Unit 11: Evolution
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/94
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
1
New cards
Evolve
Change
2
New cards
Microevolution
Any change in allele frequency in the gene pool of a population
3
New cards
Macroevolution
An accumulation of many small genetic changes that result in the formation of a new species from a pre-exsiting species
4
New cards
What are the two theories to how Earth formed?
1. Intelligent design/ creationism (God created)
2. The Big Bang Theory
5
New cards
What is The Big Bang Theory?
* All matter in entire universe condensed in one location
* Explodes, everything/particles goes flying
* Gases and reactions following explosion forms galaxies, planets, suns, ect.
* Earth was super hot from explosion and cooled to form a crust
* Earth has solid iron core and has magma under crust
* Explodes, everything/particles goes flying
* Gases and reactions following explosion forms galaxies, planets, suns, ect.
* Earth was super hot from explosion and cooled to form a crust
* Earth has solid iron core and has magma under crust
6
New cards
When does The Big Bang Theory say Earth was formed?
4\.5 billion years ago
7
New cards
When does intelligent design say Earth was formed?
12,000 - 200,000 years ago
8
New cards
Where does Oparin’s Hypothesis say CHNO (part of SCHNOP) came from?
Simple gas molecules
9
New cards
Where does Oparin’s Hypothesis say carbon (C) came from?
Methane gas (CH4)
10
New cards
Where does Oparin’s Hypothesis say hydrogen (H) came from?
Hydrogen gas (H2)
11
New cards
Where does Oparin’s Hypothesis say nitrogen (N) came from?
Ammonia gas (NH2)
12
New cards
Where does Oparin’s Hypothesis say oxygen (O) came from?
Water vapor (H2O)
13
New cards
What is Oparin’s Hypothesis?
* Methane gas, hydrogen gas, ammonia gas, and water vapor collided and reacted with each other because of all the energy present where eventually organic molecules formed
* They rained down into the seas (“Organic soup”) while continuing reacting with each other
* Lots of time passes then 1st cells are made
* They rained down into the seas (“Organic soup”) while continuing reacting with each other
* Lots of time passes then 1st cells are made
14
New cards
What are examples of energy present that caused organic molecules to form?
* Heat
* Light
* Radiation
* Lightning
* Volcanic eruptions
* Light
* Radiation
* Lightning
* Volcanic eruptions
15
New cards
What is Miller’s test?
* Tested Oparin’s hypothesis
* Uses distillation apparatus (made of glass tubing)
* Created water cycle
* Let experiment run for 24 hours
* Uses distillation apparatus (made of glass tubing)
* Created water cycle
* Let experiment run for 24 hours
16
New cards
What were the results of Miller’s test?
Second time run: 2 amino acids (Glycine & Alanine)
17
New cards
How many years ago is Earth said to have been created according to the Big Bang Theory?
4\.5 billion years ago
18
New cards
How many years ago were the 1st cells said to have been created according to the Oparin’s hypothesis?
3\.5 billion years ago
19
New cards
How many years ago were the 1st cyanobacteria said to have been created?
2\.5 billion years ago
20
New cards
Why is the appearance of the 1st cyanobacteria important?
They photosynthesize and bring oxygen into the air
21
New cards
How many years ago were the 1st eukaryote cells said to have been created?
1\.5 billion years ago (took 2 billion years to develop)
22
New cards
What are the first cells according to Oparin’s hypothesis?
* Cell membrane
* Cytoplasm
* RNA
* Ribosomes
* Cytoplasm
* RNA
* Ribosomes
23
New cards
What are the traits of the first cells according to Oparin’s hypothesis?
* Anaerobic (no oxygen in air)
* Aquatic (formed in water)
* Glycolysis (1st respiration process)
* Smaller
* Divided A-sexually by fission
* Heterotrophs (ate each other)
* Chemosynthesis (ate inorganic food)
* Did not photosynthesize
* Aquatic (formed in water)
* Glycolysis (1st respiration process)
* Smaller
* Divided A-sexually by fission
* Heterotrophs (ate each other)
* Chemosynthesis (ate inorganic food)
* Did not photosynthesize
24
New cards
What are fossils?
Remains of past life
25
New cards
What are the different kinds of fossils?
1. Could be an imprint (perfect impression)
2. Could be cast (stone replica)
26
New cards
What can be learned from fossils?
How the organism died, what lived with it (past life)
27
New cards
What are the methods of fossilization?
1. Tar pits
2. Ice caves
3. Amber
4. Volcanic ash
5. Peat bog
6. Sedimentary rock
28
New cards
What is amber?
