Unit 5. Concept 1. Mendelian Genetics.
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
explain mendels law of dominance
a dominant (strong) allele will express itself over a recessive (weak) allele
2
New cards
explain mendels law of segregation
when chromosomes separate in meiosis, each gamete will
receive only one chromosome from each pair
receive only one chromosome from each pair
3
New cards
explain mendels law of independent assortment
the assortment of chromosomes for one trait doesn't affect the assortment of chromosomes for another
4
New cards
what is a gene
basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA
5
New cards
what is an allele
a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule
6
New cards
what are homologous chromosomes
Two chromosomes in a pair – normally one inherited from the mother and one from the father
7
New cards
who was gregor mendel
father of genetics/the pea guy
8
New cards
what were the conditions of mendels experiments
controlled plant breeding / only purebred plants / observed “either-or” traits
9
New cards
what is cross
the mating of two organisms
10
New cards
what does P stand for
parental generation
11
New cards
what does F1 stand for
first generation
12
New cards
what does F2 stand for
second generation
13
New cards
what is a dominant gene
a gene with and allele that will always have the trait shown
14
New cards
what is a recessive gene
a gene with an allele that will only show in absence of (fully) dominant allele
15
New cards
what is a genotype
the actual allele inherited
16
New cards
what is a phenotype
the physical traits and characteristics of an organism
17
New cards
what does homozygous mean
2 of the same allele (homo = same)
18
New cards
what does heterozygous mean
2 different alleles (hetero = different)
19
New cards
what is a punnet square
a diagram that shows the probability of inheriting traits from
parents with certain genes
parents with certain genes
20
New cards
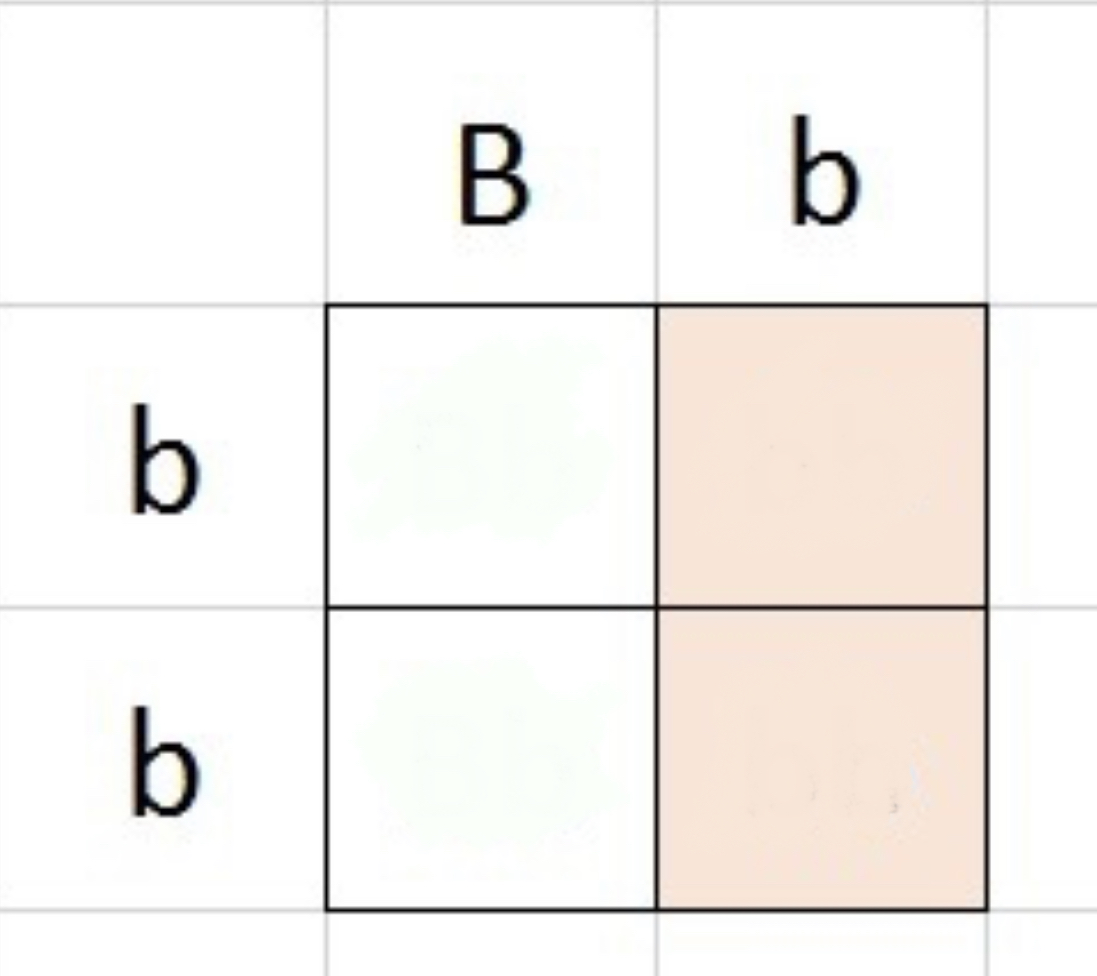
complete this 2x2 punnet square and predict the phenotype and genotype ratios
Phenotype: 2:2 Genotype: 2:2
21
New cards
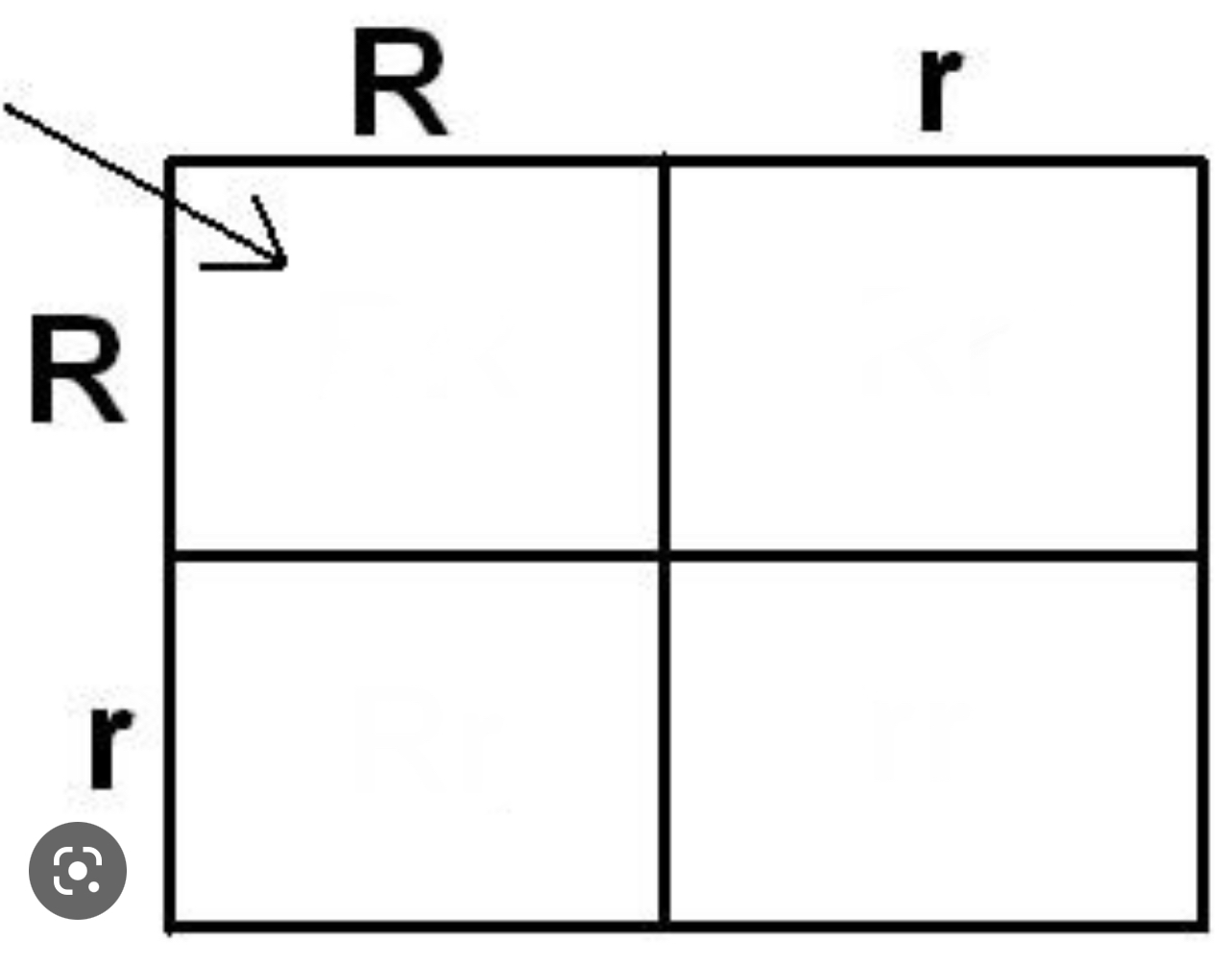
complete this 2x2 punnet square and predict the phenotype and genotype probability
Step 1: Write out your key in terms of what's dominant and recessive. Step 2: Determine the genotypes of the parents and write out the cross. Step 3: Figure out what kinds of gametes each parent can produce. Step 4: Set up a Punnett square for your mating.
