Sources of energy in costal environments
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Sources of energy
Wind, waves, tides and currents are the energy inputs in the coastal system, as well as important erosion and transport
Creating wind
Air moving from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure
How wind forms waves
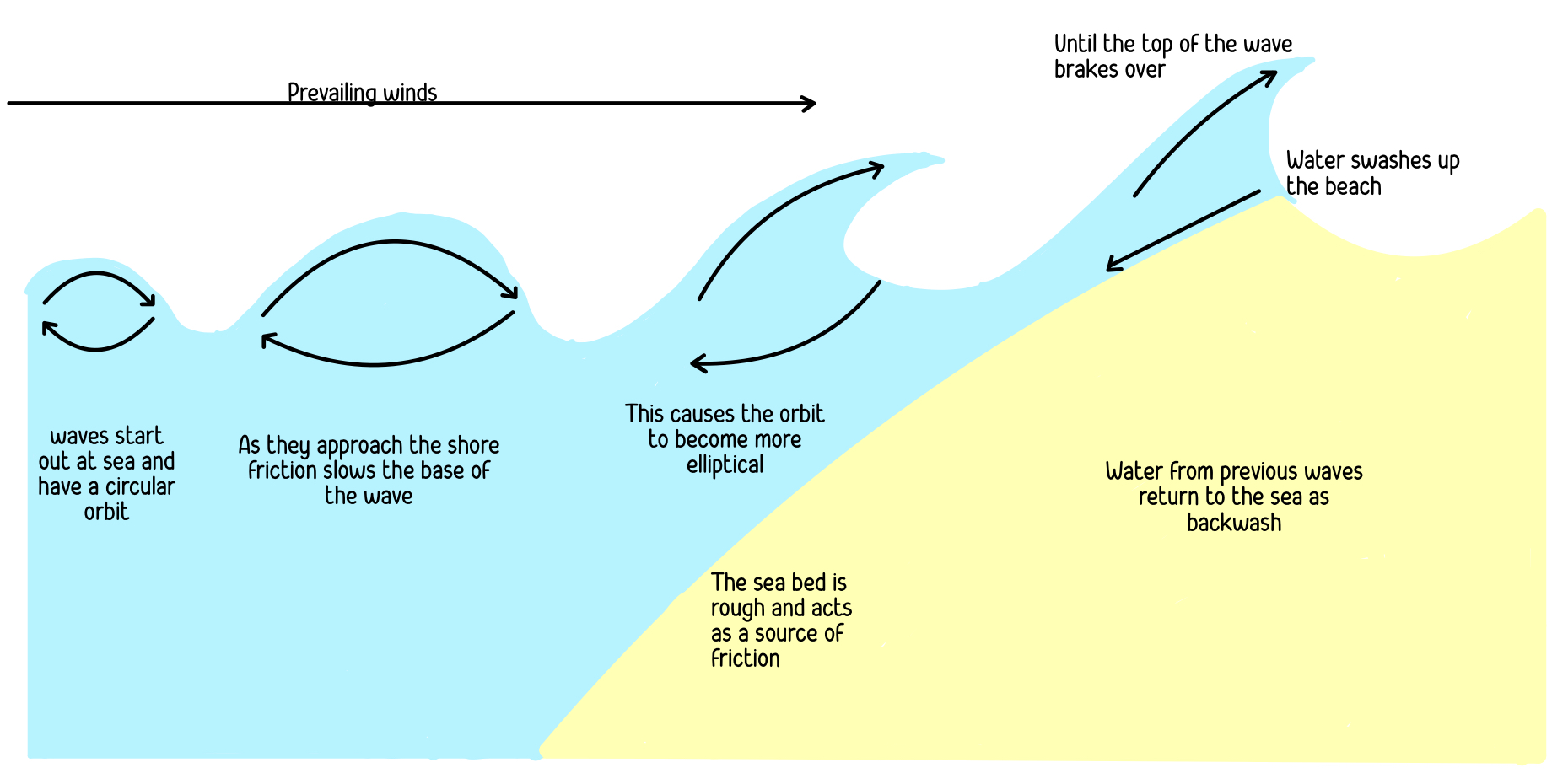
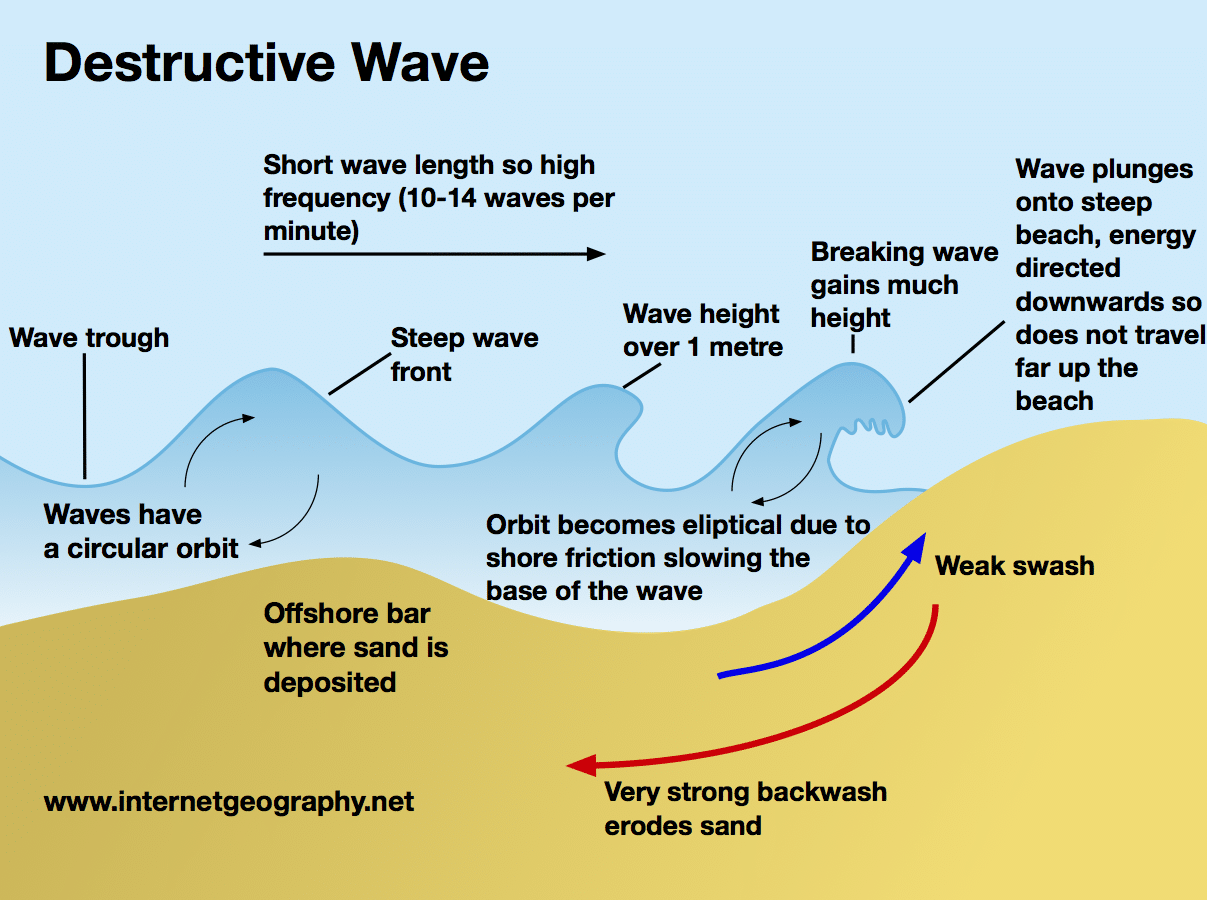
Deconstructive waves
high and steep
more of a circular cross profile
higher frequency (10-14 waves per min)
stronger backwash
weak swash
erosion
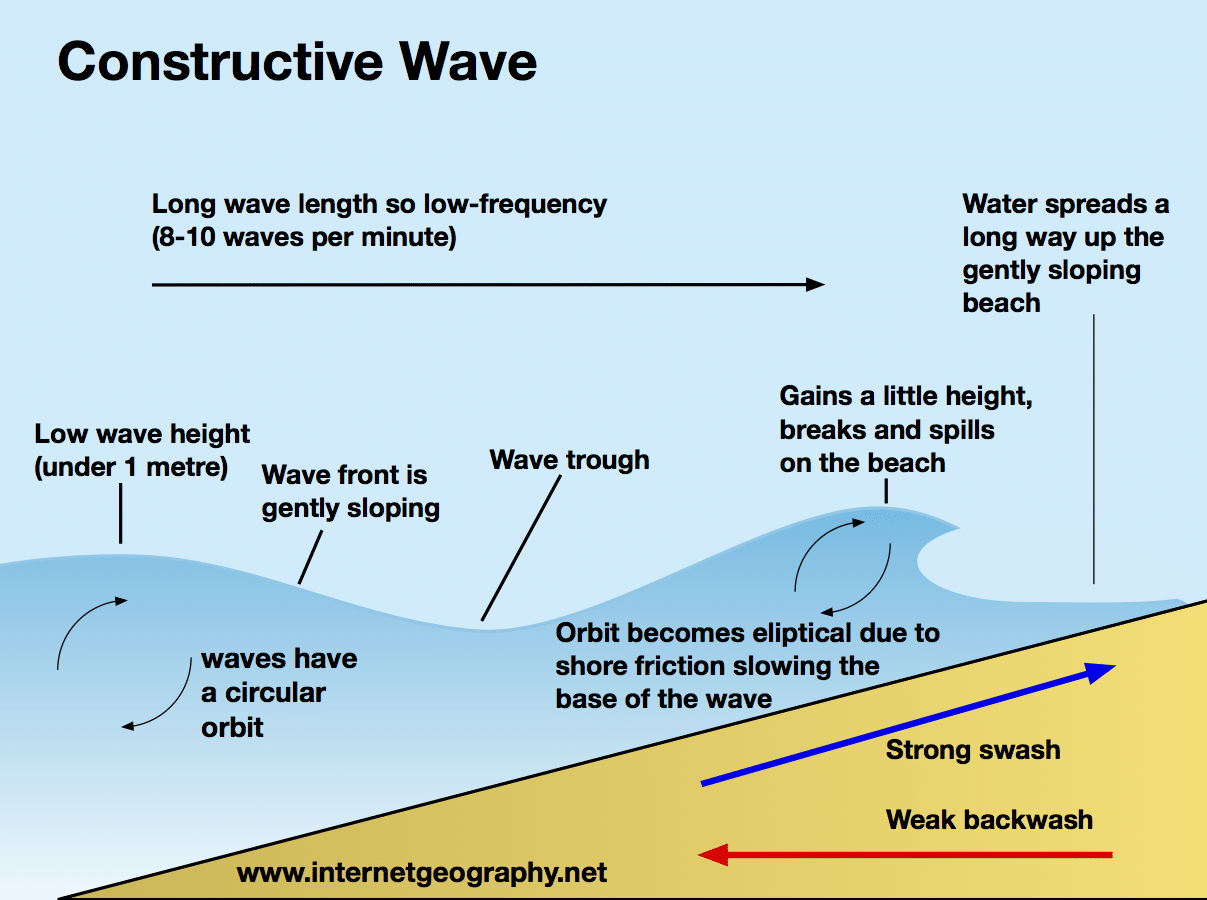
Constructive waves
Lover frequency (8-10 waves per min)
low and long waves
stronger swash
