Paper Chromatography
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Method for chromatography of single food colouring.
Draw a pencil line about 2cm from the bottom of the chromatography paper. Pencil will not mix with the dyes.
Use a capillary tube to place a spot of food coloring on the line
Pour about 1cm of water/oil into a beaker
Attach paper to glass tube with tape and hang from beaker. Make sure the paper is dipped into the solvent but solvent line is below the pencil line.
Place a lid on the beaker to prevent evaporation of water
Remove the paper when the solvent reaches about 3/4 up the paper and mark solvent front by drawing a straight line
Hang up to dry
Why do we use a capillary tube?
To place small dots so dyes do not mix with eachother
How to find the Rf value?
Rf= distance travelled by substance/distance travelled by solvent
Mobile phase
where molecules can move
Stationary phase
where molecules can’t move
What happens to a substance which is more soluble in the solvent?
will spend more time in the mobile phase
move further up the paper
What happens to a substance which is more attracted to the paper?
will spend more time in the stationary phase
stays lower down the paper
How does the number of spots change with different solvents?
distribution of chemicals will change
How to calculate Rf value?
distance travelled by substance/ distance travelled by solvent
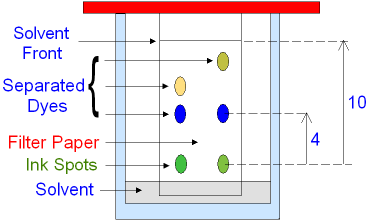
How to know if the reference value is the same as the compound value?
Test in different solvents and see if Rf values are the same
How are different solvents at different positions on the chromatography paper?
solvent moves through paper
different dyes have different solubilities in solvent
and different attractions for the paper
and so are carried different distances
What is gas chromatography used for?
separate complex mixtures
What is the mobile phase in gas chromatography?
inert gas
What is the stationary phase in gas chromatography?
inert liquid