Introduction to Molecular Genetics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Life is WHAT
Diverse
1.7 million WHAT species about HOW MUCH of the estimated number on earth
1.7 million EXTANT (living) species about 1/5 of the estimated number on earth
Most species are WHAT about HOW MANY since life first formed
Most species are EXTINCT about 850 million since life first formed
Genetics
Study of HEREDITY and VARIATION in cells, individuals and populations
Gene
Functional unit of heredity and variation
Genetics is simply the study of WHAT
Genes
Molecular genetics is WHAT
The study of structure and function of genes at the molecular level (DNA)
Why is studying molecular genetics important
Human health
Forensics
Agriculture
Environment
Evolutionary biology
Human health
Better understanding of disease results in better drugs and organ matching
Forensics
Crime, paternity test
Agriculture
Superior live stock
Environment
Molecular ecology
Evolutionary biology
Phylogenetics (following one trait in a species) and Phylogenomics (following multiple traits)
Gene
Specific DNA sequence that codes for specific mRNA (and protein) (functional unit of hereditary)
Genome
All genetic information of an organism (entire DNA sequence)
Allele
Variant forms of a gene caused by differences in DNA sequence
Genotype
The specific genes inherited by an individual (combination of alleles that you have)
Phenotype
Visible traits (expression of traits) (has an environmental component)
What is gene expression
Turning on (expressing) a gene to produce RNA and protein
Turning the genotype into a phenotype
Follows the central dogma of biology
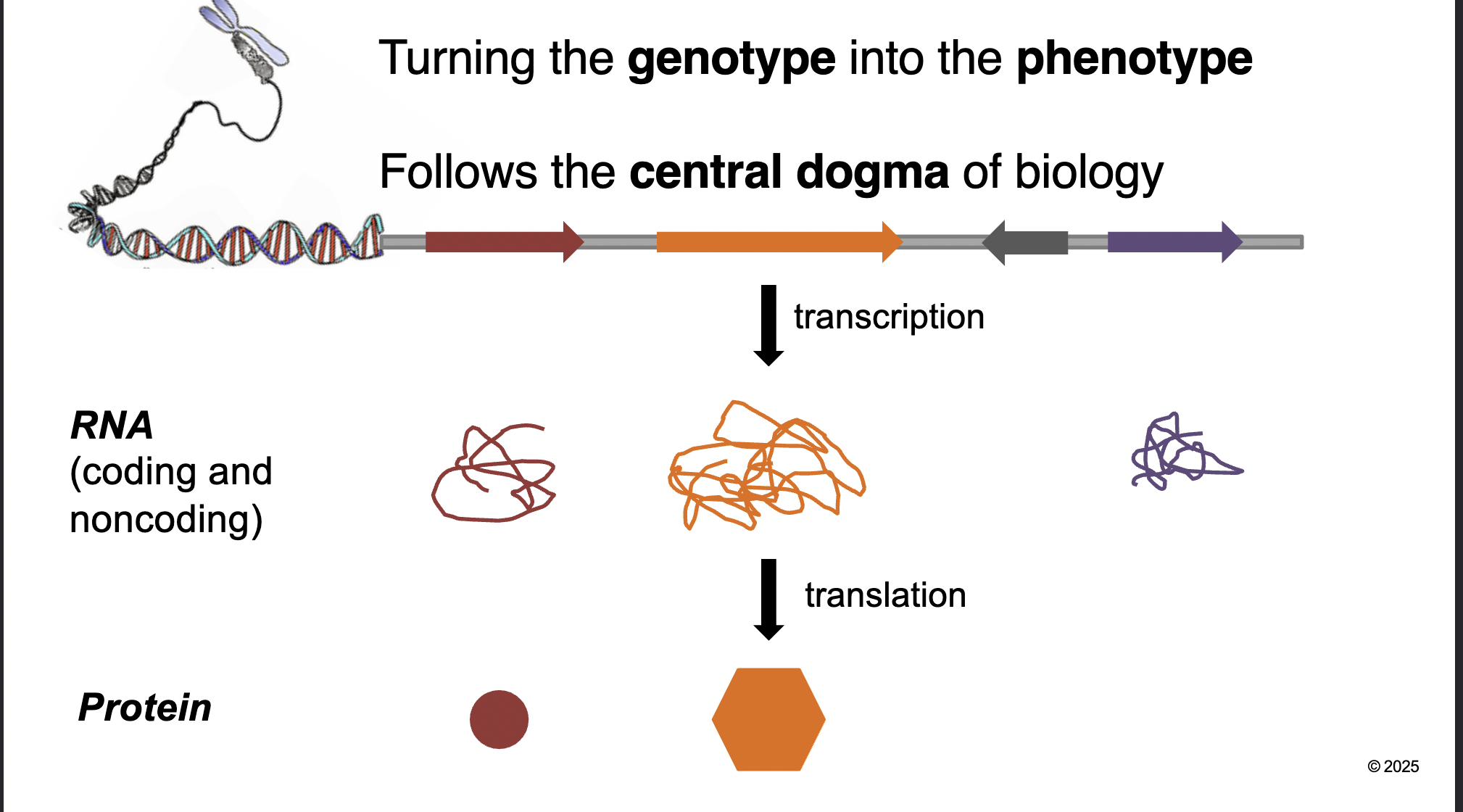
Amount of WHAT made varies in a WHAT
Amount of PROTEIN made varies in a POPULATION (the type and abundance in a cell)
Protein expression specifies WHAT
Phenotypes
Although DNA is the information molecule that directs protein expression, WHAT ultimately determine the phenotypes of cells because they are the WHAT
Although DNA is the information molecule that directs protein expression, PROTEINS ultimately determine the phenotypes of cells because they are the TRAITS encoded by the DNA
What proteins are involved
Enzymes
Structural proteins
Signally (communicating) proteins
Enzymes
Catalyze the synthesis and transformation of all biomolecules
Structural proteins
Maintenance of cell shape
Signally (communicating proteins)
Hormones and receptors
What makes individuals different form one another