Crystalized tree sap
29
New cards
What does amber fossilize?
Small animals/insects
30
New cards
What is a peat bog?
Muddy swamp like quicksand that is acidic
31
New cards
What is the most common method of fossiliztion?
Sedimentary rock
32
New cards
What is relative dating?
Comparing the age of fossils by observing how deep they are in the rock layer
33
New cards
What is absolute dating?
Using radioactive isotopes to find age
34
New cards
Is it better to have long or short half life for absolute dating?
Longer
35
New cards
What is half life?
The time it takes for half of radioactive material to decay
36
New cards
How do you use absolute dating?
* Guess the measurement of grams of radioactive isotope at death
* Calculate grams to half life of radioactive isotope till get 1 gram
* Calculate grams to half life of radioactive isotope till get 1 gram
37
New cards
Why isn’t absolute dating perfect or always accurate?
* Number of grams is only an estimate
* Measured assuming constant half life rate
* Measured assuming constant half life rate
38
New cards
What is the geologic time scale?
The entire history of Earth (includes history of life)
39
New cards
What is the geologic time scale divided up into?
Four eras of time
40
New cards
What are eras divided up into?
Periods
41
New cards
What are periods divided up into?
Epoch
42
New cards
What are the four eras of time?
1. Precambrian
2. Paleozoic
3. Mesozoic
4. Cenozoic
43
New cards
When was the Precambrian era?
4600-543 years ago (4 billion years long)
44
New cards
When was the Paleozoic era?
543-245 years ago (250 million years long)
45
New cards
When was the Mesozoic era?
245-65 million years ago (180 million years long)
46
New cards
What is considered to be the age of dinosaurs?
Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous periods in the Mesozoic era
47
New cards
What is our current era?
The Cenozoic era
48
New cards
When was the Cenozoic era?
65 million years ago - current time
49
New cards
What is the trend that ends an era?
Mass extinction of life (though some survive)
50
New cards
Why are eras getting shorter?
Change is happening faster
51
New cards
What should be seen in the fossil record?
Lots of gradualism, small steady changes over time to get to modern species
52
New cards
Why isn’t the fossil record not perfect evidence of macroevolution?
* Not seen in most species
* Record is incomplete, can miss species
* Not always interpreted correctly
* No way to know if correct
* Can’t always go off DNA or appearance
* So much unknown
* Record is incomplete, can miss species
* Not always interpreted correctly
* No way to know if correct
* Can’t always go off DNA or appearance
* So much unknown
53
New cards
What are homologous structures?
Has similar bone/internal structure/pattern, don’t have same function
54
New cards
What is an explanation for homologous structures?
Common ancestor
55
New cards
What are vestigial structures?
Left over/extra reminate body parts no one of species uses
56
New cards
What is an explanation for vestigial structures?
Had a common ancestor that once used the body part
57
New cards
Can you live without a vestigial body part?
Yes
58
New cards
What are examples of vestigial structures?
* Human coccyx (tailbone)
* Human appendix
* Human appendix
59
New cards
What are homologous vertebrate embryos?
When all vertebrate (backboned) at some point goes through stage when embryo
60
New cards
What are physical traits of being homologous vertebrate embryos?
* Curved spine, ends at tail
* Big eyes
* 4 limb buds
* Gill slits
* Big eyes
* 4 limb buds
* Gill slits
61
New cards
What is an explanation for homologous vertebrate embryos?
Common ancestor
62
New cards
What is the most important difference between species that beats all others?
Developmental (homologous vertebrate embryos)
63
New cards
What are homologous molecules?
2 main molecules compared between species: DNA gene sequence and proteins
64
New cards
What is an explanation for homologous molecules?
Common ancestor
65
New cards
What is Lamarck’s theory?
1. Inheritance of acquired characteristics (wrong- anything you inherit must come from DNA)
2. Vestigial organs go away if we decide we don’t need them anymore (wrong- not choice, though over time could possibly disappear)
3. Organisms have an innate desire to change (wrong- change isn’t a choice)
66
New cards
Who is Charles Darwin?
Considered the father of modern evolution
67
New cards
What is Darwin’s story on the Galapagos Islands?
* Found 13 different kinds of finch (only 1 kind in Ecuador)
* Guess original had children with different beak mutations, had to find new food
* Kept alive because no predators, no competition
* Don’t reproduce together by choice
* Guess original had children with different beak mutations, had to find new food
* Kept alive because no predators, no competition
* Don’t reproduce together by choice
68
New cards
What are Darwin’s observations?
