11 Stress
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What are the three types of stress?
Neurologic. Endocrine, Immune
True or false: The brain and body respond to physical and emotional abuse in different ways.
False: They only respond to attack.
What nervous system does the stress response activate, and via what control?
sympathetic nervous system, via hypothalamic control
What are the influences of stress?
Duration
Type
Context
Age
Sex
Genes
What are the mediators for stress?
Noradrenaline
Dopamine
Serotonin
CRH
Urocortins
Vasopressin
Orexin
Dynorphin
Corticosteroids
Neurosteroids
What does the sympathetic nervous system do?
Activates fight-or-flight response
increases HR, blood flow, and RR to help us deal with the situation
What does the adrenal cortex do?
secretes cortisol
What is cortisol, and what is its function?
stress hormone secreted by adrenal cortex
increases blood glucose, breaks down protein
What does the adrenal medulla do?
releases epinephrine and norepinephrine
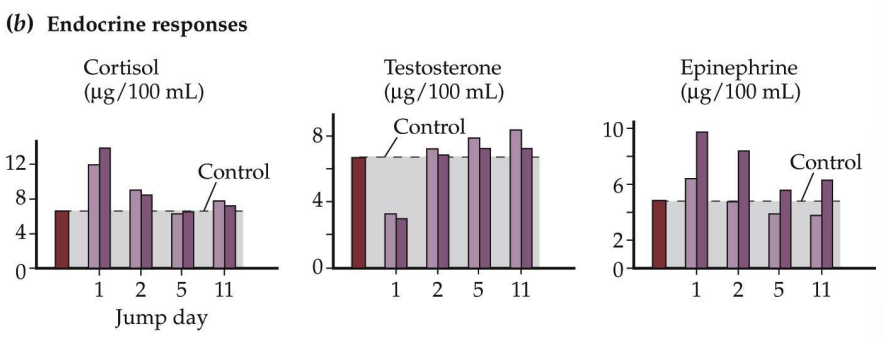
How do cortisol, testosterone, and epinephrine levels change from the first time a person skydives to when a person skydives again and again?
cortisol and epi go down, testosterone goes up
“each time we face our fear, we gain strength, courage, and confidence.”
Does stress have to be caused from physical danger?
No - a crowded train trip can cause stress
What do the hypothalamus, pituitary, and adrenal glands do during acute stress?
Hypothalamus/pituitary stimulate adrenal glands
adrenal glands release:
epi/norepi - increase heart output, liberate glucose
cortisol - provides sustained release of energy to cope
immune system is boosted
Can you die from too much acute stress?
Yes - acute stress can cause cardiac problems such as heart attacks.
What does chronic stress do to the body?
interferes with memory, appetite, sexual desire, and performance
deplates energy and disrupts mood
increases body inflammation
compromises immune system
stress response exhaustion
What are DAMPs?
Danger/damage associated molecular patterns
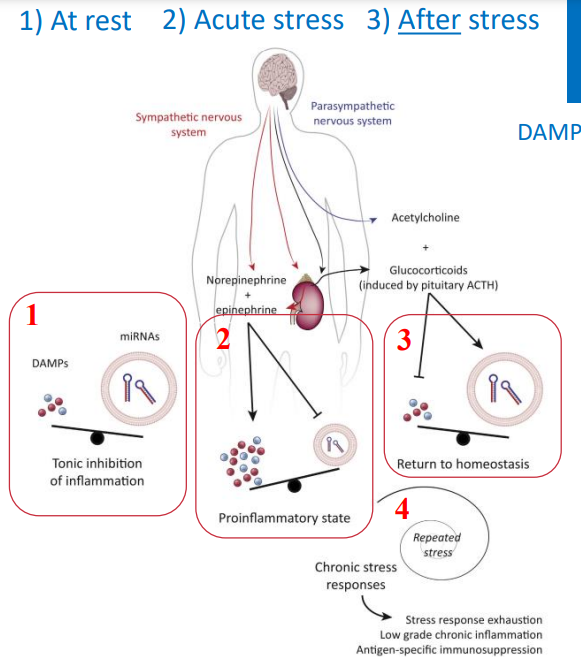
What happens to DAMPs at rest, during accute stress, after stress, and during chronic stress?