22
New cards
what are the steps to solving dihybrid punnet squares
23
New cards
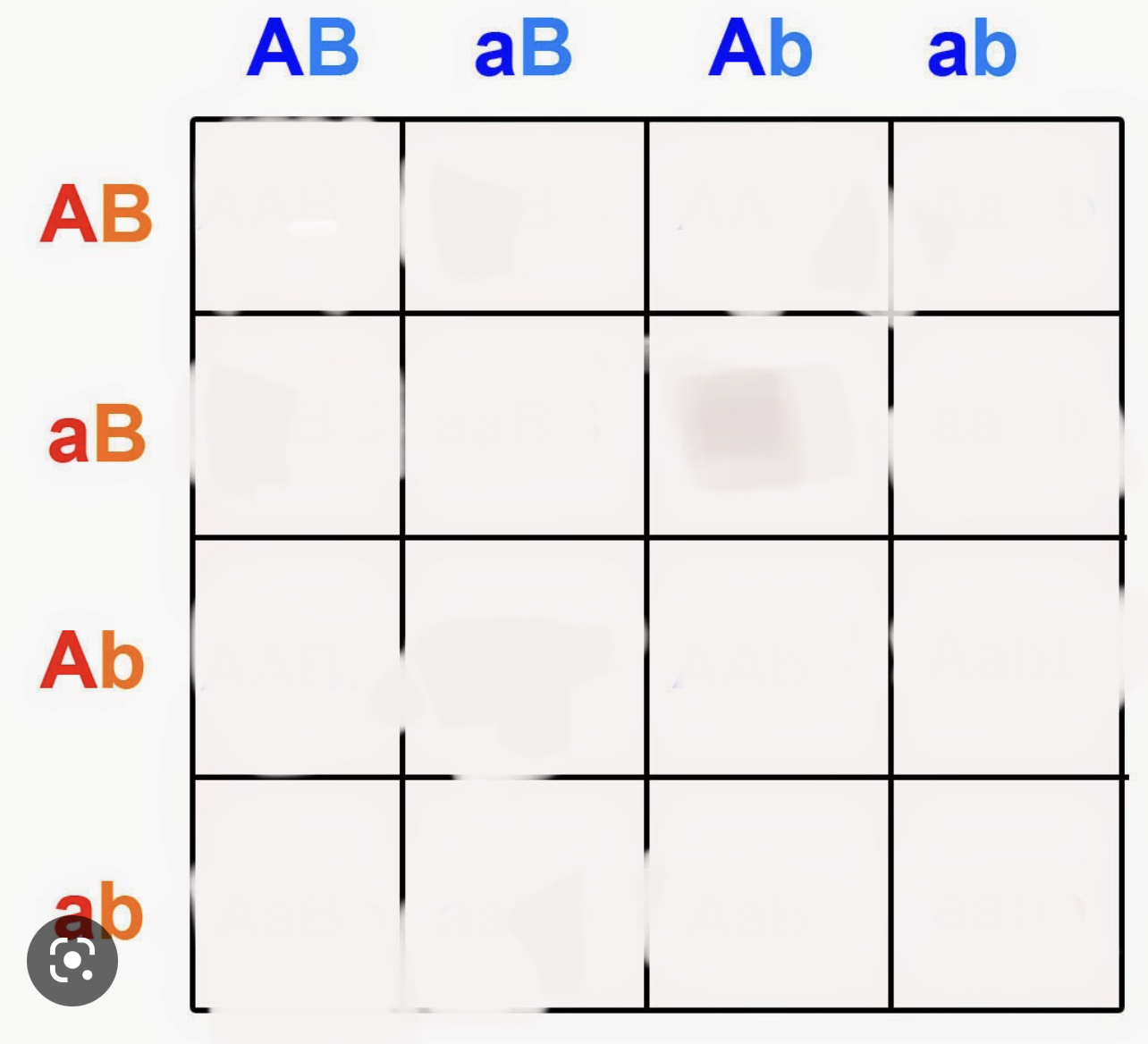
complete this 4x4 punnet square and predict the phenotype and genotype probability
24
New cards
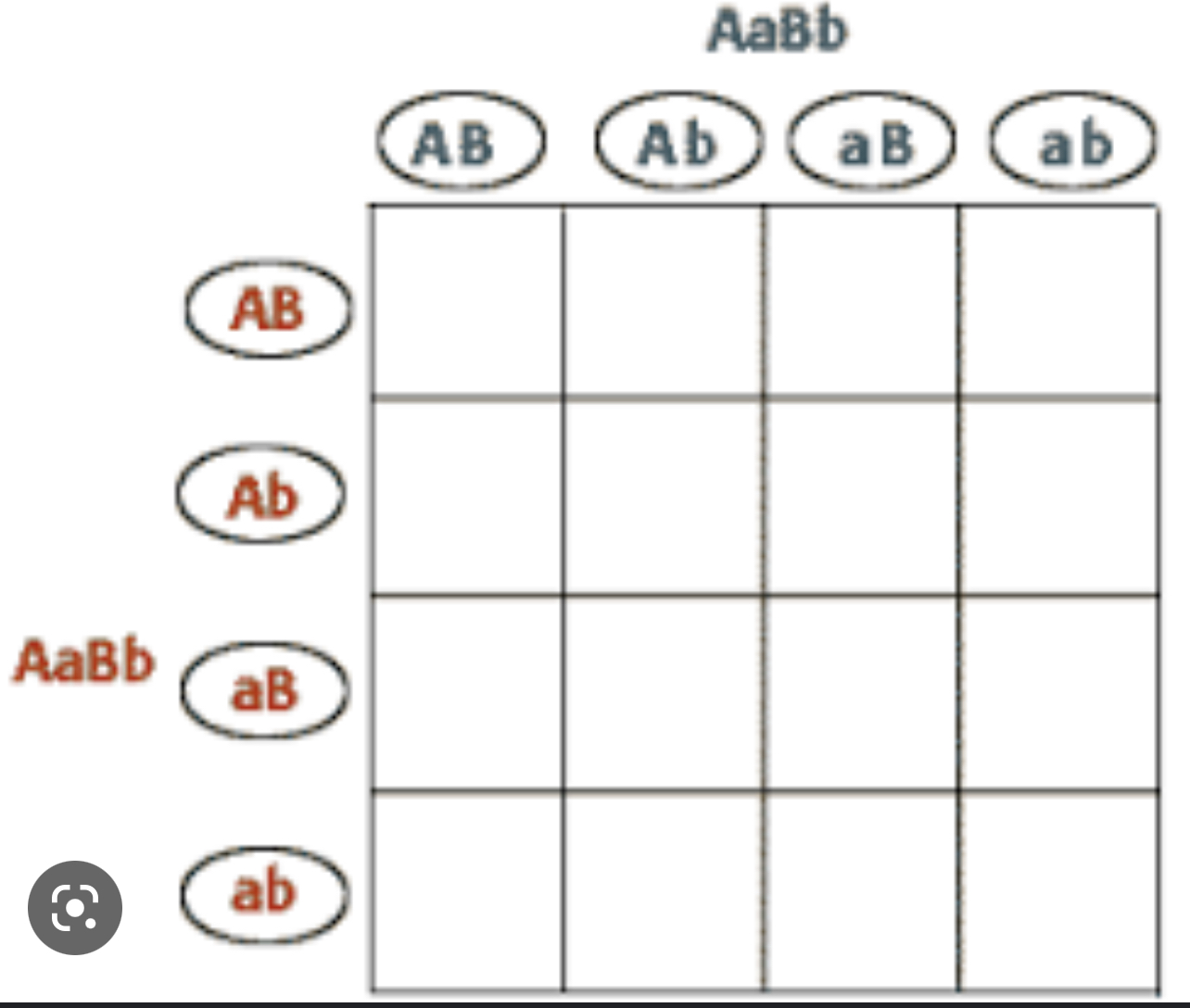
complete this 4x4 punnet square and predict the phenotype and genotype probability
25
New cards
how can you use probability to determine the possibility of getting a specific genotypes
1. Perform a monohybrid cross for each individual gene
and determine the odds of getting each genotype (in
fraction form)
2. Multiply the odds to determine the odds of getting this and this and this and etc…