Exp. 7: Water: Its properties and purification
4.3(4)Studied by 67 people
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Last updated 2:04 AM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Water
_______ is one of the most abundant compound on Earth. It is essential in all living organisms and necessary to sustain life. Its chemical components that consists of 2 hyrdogen atoms and an oxygen atom covalently bonded together. Its unique physical properties, it can exists in three state of matter.
2
New cards
high polarity characteristics
Water is known to be a universal solvent due to its ________ characteristics as a molecule.
3
New cards
Hydrate
A compound containing water molecules
4
New cards
Anhydrous compound
a compound does not contain water molecules.
5
New cards
Efflorescence
property of a crystal releases water when exposed to atmosphere with low vapor pressure, it becomes anhydrous. ex. Gauleber's salt (Na 2SO 4 ● 10 H 2O (s)
6
New cards
No reaction
Gauleber's salt (Na 2SO 4 ● 10 H 2O (s) ) on watch glass for 5 mins. Reaction?
7
New cards
Deliquescence
property of a crystal that absorbs water from the atmosphere with high vapor pressure, it becomes hydrated. ex. CaCl2
8
New cards
Dissolved (liquid state)
Anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2), white powder, on watch glass for 5 mins. Reaction?
9
New cards
Light blue to White
Heated blue vitriol
CuSO 4 ● 5 H 2O (s) + heat -> CuSO 4 (s) + 5 H 2O (g) Reaction?
CuSO 4 ● 5 H 2O (s) + heat -> CuSO 4 (s) + 5 H 2O (g) Reaction?
10
New cards
white crystal to light blue
Anhydrous copper (II) sulfate
CuSO 4 (s) + 5 H 2O (l) -> CuSO 4 ● 5 H 2O (s)
Reaction?
CuSO 4 (s) + 5 H 2O (l) -> CuSO 4 ● 5 H 2O (s)
Reaction?
11
New cards
solvent and dilution
Uses of water
12
New cards
solute
_______ is the one that dissolves
13
New cards
solvent
______ is the one that does the dissolving
14
New cards
dilution
resulting for a less concentrated solution
15
New cards
precipitate
a reaction between two solutions forming a solid substance
16
New cards
No reaction
Mixed barium chloride (BaCl2) (white) and potassium chromate (K2CrO4) (egg yellow) on a dry test tube. Reaction?
17
New cards
dissolves in water
Mixed barium chloride (BaCl2) and potassium chromate (K2CrO4) + water. Reaction?
18
New cards
egg yellow precipitate
Mixed barium chloride (BaCl2) and potassium chromate (K2CrO4) on a dry test tube added with water after 5-10 mins.
BaCl2(aq) + K2CrO4(aq) BaCrO4(s) --> 2 KCl(aq)
Reaction?
BaCl2(aq) + K2CrO4(aq) BaCrO4(s) --> 2 KCl(aq)
Reaction?
19
New cards
blue green solution, brown gas
Copper wire with 1 mL concentrated Nitric acid (HNO3).
4 HNO3(l) +Cu(s) -> Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NO2(g) + 2 H2O(l)
Reaction?
4 HNO3(l) +Cu(s) -> Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NO2(g) + 2 H2O(l)
Reaction?
20
New cards
blue solution, yellow gas
Copper wire with 1 ml Nitric acid (HNO3) + 2 mL water.
8 HNO3(aq) +3 Cu(s) -> Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NO(g) + 4 H2O(l)
Reaction?
8 HNO3(aq) +3 Cu(s) -> Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NO(g) + 4 H2O(l)
Reaction?
21
New cards
Hydrolysis
a chemical process of decomposition involving the splitting of a bond and the addition of the hydrogen cation and the hydroxide anion of water
22
New cards
Yellow, clear liquid
Water + ferric chloride. Reaction?
23
New cards
Brown acidic solution
Water + ferric chloride + heat (5mins). Reaction?
24
New cards
Surface Tension
the tension of the surface film of a liquid caused by the attraction of the particles in the surface layer by the bulk of the liquid, which tends to minimize surface area.
25
New cards
Diffusion
is the movement of a fluid from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
26
New cards
Turbidity
is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air.