At rest: miRNAs balance out DAMPs
Acute stress: epi and norepi cause immune cells to release DAMPs
After stress: balance is restored by cortisol/glucocorticoids
Chronic stress: low-grade excess production of DAMPs or block of miRNAs
DAMPs during stress diagram
what does stress do to our defensive walls?
pokes holes
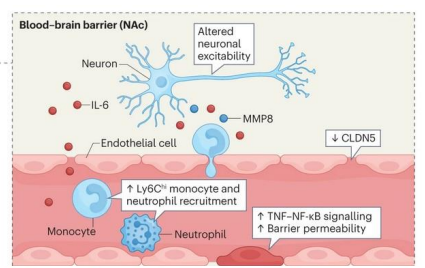
What does stress do to the blood brain barrier (BBB)?
stress triggers inflammatory TNF/NF-kB - increased barrier permeability
stress downregulates claudin 5 (CLDN5) - opens BBB
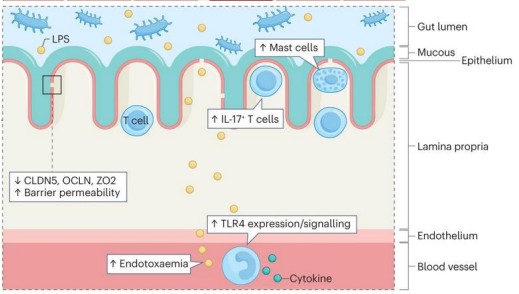
What does stress do to the gut?
increase IL-17 + T cells
LPS enters blood to activate inflammation
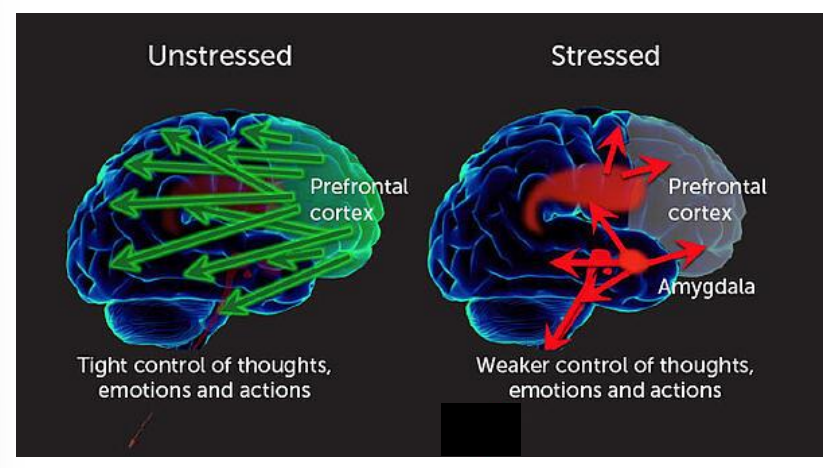
What regions of the brain dominate when we are unstressed vs stressed?
unstressed: prefrontal cortex
tighter control of thoughts, emotions, actions
stressed: PFC, amygdala
weaker control
norepi is [lower/higher] in introverts
higher - blocks immune system
cortisol is [lower, higher] in married adults
lower
When does PTSD develop?
after an exceptionally threatening or catastrophic event (ex: assault, car wreck, rape, war)
What are PTSD symptoms
re-experiencing (flashbacks, nightmares)
avoiding triggers
hyperarousal symptoms (panic)
what are PTSD treatments
behavioral desensitization (“let me take you back to that time”)
ecstasy, psilocybin
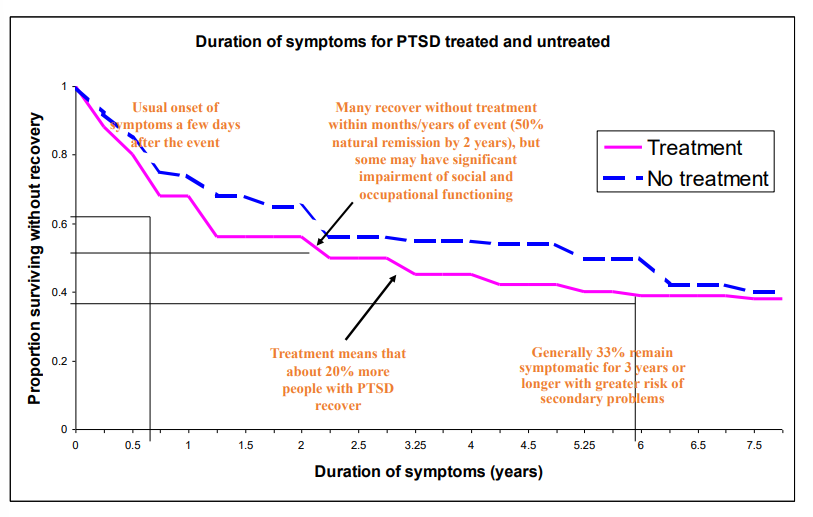
treamtent means that about ___% more people with PTSD recover
20
true or false: all ptsd patients will recover naturally after 2 years
false - 50% natural recovery after 2 years, some may have significant social and occupationsal impairments
what percentage of PTSD patients remain symptomatic for how long?
