Latin America Climate, Biomes, and Environmental Changes
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
altitudinal zonation
The relationship between high elevations, cooler temps, and changes in vegetation/ agricultural crops that result from the environmental lapse rate
ITCZ
A global belt of high insolation and low atmospheric pressure situated parallel to the Equator that draws in the Trade winds and ocean moisture from both hemispheres
Tropical forest biome
a major ecological community of organisms adapted to a particular climate or environmental condition on a large geographic area in which they occur
the arc of deforestation
deforestation along the southern edge of the Amazon Basin
The Pristine Myth
The generally false idea that the americas was a sparsely populated, untouched wilderness prior to the arrival of the europeans in the 15th/16th century
the tropics (aka tropical region)
the portion of the world situated between the Tropic of Cancer (23'30'N) and the Tropic of Capricorn.
climate
average, long term meteorological conditions for a place, a region, or the world
shifting cultivation
The use of tropical forest clearings for crop production until their fertility is lost. Plots are then abandoned, and farmers move on to new sites.
climate controls
** Latitude
** Land/Water Heating Differences
** Geographic Position & Prevailing Winds
** Mountains & Highlands
** Ocean Currents
** Global Pressure & Wind Patterns
tropical cyclones
large storm systems with abnormally low pressure centers, high sustained winds, very heavy rainfall, and storm surges that usually form during the warm months
forest (according to the UNFAO)
- land expanding across an area more than .5 hectares in size
- trees higher than 5 meters
- a canopy cover of more than 10%, or trees able to reach these thresholds in situ.
insolation
incoming solar radiation (sunlight)
tropical deforestation
The clearing and destruction of tropical rainforests in order to make way for expanding settlement frontiers and the exploitation of new economic opportunities.
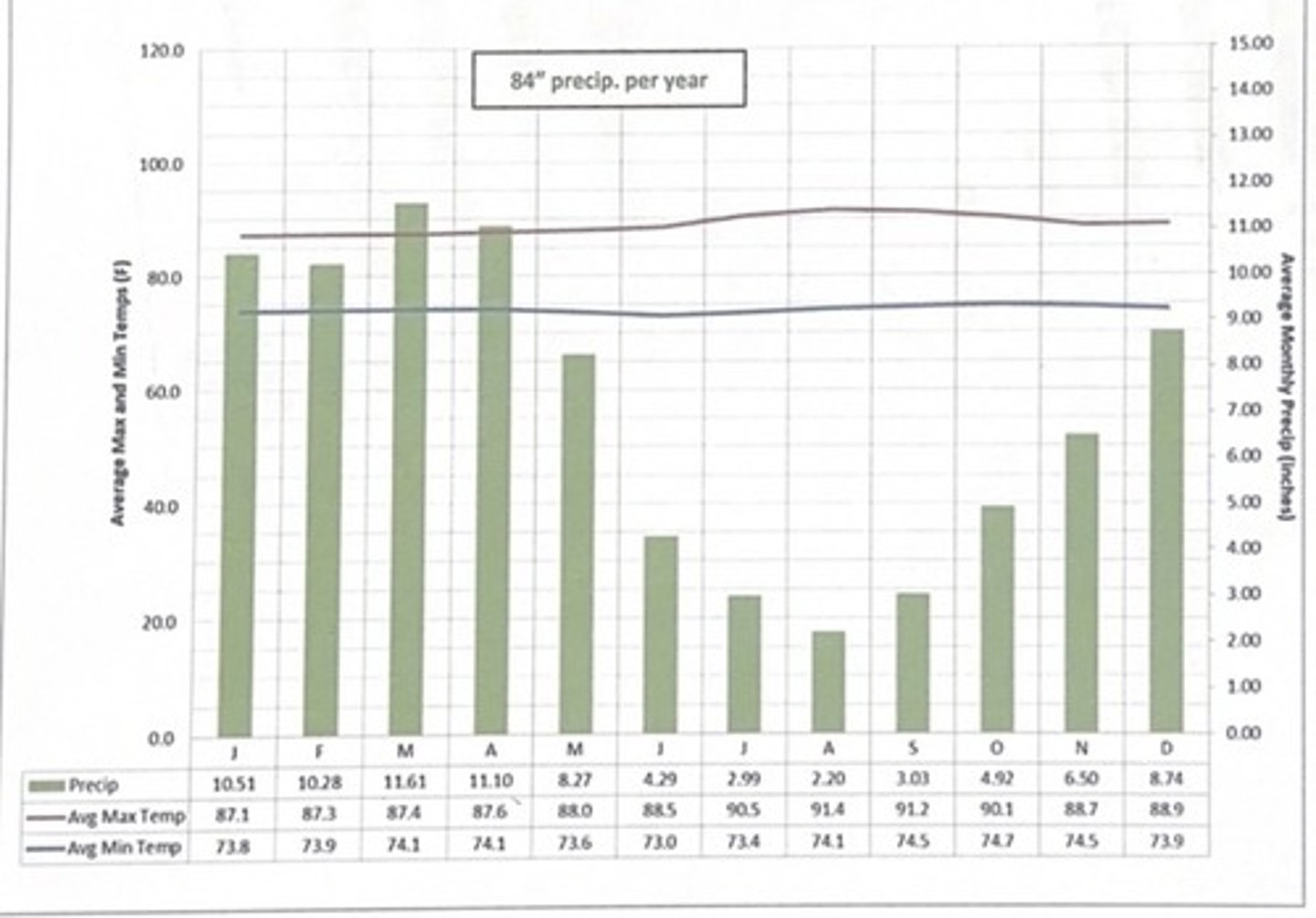
manaus, brazil climate
- climograph illustrates a very typical
Tropical Rainforest climate type
- very similar temp averages for
each and every month.
- it has abundant rainfall with a total of
84" per yr, but also a relatively "dry" seasonfrom June - sept
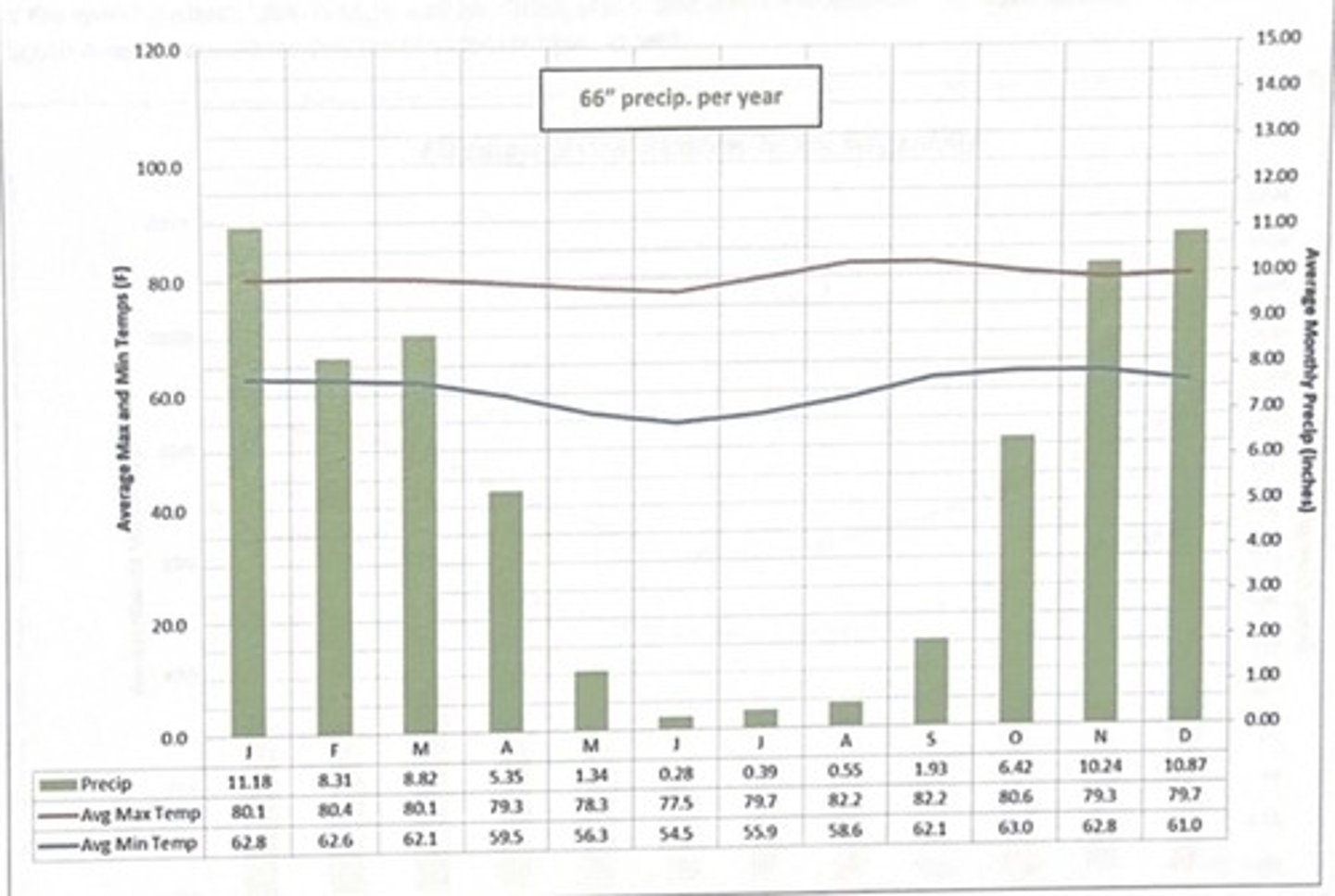
brasilia, brazil climate
- tropical savanna- dry winter (Aw)
- has rather warm and steady temps all yr long
- is distinguished by its rather dry, almost rain free winters and very wet summers.