weaker backwash
deposition
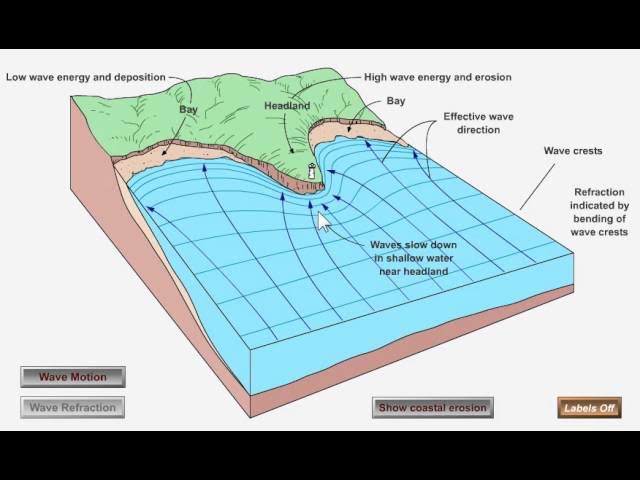
Wave refraction
As waves approach a coast, due to the uneven coastline, they are refracted so that thier energy is concentrated around headlands but reduced around bays. Waves then tend to approach coastlines parallel to it, and thier energy decreases as water depth decreases.
