with treatment (immunomodulatory drugs).