- "winter" occurs between june-sept
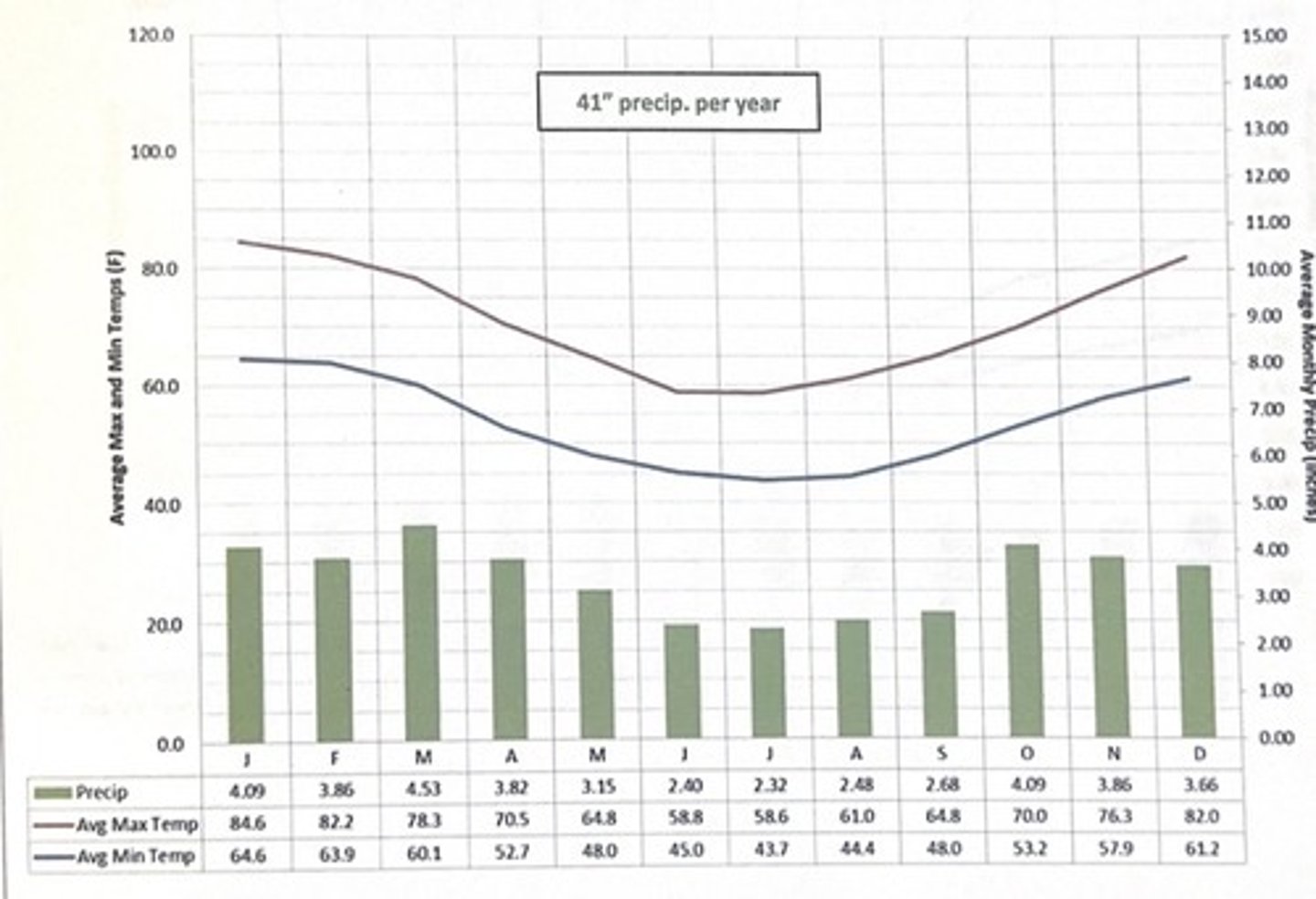
Buenos Aires, Argentina climate
- Humid suptropical (fa) climate type
- The climograph illustrates moderate temps that vary w the seaons and fairly similar - and, again moderate -- lvls of precip each and every month (totaling 41'' for the yr on average.) same climate as TN
Punta Areanas, Chile Climate
- Marine West Coast (Cfb)
- characterized by cool (not cold) temps and light - and - frequent showers.
