Cell Divison: Meiosis
1/52
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Chromosomes are __
Passed on from parents to offspring
Contain __
Located in the nucleus
made of DNA and protein
genes that code for traits
Homologous chromosomes are __
One set of chromosomes comes from each parent
Similar but not identical
Carries the same genes in the same order
Alleles for each trait may not be the same
two corresponding chromosomes that carry the same genes.
Meiosis is the process by where a single cell divides twice to produce four daughter cells that contain half the amount of chromosomes of the parent cell.
__
Male gametes are sperm
Female gametes are eggs
Meiosis creates four (4) sex cells called gametes
Non-reproductive body cells are called somatic cells.
__
Represented by __
One set comes from each parent
Humans diploid cells contain __ chromosomes
Somatic cells are diploid because they contain 2 sets of chromosomes
2N
46
Gametes are __
Haploid cells are represented by the letter __
Human’s gametes each contain __ chromosomes
haploid, meaning that they contain half the number of chromosomes of a body cell.
N
23
Two haploid gametes fuse together during fertilization to create a diploid cell with two complete sets of chromosomes
When an egg cell is fertilized, it becomes diploid and is called a __
zygote
Meiosis is a __
In humans, the starting cell has 46 chromosomes, and the ending cell has 23 chromosomes.
Chromosomes are reduced by division
reduction division process
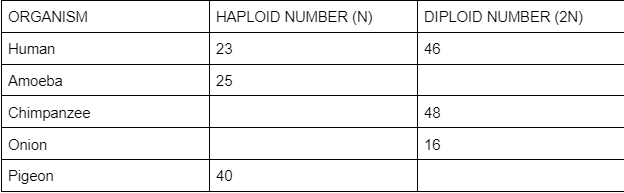
Fill in the blanks
50
24
8
80
Meiosis creates__ with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Sexual reproduction
Makes sex cells (gametes
Makes haploid (N) cells
__ to make 4 haploid cells from 1 diploid cell
Meiosis I and Meiosis II
genetically unique gametes
Divides twice
Like in mitosis, interphase must occur before meiosis takes place.
During the S phase of interphase __
Each duplicated chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids attached at the centromere
Centrioles also replicate
DNA is replicated
Meiosis takes place in two stages of division: Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2
PMAT occurs twice
__
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
__
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
Meiosis I
Meiosis II
In prophase I, each __
Forms a tetrad, containing 4 chromatids
Spindle fibers form
Longest stage of meiosis (90%)
nuclear envelope starts to dissolve
Homologous chromosomes complete crossing-over (reason for extended duration)
Crossing over is __
replicated chromosome pairs up with its homologous chromosome
the physical exchange of genetic information
Synapsis holds the chromosomes together at a location called a chiasma.
Crossing over produces new combinations of genes
__
accounts for genetic diversity
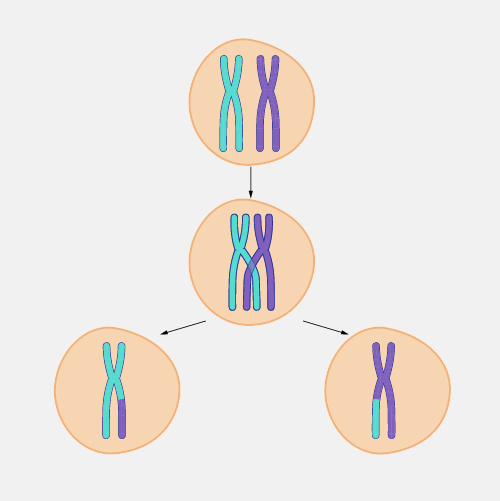
What is the name of the first, second, and third and fourth image (stage/phase)?
Homologous pair
Synapsis
After Crossing-over
During metaphase I, paired homologous chromosomes __ (middle) of the cell.
Spindle fibers extend from the centriole and attach to the centromere
Hint* M for Metaphase = M for Middle
line up across the equator
During anaphase I, spindle fibers pull each homologous chromosome pair towards the opposite ends of the cell.
