Rivers in the upper course; Geography B
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Typical landforms in upper courses:
Small rapids/waterfalls in upper course because of gradient.
Solution
transportation process: Dissolved load
Erosive process: Soluble rocks being dissolved
Solution
transportation process: Dissolved load
Erosive process: Soluble rocks being dissolved
Suspension
Transportation process: Small sediment held in river (near-ish to surface)
Saltation
Transportation process: ‘bouncing’ of particles too heavy to be suspended but too light to be rolled.
Hydraulic action
Erosion process: water is forced into cracks breaking up the bank
Hydraulic action
Erosion process: water is forced into cracks breaking up the bank
Attrition
Erosion process: rocks wear each other away as they knock together
Abrasion
Erosion process: Rocks wear away the river bed
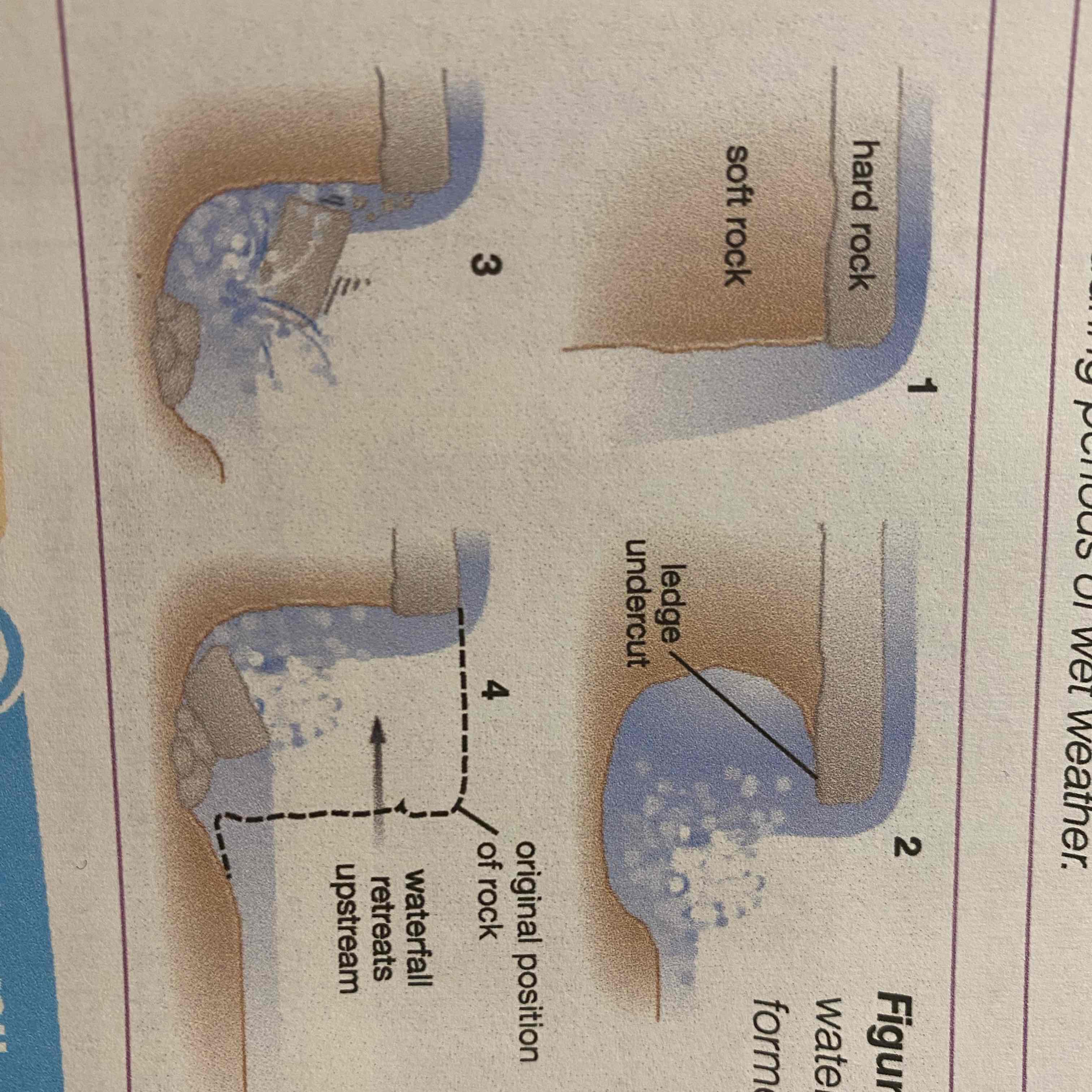
First step of waterfall formation:
Waterfalls occur when a river crosses a bed of more resistant rock
Second step of waterfall formation
Erosion of less resistant rock undercuts the hard rock above it. River’s energy creates a plunge pool at the foot of the waterfall.
Fourth step of waterfall formation
The waterfall takes up a new position, leaving a steep valley/gorge
A river in it’s upper course flows slowly….
Because of friction with the bed
Transportation processes are?
Are how the river carries its load
Typical valleys in river’s upper course (in an upland area)
V-shaped valleys. Steep sides and a narrow bottom.
Interlocking spurs created how?
As the river (in upper course) cuts vertically into resistant Carboniferous limestone, it winds around areas of most resistant rock. This creates the interlocking spurs.
Interlocking spurs
Ridges that jut into the valley from both sides
Process involved in shaping a valley
Weathering processes: Physical/chemical/biological
Physical weathering:
When physical force breaks down rock.
E.G Freeze thaw weathering attacking outcrops of rock
Biological weathering
When plant roots/birds/animals/ break up rock
Chemical weathering
Is any chemical change causing the decay of solid rock.
Mass movement
The movement of weathered fragments downslope by gravity.
Can be rapid/slow.
Two examples of rapid mass movement
Landslides And Mudflows
Example of slow mass movement
Soil creep
Effects of soil creep
Less noticeable than rapid mass movement’s effects. Over many years can cause trees/ lampposts/walls to lean
Valley shape affected by what? Three examples:
• The rate it weathering
• the rate of mass movement
• how effectively river can remove material
What happens when the river has (high) energy?
It takes material and uses it to erode the valley, making it steeper
What happens when river flow is slow?
Weathered rock would then collect at the bottom of the slope, making the valley gentler and flatter