- A more dreart climate, but people enjoy the fairy comfortable temps , cloudy skies , and frequent drizzle
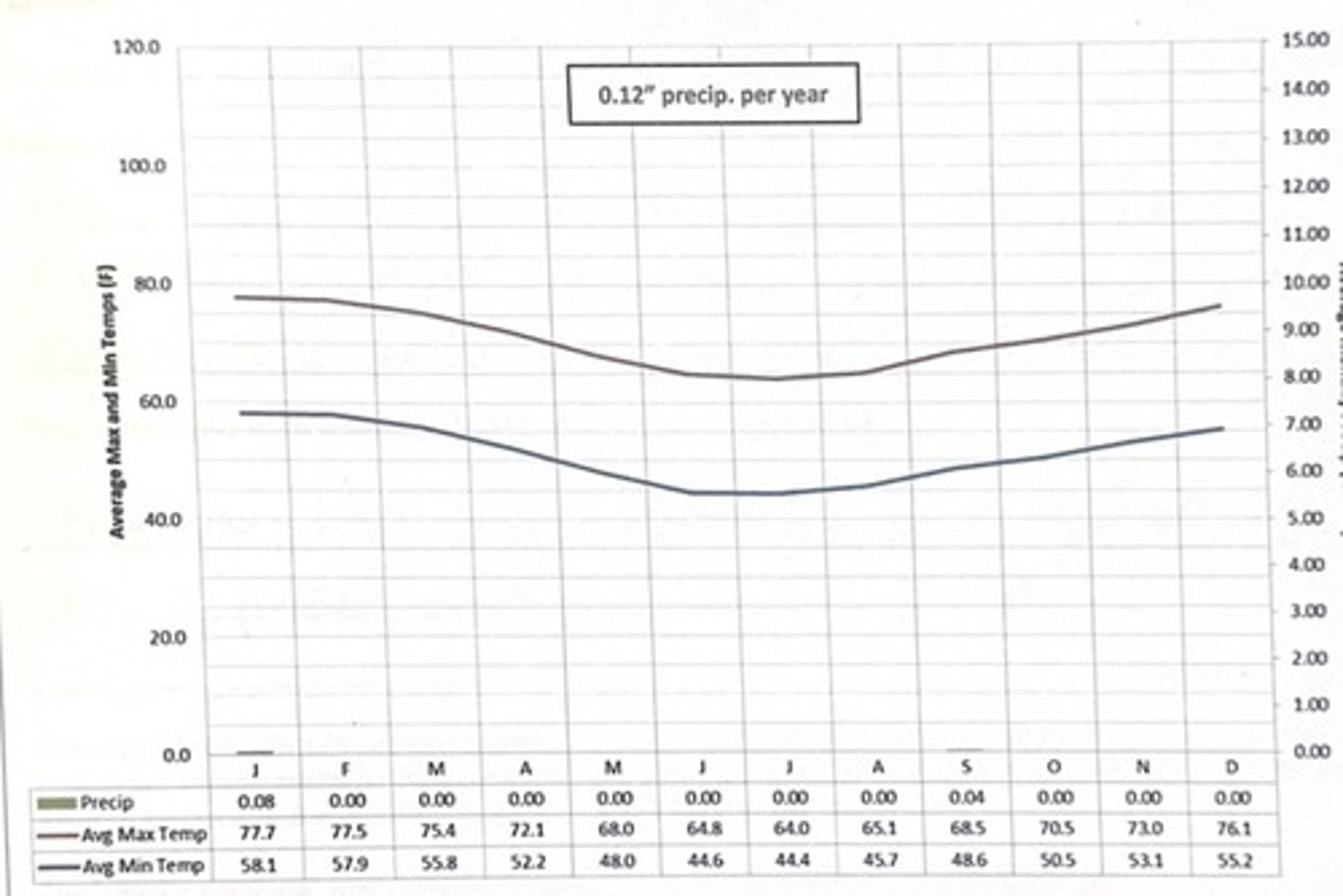
maria elena, Chile climate
- Arid-Hot
- reveals almost no precip (.12 on average)
which climate is this?