Different alleles
Slight variation in gene sequence results in changes in amino acids (eye colour)
Different regulation of gene and protein expression (pale blue vs deep blue eyes)
Unique alleles and differential regulations of thousands of genes among individuals leads to WHAT
Unlimited phenotypes possibilities
Individuals that posses similar alleles and genes regulation leads to more similar WHAT
Protein expression in phenotypes (immediate family)
Heredity / Inheritance
The transmission of traits from one generation to the next
A trait is any characteristic of an individual that is WHAT
Heritable
Humans have been studying inheritance for centuries - WHAT in crops and livestock to artificially select for WHAT
Humans have been studying inheritance for centuries - BREEDING in crops and livestock to artificially select for DESIRABLE TRAITS (size, flavour, seeds etc)
Gregor Mendel:
Studied inheritance in WHAT
Tracked changes in WHAT (and other characteristics) in thousands of pea plants
Worked out the mechanism showing how WHAT from one generation could be WHAT to the next - heritable traits result from a mixing of WHAT
Gregor Mendel:
Studied inheritance in GARDEN PEAS
Tracked changes in FLOWER COLOUR (and other characteristics) in thousands of pea plants
Worked out the mechanism showing how TRAITS from one generation could be PASSED DOWN to the next - heritable traits result from a mixing of PARTICULATE FACTORS (genes)
Chromosome theory of inheritance:
Individuals have HOW MANY copies. of each chromosome
Similar (WHAT) chromosomes WHAT during meiosis
WHAT : have 1 copy of each chromosome
WHAT : Are a random combination of 2 gametes
Chromosome theory of inheritance:
Individuals have 2 copies. of each chromosome
Similar (HOMOLOGOUS) chromosomes SEPARATE INDEPENDENTLY during meiosis
GAMETES : have 1 copy of each chromosome
ZYGOTES : Are a random combination of 2 gametes
Chromosomes are composed of both WHAT and WHAT
Chromosomes are composed of both PROTEINS and DINA
Proteins (WHAT-WHAT%)
Composed of HOW MANY amino acids
Millions of possible WHAT
Complex enough to store WHAT
Proteins (50-60%)
Composed of 20 amino acids
Millions of possible 3D STRUCTURES
Complex enough to store HERITABLE INFORMATION
DNA (WHAT-WHAT%)
Composed of HOW MANY nucleic acids
WHAT and limited WHAT
Thought to play a WHAT role
DNA (40-50%)
Composed of 4 nucleic acids
SIMPLE and limited 3D STRUCTURE
Thought to play a STRUCTURAL role