1. There is variation within a population
2. More organisms are produced than the environment can support
3. Population size remains constant over time
4. The Earth is slowly but constantly changing
69
New cards
What is Darwin’s theory of macroevolution?
1. There is fierce competition for resources
2. Natural selection
3. What is considered fit to survive is constantly changing as environment is constantly changing
70
New cards
What is fitness?
* Whatever helps you survive better
* Lives long enough to pass fit trait, reproduce
* Adaptations are fit traits
* Eventually everyone in population will have fit trait, those without had died
* Lives long enough to pass fit trait, reproduce
* Adaptations are fit traits
* Eventually everyone in population will have fit trait, those without had died
71
New cards
What is natural selection?
* Main mechanism for change
* Nature/environment determines fitness
* Nature/environment determines fitness
72
New cards
How much life has gone extinct? Why?
95%, couldn’t mutate and change with environment
73
New cards
What is speciation?
The making/forming of new species from a pre-existing species
74
New cards
What are species (only applies to animals)?
* Must naturally mate/reproduce in wild
* Offspring viable (they must be able to reproduce when they grow up)
* Both criteria must be met to be determined as the same species
* Offspring viable (they must be able to reproduce when they grow up)
* Both criteria must be met to be determined as the same species
75
New cards
What is allopatric specation?
* Geographic barrier causing split in species
* Reproductive isolation
* Each population gets different mutations till becoming different species
* Reproductive isolation
* Each population gets different mutations till becoming different species
76
New cards
What is sympatric speciation?
* In same location
* A group gets mutation
* Can still reproduce together
* Mutated and normal group may choose to reproduce separately, eventually becoming a new species
* A group gets mutation
* Can still reproduce together
* Mutated and normal group may choose to reproduce separately, eventually becoming a new species
77
New cards
What is adaptive radiation?
When one species enters a new territory and quicky radiates out into multiple species (all shares common ancestor)
78
New cards
Why is adaptive radiation possible?
* No competition, no preators in new area
* Can adapt to different environments predators to fill different niches in area
* Can adapt to different environments predators to fill different niches in area
79
New cards
What is an example of adaptive radiation?
Darwin’s finches
80
New cards
What is convergent evolution?
Two different unrelated species in different locations evolve similarly, has similar adaptations
81
New cards
Why is convergent evolution possible?
* They live in similar environments
* Natural selection is similar
* Natural selection is similar
82
New cards
What is an example of convergent evolution?
Sugar glider (Australia) & flying squirrel (North America)
83
New cards
What are analogous structures?
* Similar adaptations to different species
* Looks similar outwardly
* Has same function
* Different origin
* Different inside
* Exact opposite of homologous structures
* Looks similar outwardly
* Has same function
* Different origin
* Different inside
* Exact opposite of homologous structures
84
New cards
What is gradualism?
Small gradual changes in species over time (very rare)
85
New cards
What is equilibrium?
Species doesn’t change at all, living fossils (species millions of years old that still exist today: sharks)
86
New cards
What is punctuated equilibrium?
Short burst of rapid change (most common)
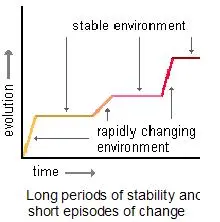
87
New cards
What could cause rapid change in punctuated equilibrium?
* Big natural disasters
* New species migrated
* New species migrated
88
New cards
What are the 5 conditions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (no change in allele frequency of a gene pool)?
1. No mutations (can’t create new allele or change allele)
2. No natural selection (everyone must be equally fit, has equal chance of survival)
3. No migration in or out
4. Large population size (couple losses won’t change allele frequency, smaller populations change faster as affected more by loss)
5. Random mating (no selectiveness, everyone is equal)
89
New cards
What was Hardy-Weinberg’s conclusion?
Can’t meet all 5 conditions for prolonged periods of time, therefore change in allele frequency is inevitable (must happen)
90
New cards
What are the equations to calculating allele frequencies?
p^2 + 2 pq + q^2 = 1
p+q=1
p+q=1

91
New cards
What does “p” represent?
Frequency of dominate allele (A)
92
New cards
What does “q” represent?
Frequency of recessive allele (a)
93
New cards
What does “q^2” represent?
Frequency of homozygous dominate genotype (AA)
94
New cards
What does “pq” represent?
Frequency of heterozygous genotype (Aa)
95
New cards
What does “p^2” represent?
Frequency of homozygous recessive genotype (aa)