maria elena, chile
3 multiple choice options
which climate is this?
Manaus, Brazil
which climate is this?
brasilia, brazil
3 multiple choice options
which climate is this?
buenos aires, argentina
3 multiple choice options
which climate is this?
punta arenas, chile
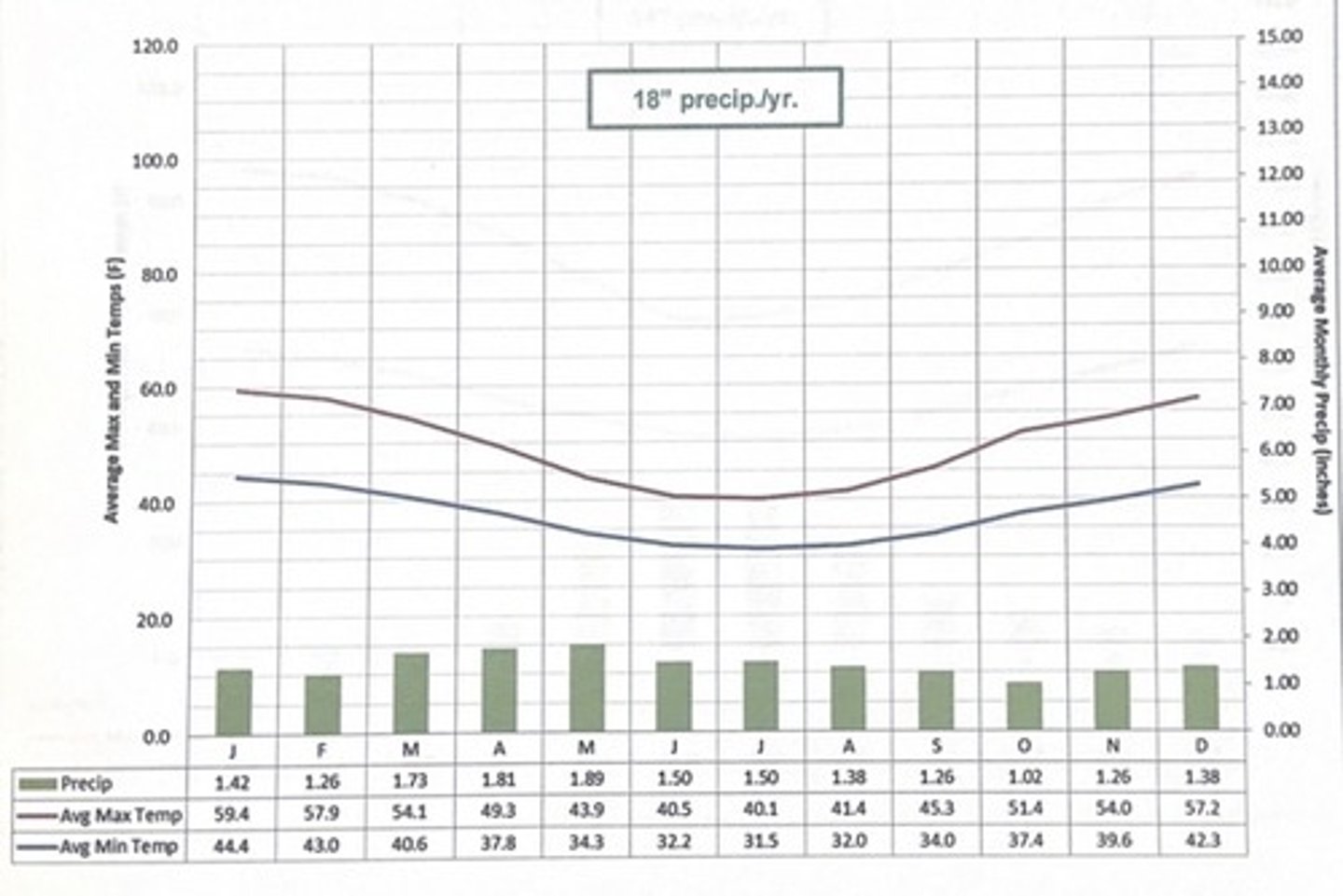
which climate is this?
