ap gov unit 1
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
the declaration of independence (3)
justified american revolution and outlined core principles:
natural rights
popular sovereignty
social contract
natural rights
inalienable rights that all humans possess (life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness)
popular sovereignty
gov authority comes from consent of the people
social contract
indivs give up some freedom to gain protection for natural rights
forms of democracy (elite, pluralist, participatory)
elite: elected representatives legislate for the ppl
appointing of SCOTUS judges, electoral college
pluralist: political parities & interest groups
NAACP, indiv US states
participatory: ppl exercise 1st amendment
initiatives (measures on ballots) & referendums (oppose laws)
republicanism
citizens elect representatives to rule for the common good (practice popular sovereignty)
article i
great compromise
elastic clauses
commerce clause
bill → law
slavery
(and enumerated powers)
LEGISLATIVE -
bicameral congress - great compromise (balance virginia (pop based) + NJ (equal rep.))
house: 2 yr, pop elected
senate: 6 yr, 2 per state
commerce clause: regulate interstate trade
+ can’t tax exports
elastic clause: allow congress to make “necessary & proper” laws to carry out the constitution
bill → law
originate in house/senate → committee reviev
floor debate & voting (2/3rd)
president vetos/signs into law
SLAVERY -
3/5th compromise: slave is 3/5th of a vote for electoral college
importation of slaves: congress can’t regulate slave trade for 20 yrs
article ii
EXECUTIVE -
president appoints judges/officials, treaties, veto
electoral college
impeachment, 2/3rd congress veto override
article iii
JUDICIAL -
establishes federal courts (including SCOTUS)
judicial review to interpret the constitution
article iv
STATES -
equal treatment: honor other state laws
privileges & immunities clause: protect fundamental rights
article v
CHANGE THE CONSTITUTION
proposing amendments:
2/3 of congress or states (or conventions)
ratifying amendments:
3/4 of states or conventions
*no amendment can reduce a state’s senate rep without its consent
article vi
FEDERAL LAW IS SUPREME LAW
also no religious tests
article vii
RATIFICATION OF CONSTITUTION
9/13 of states required (bill of rights swayed reluctant ones)
the articles of confederation (4)
PROS:
avoided tyranny of a central government
CONS:
no exec or judicial branch
no money (can’t tax the states, no currency)
impossible to reach unanimity
no national army
federalists vs anti federalists (style of gov? factions?)
federalist:
republican style gov
minorities are represented on state level (federalism)
diverse factions = compromise is necessary
controlled by checks/balances
anti federalist:
participatory style gov
reps dont work bc US is too large/diverse
N&P + supremacy clauses gives too much power
brutus 1
broad, participatory
large republic is dangerous (representatives are out of touch)
powerful central gov leads to tyranny
federalist 10
pluralist with elite filter
impossible to remove factions
direct democracy would lead to unwise decisions
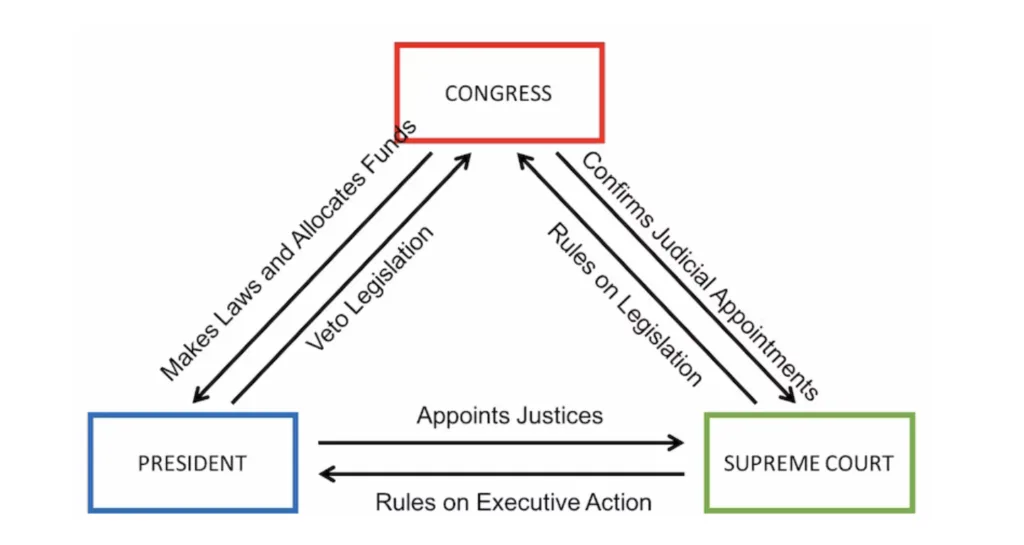
federalist 51
checks and balances on each branch
legislative: lawmaking + funding, confirm judicial & exec appointments
executive: veto or enforce laws, appoint justices
judicial: judicial review
federalism (exclusive, reserved, concurrent powers)
balance of power btwn federal & state governments
exclusive: constitution → federal gov
declare war
immigration and naturalization
reserved: kept by states (10th amendment)
schools, cities, companies
health, safety
concurrent: shared by both
levy taxes, enforce laws
selective exclusiveness
commerce clause is exercised by congress only when uniformity among states is required
fiscal federalism (categorical & block grants, mandates)
categorical: must comply with fed standards
block: broad purpose, states determine specifics (new federalism)
mandates: requires compliance to directives and gives $$$ to do so