1.4 Managing People
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Human resource management –
Managing the people withing a business in order to achieve corporate objectives. This involves tasks such as recruiting and training employees as well as designing performance management systems
Staff as an asset -
When businesses view employees as a valuable resource to be invested in and ideally retained long-term.
Staff as a cost -
When businesses view employees as an expense to be minimised
Pros and cons for staff as an asset
Advantages | Disadvantages |
•More skilled employees > easier to adapt to market change •Higher levels of staff retention > reduce recruitment and training costs in the long run •A more motivated workforce > higher labour productivity •Reputation for being a good employer > easier to attract good people. |
|
Staff as a cost
Advantages | Disadvantages |
•Easy to adapt the size & composition of the workforce in response to business needs – important in dynamic market •May lead to lower labour costs – especially in the short run – important if competing on price •Employees can be tightly controlled and supervised > important if relatively unskilled
| •Demotivated staff > higher labour turnover/absenteeism /low productivity. •Poor reputation as an employer > harder to attract new staff, important in a tight labour market.
|
Labour productivity –
measures output per worker per time period
Labour productivity formula
= output per time period
number of employee
Labour turnover –
measures the % of workers that leave in a given time period
Labour turnover formula
= number of staff leaving x 100
Average number of staff
Labour retention -
Measures a firm’s ability to keep its workforce normally for more than one year
Labour retention formula =
No of employees serving for more than 1 year x100
Average number of staff
Absenteeism -
Usually measures the % of days lost to absence
Absenteeism formula =
Number of days lost to absence x 100
Total potential working days
Why does Labour productivity matter>
The more productive the workers, the fewer workers needed to make goods/provide services, therefore the lower the cost per unit. This gives businesses scope to lower prices or increase profit margins.
how to improve it
It depends why it is low, which managers would need to investigate. But options include:
Improved recruitment process, training, better equipment, financial and non-financial motivators
Why does Labour turnover matter
High labour turnover is expensive, e.g. it will require more recruitment and the training of replacement staff.
Lots of vacancies/new staff puts increased pressure on the remaining staff
Lack of staff/lots of inexperienced staff may reduce production / productivity/ quality
how to improve it
Improved recruitment and selection – employees are more likely to leave if they are in a job that they are not suited to.
Improve terms and conditions - employees are more likely to leave if other businesses offer better pay/other rewards/ working conditions
Change the organisational structure – try to build in opportunities for promotion so that employees don't have to move on to move up
Why does absenteeism matter?
Why does it matter?
Increased costs. E.g. may need to pay for cover.
Increased pressure on other staff > morale?
Impact business performance, e.g. delayed deliveries
How to improve it....
Again, it depends! Managers would need to look into why it is high.
Approaches might include:
Improved health and safety at work practices.
Introducing/expanding flexible working
Implementing an employee wellness programme, e.g. offering counselling.
Improved job design to increase motivation
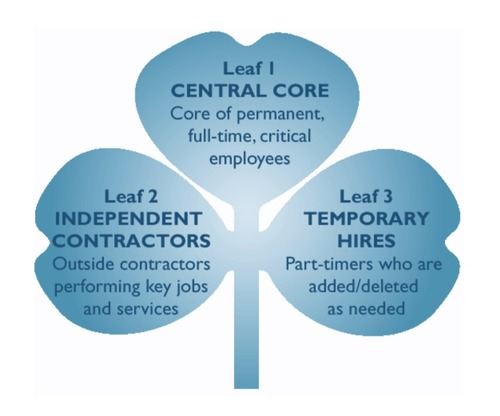
Flexible workforce –
Using permanent employees that carry out core tasks and peripheral workers that provide numerical and/or functional flexibility to allow a business to respond to changes in demand.
Numerical flexibility –
The ability to flex the size of the workforce up or down e.g. using temporary or past-time workers.
Functional Flexibility -
The ability to vary the tasks that a workforce can do, e.g. by multi-skilling or outsourcing.
Multiskilling –
Employees’ skills are enhanced so that they are able to carry out a range of different jobs
Outsourcing –
contracting out certain business functions to another business. Commonly outsourced tasks include cleaning, catering and IT.
Part-time work –
Employing staff on contracts that are typically less than 30 hours per week. This can help the business to cut costs, only paying a part-time wage if only part-time work is required. Sometimes part-timers are asked to do extra work during busy times, further increasing flexibility.