santiago chile
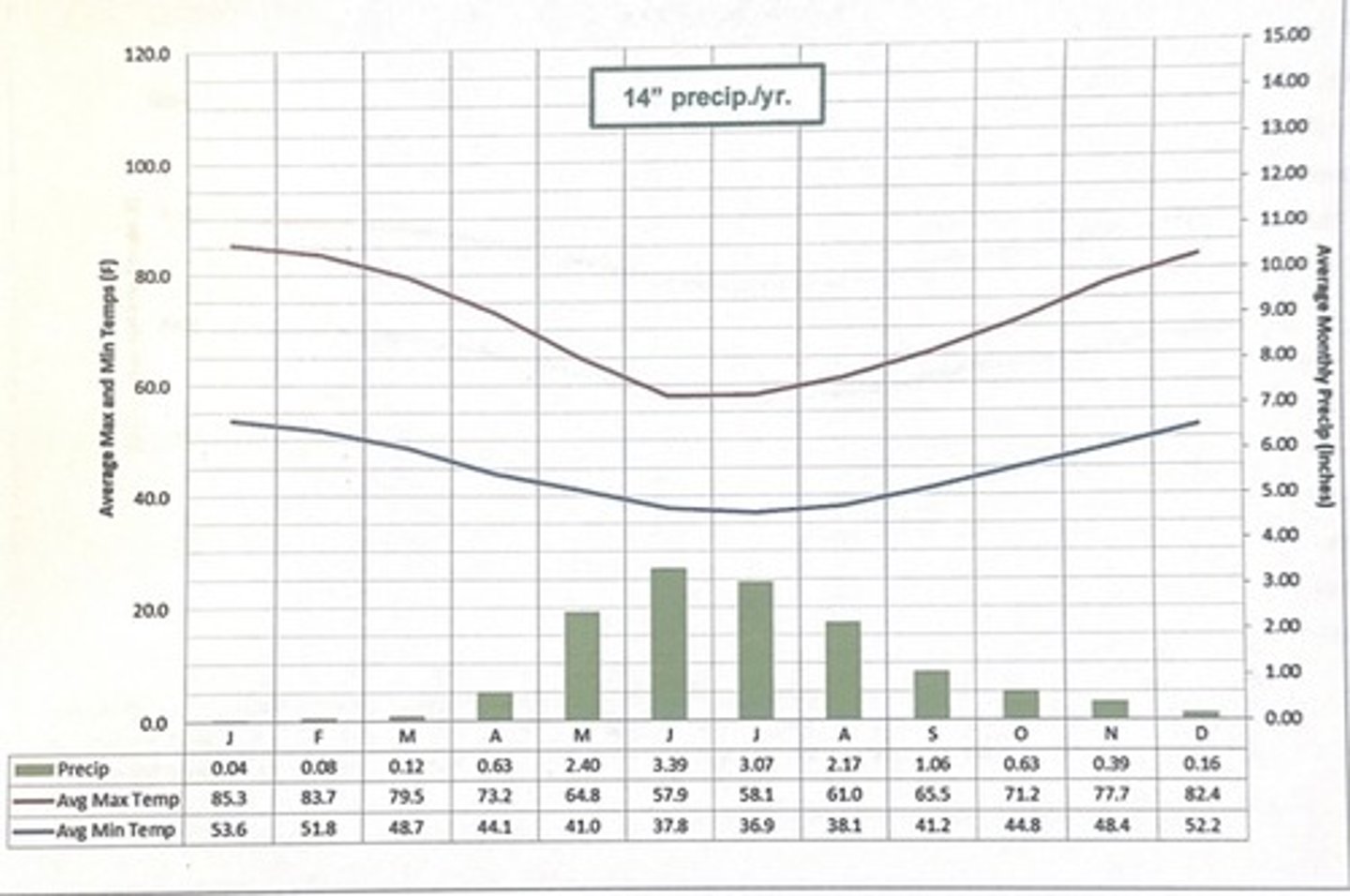
Technicaly speaking, what makes the tropical region of the world different from the non-tropical world ?
