waves and technology
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Waves
Carriers of energy that transfer energy through different media.
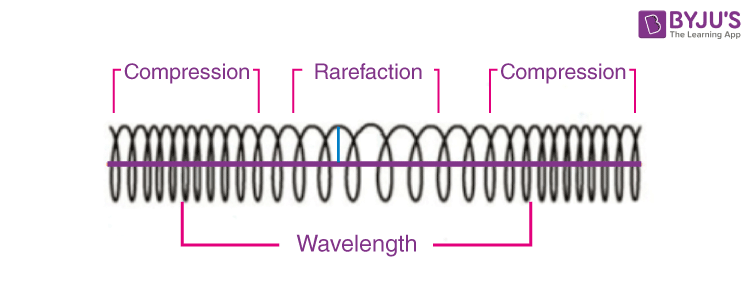
Longitudinal Waves
Waves that move in a compression motion, where particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of the wave.
Transverse Waves
Waves that move in a motion where particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
Mechanical Waves
Waves that require a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) to travel through.
Electromagnetic Waves
Waves that do not require a medium and can travel through a vacuum.
Wave Model
A model used to describe features of waves, including frequency, period, wavelength, and speed.
Particle Model
A model used to explain the transmission of sound in different media (solids, liquids, gases).
Sound Waves
Waves that pass through the ear, allowing us to hear.
Visible Light
A form of electromagnetic radiation that can be seen by the human eye.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The range of all types of electromagnetic waves, including visible light.
Reflection of Light
The bouncing back of light from surfaces, such as plane and curved mirrors.
Ray Diagrams
Diagrams used to locate images in mirrors and describe the path of light.
Refraction of Light
The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another of different optical density.
Optical Density
A measure of how much a medium can bend light.
Lenses
Optical devices that focus light, with different types serving various functions.
Scattering
The process by which light is spread out in different directions.
Dispersion
The separation of light into its component colors.
AM Radio Waves
Amplitude Modulated radio waves used for broadcasting.
FM Radio Waves
Frequency Modulated radio waves known for better sound quality.
Analogue Signals
Continuous signals that vary in amplitude or frequency.
Digital Signals
Discrete signals that represent information in binary form, offering advantages like noise resistance.
Coaxial Cable
A type of electrical cable used for transmitting data and signals.
Wireless Technology
Technology that allows communication without physical connections.
Optical Fibre Technology
Technology that uses light to transmit data over long distances.
Sound in Everyday Life
The role of sound in communication, navigation, and medical applications like ultrasound imaging.