Tides
Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the sun and moon. Tides are long-period waves that appear to move through the oceans due to the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun. There apparent movement towards the coast creates a rise of the sea surface, though due to the earth’s rotation it is the coast rolling into a deeper bulge of ocean that created the effect. Where the sea surface rises to its highest point, this is known as spring tide and at the lowest point, this is known as neap tide. The difference is tidal range.
Tidal range
Macrotidal - more than 4m
Mesotidal - 2-4m
Microtidal - Less than 2m
Storm surges
A storm surge is a change in sea level that is caused by a storm
Storm surge flooding of 8.2m above normal tide levels was associated with Katrina, water travelling up to 19km inland
The main cause of a storm surge is high winds pushing the sea water towards the coast, causing it to pile up there. There is also a smaller center of the storm “pulling” the water level up, by about 1cm for every 1 millibar change in pressure
The strong winds in the storm generate large waves on top of the sea defences, or spill over the top adding to the flood risk. In the case of tropical storms (such as hurricanes), there may also be very large amounts of rain which further increases the risk of flooding.
Currents
Ocean currents are flows in water in one direction these are caused by:
Winds
Variations in water temperature
Changes in salinity
Costal Zones
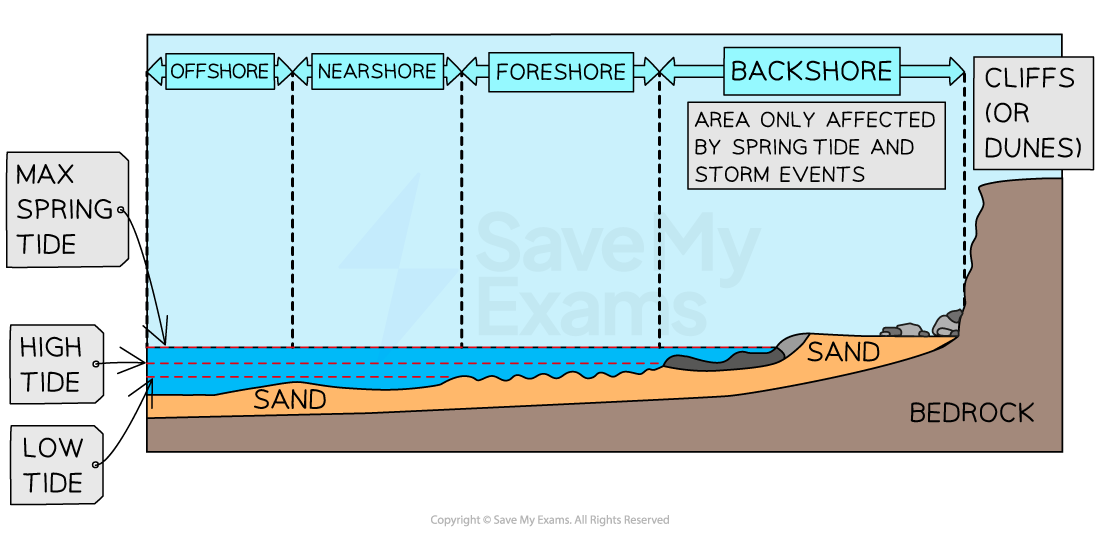
Low energy coasts
Waves are not powerful for a significant part of the year
The rate of deposition exceeds the rate of erosion
Characteristic landforms include beaches and spits
High energy coasts
Waves are powerful for a significant part of the year
The rate of erosion exceeds the rate of deposition
Characteristic landforms include headlands, cliffs and wave cut platforms