tropical regions receive more direct solar radiation throughout the year
what do the dashed lines on the world map labeled the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn technically represent?
the northernmost and southernmost limits where the sun can appear directly overhead at noon
the angles of insolation during the course of a full year
The angle of insolation varies throughout the year due to Earth's axial tilt of 23.5∘23.5 raised to the composed with power 23.5∘, causing the angle to be highest
Where are the sun's rays hitting the earth's surface most directly?
the equator
Where in Latin America/Caribbean do you find cool coastal ocean currents?
along the western coast of South America, where the Humboldt Current flows north, and along the northern coast of South America, where the Guiana Current flows northwest
What are the general climate characteristics of these coastal areas in west coast of south america?
arid coastal deserts (due to the Humboldt Current and Andes mountains), humid temperate rainforests (especially in the south, with high rainfall), and tropical humid climates (in the north, with a distinct wet and dry season)
What is "altitudinal zonation" ?
the natural layering of ecosystems into different bands along the slope of a mountain, which occurs as a result of changing environmental conditions with increasing elevation
What are the names of the altitudinal zones in Latin America ?
Tierra Caliente (hot land), Tierra Templada (temperate land), Tierra Fría (cold land), Tierra Helada (frost land), and Tierra Nevada (snowy land)
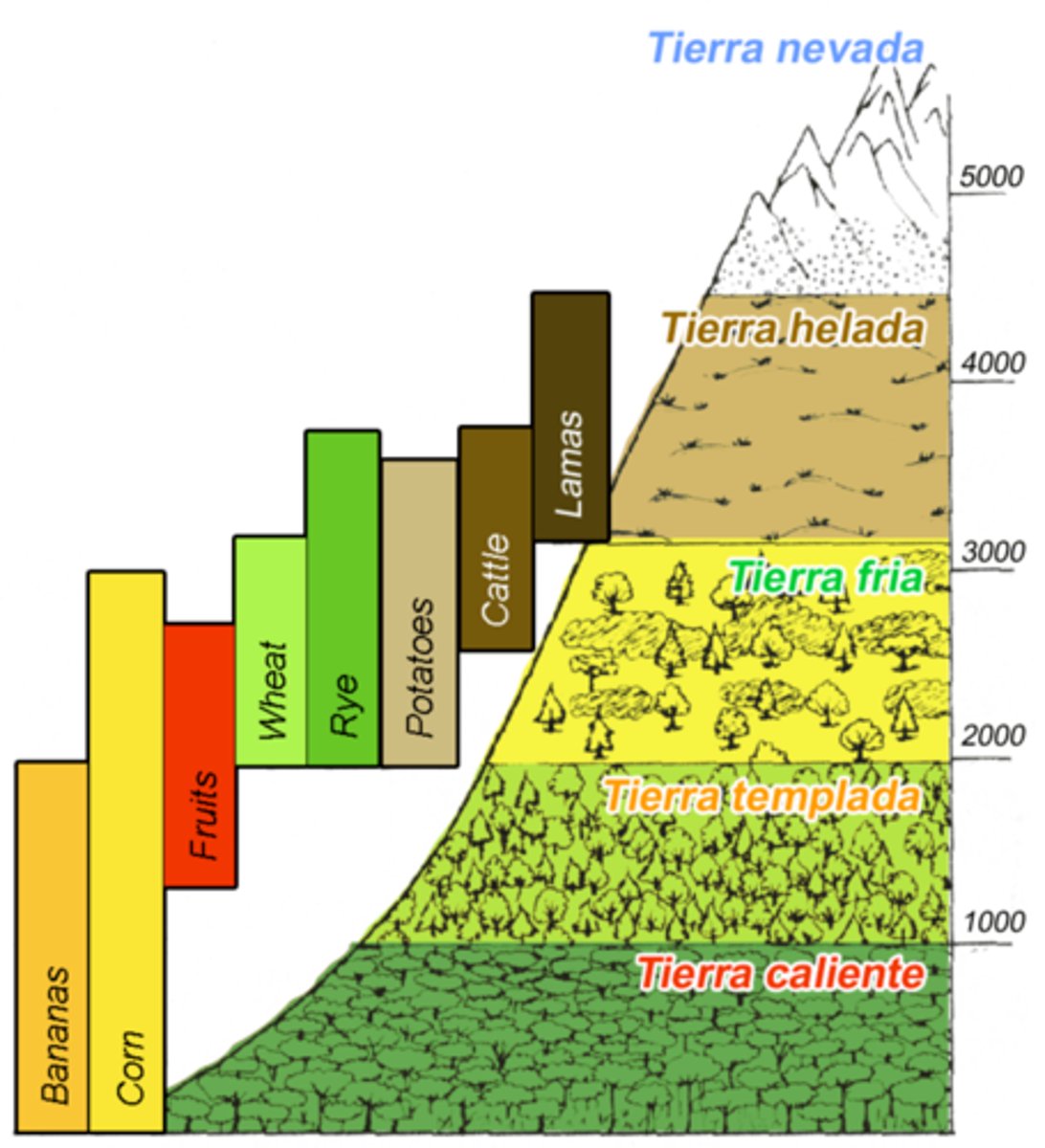
Where are these zones in south america, in terms of relative elevation?