Temporary staff –
these can be either full-time or part-time but are on a fixed term contract, for example when schools hire supply teachers to cover teacher illness or maternity/paternity leave and retailers use seasonal staff at Christmas
Flexible hours –
This can involve a range of possible contracts, but examples include: flexi-time, where employees work core hours but have some freedom over start/end times and zero hours contract where employees only work/get paid when the business actually needs them
Working from home / Mobile working –
The ability of an employee to carry out their job from their own home rather than going into an office or workplace
CHARLES HANDY’S SHAMROCK ORGANISATION
Pros and cons of a flexible workforce
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Can reduce labour costs, e.g. by: •only paying staff when they are needed. •reducing training costs – the firm can “buy in” specialists when they are needed. Improved customer service - can help the business cope effectively with surges in demand. Can help with recruitment / retention / motivation – many workers like flexible working e.g. flexible hours /multiskilling
| Can be expensive:
Quality may deteriorate – e.g. as multiskilled workers are less specialist/permanent staff are under pressure when support temps. Communication can deteriorate, e.g. as staff are not always working at the same time/rely on digital communication.
|
Multi-skilling pros and cons
Advantages | Disadvantages |
• Better able to respond to surges in demand > maintain lead times > improved customer experience
• Higher labour productivity > workers can be moved around depending on demand so fewer workers are needed > reduced unit costs.
• Increased motivation > workers are less likely to be bored > likely to reduce labour turnover.
• Reduced disruption associated with absence. |
|
Out sourcing pros and cons
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Focus on core competencies: Outsourcing allows a company to focus on its core business activities while paying specialists to carry out non-core functions (e.g. IT, HR, accounting).
Access to expertise: Outsourcing providers are often specialists in their fields, which means the company can benefit from the expertise and experience of professionals in that specific area. This could mean better quality and can also help to overcome problems with skills shortages.
Cost savings: Outsourcing often leads to cost reductions for lots of reasons, e.g.:
| Lack of control > quality concerns: In some cases, outsourced providers may not deliver the expected level of quality, leading to dissatisfied customers/damage to the brand
Increased power of suppliers: Overreliance on outsourcing partners can pose risks, especially if provider a crucial service.
Ethical concerns: where work is outsourced to unethical businesses, e.g. those with very poor working conditions. This may damage the brand or lead to dissatisfied stakeholders, e.g. shareholders or customers
Cost: Sometimes specialist contractors are very expensive.
|
Employee-employer relations -
the process of discussing/negotiating and agreeing to changes in the terms of conditions of work
Dismissal -
when an employee loses their job due to misconduct (such as theft) or because they are incapable of doing their job
Redundancy -
when an employee loses their job because there is insufficient work for the employee to do (they will be entitled to a redundancy payment).
Trade union -
Organisations that work to protect members’ interests and improve their terms and conditions at work.
Works council –
An internal group of employees representing a workforce in discussions with their employers
Collective bargaining
- A method of determining conditions of work and terms of employment through negotiations between employers and employee representatives, such as trade unions.
Industrial action –
Collective activity by workers to put pressure on employers, usually over terms and conditions of employment. Examples include strikes, overtime bans and work-to-rule.
Individual approach -
When workers' conditions of work and terms of employment are negotiated individually between employees and management
Pros and cons of collectivised bargaining
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Can be quicker to negotiate collectively > important if change needs to be implemented quickly. Outcomes are more likely to be accepted by employees if they feel employers have negotiated with representatives > avoid industrial action e.g. strikes Employees may feel that they are being treated fairly, as bargaining collectively gives them more power when negotiating with a large employer. | Can lead to higher labour costs as unions push for better terms and conditions for workers.
May lead to industrial action of agreement cannot be reached.
Collective bargaining usually leads to standardised terms and conditions, e.g. nationally negotiated pay scales. This makes to pay workers differently, e.g. depending on their level of productivity, or in response to labour market conditions. |
Recruitment -
Searching for and attracting potential candidates to fill job vacancies.
Selection -
Choosing the right person for a job from a field of candidates
Internal recruitment –
Filling a job vacancy with current employees. This can involve promotion, but could also just be a change of role.
External recruitment -
Filling a job vacancy with candidates from outside the organisation.
Job description –
Sets out the tasks and responsibilities of a job. Information will include: job title, place in the hierarchy, duties, tasks and responsibilities.