Homologous pairs are __
Hint* A for Anaphase + A for moving Away
moved away from one another
During Telophase I, the __ around each cluster of chromosomes.
nuclear membrane reforms
Cytokinesis __
Splits the elongated cell into two distinct cells
Each new cell is called a daughter cell
Chromosomes unravel and decondense
separates the cytoplasm
Each new cell is genetically different from the other and the parent cell
Begins with 1 diploid parent cell and __
ends with 2 haploid daughter cells
Prophase II
As cells enter prophase II, their chromosomes consist of __
Chromosomes become visible
Do not pair to become tetrads
No longer homologous pairs
Nuclear membrane breaks down
No crossing-over takes place
Meiosis II begins with 2 haploid cells
two chromatids
Metaphase II is very similar to metaphase I
Chromosomes line up in the __ of the cells
center
Anaphase II is very similar to anaphase I
Paired chromatids are separated by the spindle fibers
Chromatids move to the __ of the cells
poles
The nuclear membrane reforms and cytokinesis occurs
The end result of meiosis II is __. Cleavage furrow, where cytoplasm pulls off in the center.
four genetically different haploid cells called gametes
Haploid cells produced by meiosis II are the gametes important to heredity.
After an egg is fertilized, the __ to eventually form a new organism.
diploid zygote cell will undergo by mitosis
asexual
In this type of reproduction, the parent passes ALL of its DNA down to the offspring.
homologous chromosomes
Name given to a pair of structurally similar chromosomes that possess genes for the same characteristics at the same loci (location).
18
If a sexually reproducing organism has a chromosome number of 2N=18, how many chromosomes will be found in the body cells of this organism?
9
If a sexually reproducing organism has a chromosome number of 2N=18, how many chromosomes will be found in the sex cells of this organism?
meiosis
What type of cell division results in cells that have half the number of chromosomes as the original cell?
sexual
In this type of reproduction, the parent passes down only half of its DNA to the offspring
haploid
Term that means that a cell has one of each kind of chromosome
prophase I
During which stage of meiosis are tetrads formed?
mating is not necessary
quick reproduction
positive genes pass on to descendants
List three advantages to asexual reproduction
lack of genetic variety
What is the disadvantage of asexual reproduction
gametes
What term is used to describe sex cells (egg and sperm cells)
metaphase I
During which stage of meiosis do tetrads line up at the center of the cell
prophase II
During which stage of meiosis do sister chromatids line up at the center of the cell
homologues
During anaphase I __ are pulled apart
sister chromatids
During anaphase II __ are pulled apart
genetic variation
What is the advantage of sexual reproduction
diploid
Term that means that a cell has two of each kind of chromosome
2N or 2X
What is the symbol for diploid
N
What is the symbol for haploid
crossing over
The exchange of genes between segments of homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
fertilization
The union of sperm and egg
zygote
A fertilized egg
they are diploid
At the end of meiosis I, are the daughter cells haploid of diploid
sperm cells
What is the result of meiosis in males
egg cells
What is the result of meiosis in females
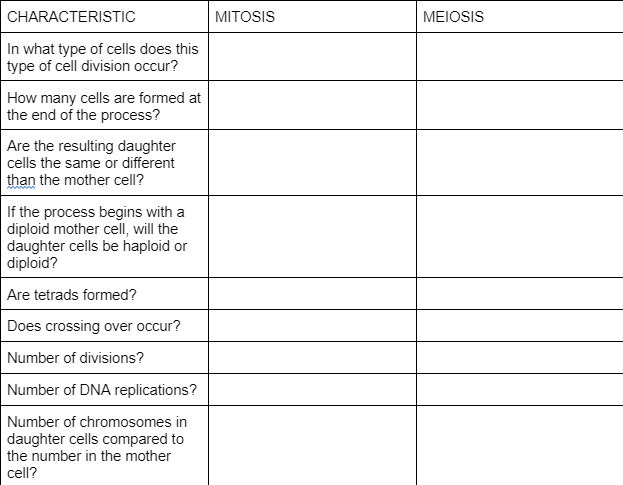
Fill in the blanks
Body cells/gametes (sex cells)
2/4
Yes-Same/Different-No
Diploid/Haploid
No/Yes
No/Yes
One/Two
One/One
double the mother’s/half the mother’s
What is crossing over? What is the importance of this event?
Crossing over is the exchange of genes in segments of homologous chromosomes in order to achieve genetic diversity. The point/importance of crossing over is to help increase the genetic diversity of the offspring.
Explain why egg and sperm cells must have half the number of chromosomes as the other cells in the body?
Egg and sperm cells (gametes) must have half the number of chromosomes as body cells because without the reduction of the number of chromosomes, the offspring(s) would have twice the normal number of chromosomes (92 instead of 46).
What are tetrads?
A tetrad is a pair of homologous chromosomes directly next to each other.