the very high Andes mountains along the western coast, the extensive and low-lying Amazon Basin to the east, and the higher, older Brazilian Highlands in the interior. Within the Andes, there are distinct vertical zones ranging from the humid, hot tierra caliente at the base to the cold, freezing tierra helada at the summits.
How does altitudinal zonation affect agricultural production ?
creating distinct zones with different temperatures, growing seasons, and soil types, which determines which crops and livestock can be farmed at each elevation
What are tropical cyclones named in the central & western Pacific Ocean?
cyclones
What are tropical cyclones called in the Indian Ocean?
severe cyclonic storms
What area(s) of Latin America and the Caribbean are most ... and least ... susceptible to tropical cyclones?
the Atlantic coast of Central America, the Greater Antilles (especially Cuba, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico), and Mexico
Where do the larger cities tend to be in Latin America and how does this relate to climate?
coastal regions and at higher elevations in mountain ranges, which offer more temperate climates compared to the hot and humid tropical lowlands
Where are the major rainforest climates and natural vegetation regions of the world ?
tropical regions between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, with the largest areas in the Amazon Basin (South America) and the Congo Basin (Africa), as well as in Southeast Asia and parts of Australia
What environmental conditions (climate, nat. veg. soils) are associated with or generally characterize tropical rainforest biomes ?
characterized by a warm, humid climate with high, consistent rainfall (often over 2500 mm annually) and high temperatures averaging around 26∘C raised to the composed with power cap C 26∘𝐶. This environment supports an incredibly dense and diverse range of native vegetation, including a four-layered canopy of evergreen trees, which, despite the lushness, grows on thin, nutrient-poor, acidic soils that have been leached by rain.
What percentage of the world's land area is forested ?
31%
- What percentage of all of the world's forests are comprised of tropical forests?
45%
What % of the world's forested area (all types) was deforested between 1990 and 2020 ?
4.19%
What % of the world's tropical forests were deforested between 1990 and 2015
10%
In what continents and countries of the world are the greatest amounts of deforestation?
south america and africa
What type of plantations are being created at the expense of natural rainforest in many parts of SE Asia, such as Borneo ?
oil palm
What is meant by "the Pristine Myth" ?
A common myth, sometimes referred to as "the pristine myth," has been perpetuated by colonization; it is the idea that the forests and lands of this area, and the Americas at-large, were relatively untouched prior to colonization
how did the pristine myth catch on?
it served to justify colonial conquest, as colonizers could claim ownership of a seemingly "empty" and "untouched" land
What happened to native American population levels and landscapes after initial contact with Europeans and Africans ?
catastrophic declines due to diseases like smallpox and measles to which they had no immunity, compounded by warfare, forced migration, and enslavement
According to some estimates, what percentage of the pre-Columbia population of the Americas was lost due to diseases
brought by European colonists and enslaved Africans during the 16th century?
between 80 and 95 percent
How can shifting cultivation be practiced sustainably ?
allowing long fallow periods for land regeneration, using manual clearing to minimize erosion, practicing crop rotation and intercropping to maintain soil fertility, and aligning with local population densities
How/why can shifting cultivation also be practiced unsustainably ?
when the fallow period is too short for the land to regenerate, typically due to population growth
In the 2 1 century, what human activity has become the single biggest driver of deforestation in the Amazon Basin ?
cattle ranching
What are the negative/undesirable impacts of tropical deforestation ?
climate change from releasing greenhouse gases, loss of biodiversity due to habitat destruction, severe soil erosion, and disruption of local and global water cycles