Person specification –
A document used within the recruitment process that describes the person required to do the job e.g. qualifications, skills and experience
Psychometric testing –
used to assess a candidate's ability and personality. Usually involves numerical and verbal reasoning tests and sometimes personality questionnaires.
Assessment centre -
an in-depth selection method that assesses candidates' competencies and suitability for roles. Usually takes place over 1-2 days and typically involves interviews, testing, group exercises etc.
Why do businesses recruit?
Business expansion due to increase in sales, developing new products, entering new markets etc.
Existing employees leave – to work with competitors, due to retirement, etc.
Employees are promoted creating a vacancy.
Workers may be required to work on a temporary basis
Business needs employees with new/different skills, e.g. due to change in the market.
The recruitment process
RECRUITMENT
Identify the vacancy and conduct job analysis to identify the various duties and responsibilities involved
Create a job description and job/person specification
Advertise the vacancy internally and/or externally to attract suitable candidates
SELECTION
Analyse the applications
Draw up a shortlist of the most suitable applicants for interview
Choose the most suitable candidate(s) using appropriate selection methods e.g. interview, testing, assessment centre, taking up references
Appoint the successful candidate (issue and sign contracts)
Internal versus External Recruitment
Advantages of internal recruitment | Advantages of external recruitment
|
|
|
COSTS OF RECRUITMENT AND SELECTIO
Direct costs – e.g. advertising in specialist publications/websites, paying a recruitment agency or a head-hunter.
Indirect costs – Depending on the skills experience of the candidates/s selected on-the-job or off-the-job training may be required. At a minimum, induction training will be needed.
Opportunity costs – Managers (sometimes senior) will need to commit time to the process, e,g, shortlisting candidates and carrying out interviews. This takes them away from their main role.
Costs of getting it wrong! Selecting an unsuitable candidate can be VERY costly. For example:
The recruit may be ineffective in their role, reducing labour productivity.
Selecting unsuitable employees has a knock-on effect on the team/line manager. It may increase their workload, and make it harder for them to do their job well. This can be demotivating, reducing their productivity.
They are more likely to leave, meaning the whole R&S process will have to be repeated.
Training -
Increasing the knowledge and skills of employees so that they can do their jobs more effectively.
Development -
Creating opportunities for employees to acquire a broader set of skills to prepare them for future roles.
Induction training –
Initial training for people starting a job. Typically includes an introduction to the business/role and a health & safety briefing.
On-the-job training –
Where an employee is trained by a more experienced employee while doing their job in the normal working environment
Off-the-job training -
Taking people away from their normal workplace to learn new information or skills, e.g. when apprentice goes to College 1 day per week
Why invest in training?
To provide higher quality products and services – especially important if the business is competing via differentiation.
Improved labour productivity – reducing unit costs – especially important if the business is competing via cost.
Increased workforce flexibility – e.g. by multiskilling employees – especially important if demand is variable or the market is dynamic.
Improved worker motivation – as employees feel valued, more confident in their job and may enjoy it more, especially if it is more varied/challenging.
Less need for supervision – especially important in a flat hierarchy where managers have a large span of control.
Pros and cons of induction training
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
Pros and cons of on the job training
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
Pros and cons of Off the job training
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
Private sector
Individuals own profits goes to individual
Public sector
Owned by the government, nonprofit, but any go to the government
Nationalisation
Moving a company from private to public sector and privatisation is the opposite
Business survival
It’s new, when a competitor enter the market, are there changes and external environment
Hard approach will include
Minimum wage, temporary training, lack of job, security, minimum investment, bad communication
Soft approach will include
Competitive structure, effective, recruitment, process, permanent processes, effective communication, lots of responsibility
Consultation strategies
Seeking opinions from employees before making decisions, which increases the feeling of worth
Pros and cons of a flexible workforce for firm
Pros, helps with recruitment, reduce labour costs, cope quickly with changes in demand
Cons, May actually increase cost, communication can deteriorate, potential loss of customers
Pros and cons for flexible working to a worker
Pros,improve worker morale, reduce costs of commuting, improved job, prospects, longer, careers
Cons can lead to increased workload, can reduce job security, lack of worker interaction, reduces effectiveness
Advantages and disadvantages of collective bargaining
Pros, negotiations, reduces favouritism, cheaper and quicker to run
Con, can be lengthy and expensive, unions may not actively represent all members, failure to agree, may result in industrial action