33% for 3 yrs
natural course of ptsd diagram
Which brain regions are reduced in PTSD patients
frontal cortex and hippocampus
frontal cortex and hippocampus volume is _______ in people with ptsd
reduced
which tissue is reduced in torture victims
cortical tissue
what causes damage due to stress, and why?
cortisol - perhaps increased receptor sensitivity
where did the monkey that died of stress have damage
hippocampus - less cells, underwent structural remodeling
what do astrocytes do during early-life stress?
excessively prune excitatory synapses on inhibitory neurons
ex: rat has early social deprivation, goes on to have abnormal neuronal firing, reduced sociability, and depressive behavior
introverts with HIV have [higher/lower] virus titers than extroverts with HIV. why is this
higher
norepi levels are higher in introverts, norepi blocks immune system
what kind of subjects do flu antibodies increase more in
high left hemisphere activity (associated with pos emotions)
What are the buddhist coping strategies?
Meditation
Mindfulness
Loving/kindness (i’m okay, you’re okay)
morality (golden rule)
impermanence (nothing lasts forever)
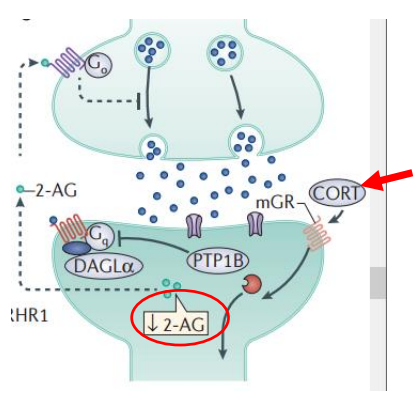
what does the eCB system do
resiliance during and/or after stress
what synthesis does chronic stress impair
stress → cortisol → impairs 2-AG synthesis
what causes habituation to stress
increased eCB system activity
diagram of the eCB synapse
What is aggression
behavior intended to harm
What are the two types of aggression
reactive - impulsive, provoked, emotionsal
proactive - premediated, unprovoked, emotionless
aggressive men and women have [large/small] amygdalae
seizure activity in amygdala [increases/decreases] aggression
murderers have higher activity of the ________ and the ____________
removing the amygdala [reduces/increases] aggression in ___________% of patients
small
increases
amygdala, hypothalamus
reduces, 33-100
Why are bullies aggressive? What brain regions become active when they watch pain inflicted on others
bullies find sadism rewarding
amygdala and striatum - feel-good areas
reactive aggressors have [higher/lower] activity in prefrontal cortex. what does this do?
lower
behave recklessly, overreact to provocation, sexually promiscuous
ex: road rage
what condition is proactive aggression seen in
psychopathy
psychopaths have:
less autonomic response to stress
impaired amygdala function
what happened in the clicker case
kept changing personas - sociopathy
what is a sociopath
incapable of remorse - may commit very violent acts
what are some examples of sociopaths
charles manson, ted bundy, CHARLES WHITMAN
what is wrong with charles whitman?
brain tumor compressing the amygdala
A man killed a whole bunch of people, including his loved ones. In his diary, he has written that he has been experiencing irrational, overwhelming, and violent impulses. What is wrong with him?
brain tumor compressing the amygdala
small amygdala = more aggression
Which hormones are released due to acute stress?
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine (Increase heart rate and makes glucose available)
Cortisol (Increases metabolism)
Which part of the brain is known as “The Integrator” for emotion?
The limbic system
Which area of the brain does disgust activate?
Insula
- Activated by guilt as well
Which hemisphere of the brain interprets the topical meaning of a message?
Left hemisphere
- Right hemisphere identifies emotional tone
What type of aggression is impulsive, provoked and emotional?
Reactive aggression
What brain structure is small in aggressive people compared to others?
Amygdala