27
New cards
Alum solution
___________ is used as coagulants or flocculants (forming large particles). It causes them to clump together so that they can settle out of the water or be easily trapped by a filter.
28
New cards
red
blue litmus paper turns _____ in an acidic solution
29
New cards
blue
red litmus paper turns _____ in an basic solution
30
New cards
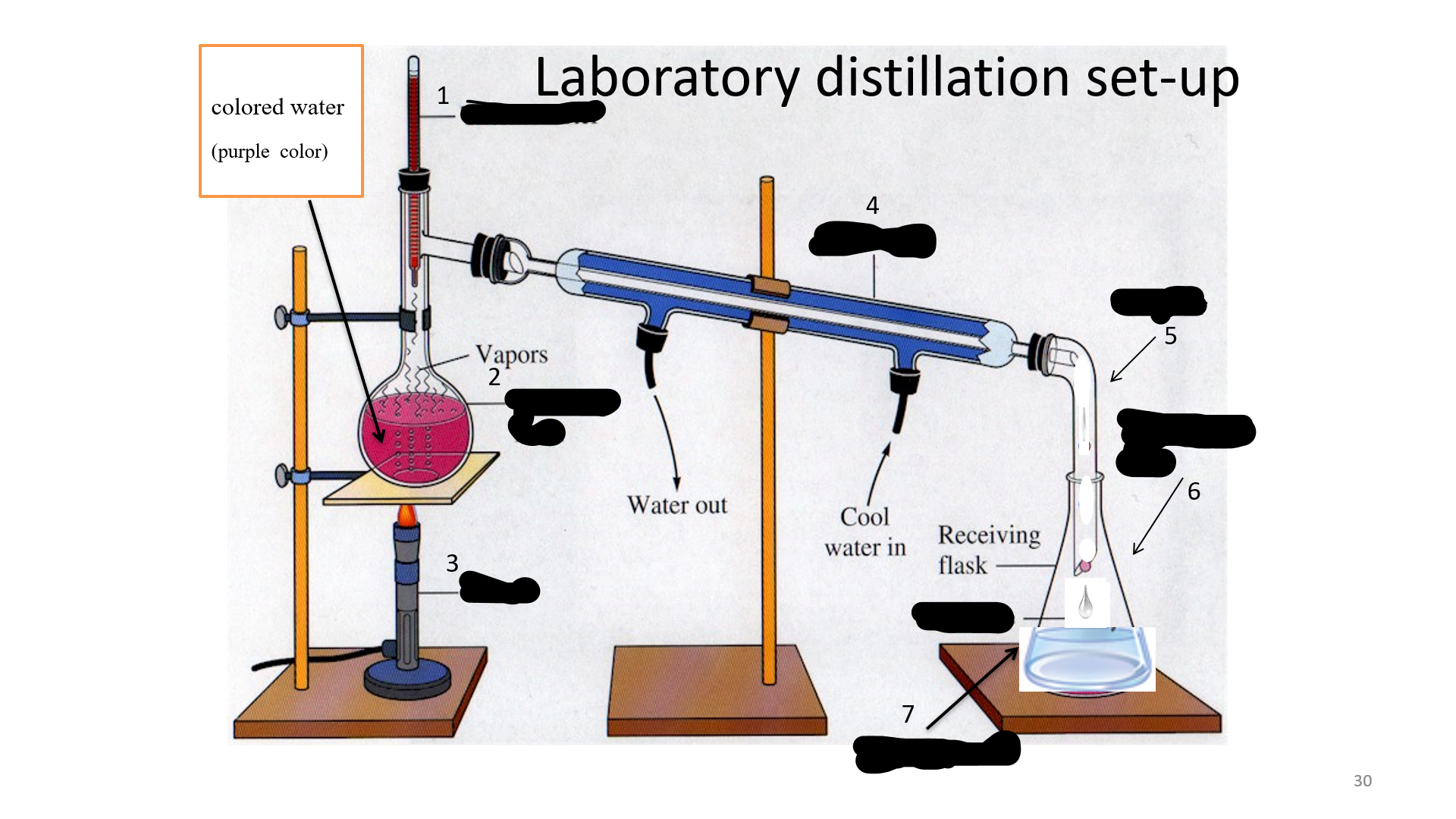
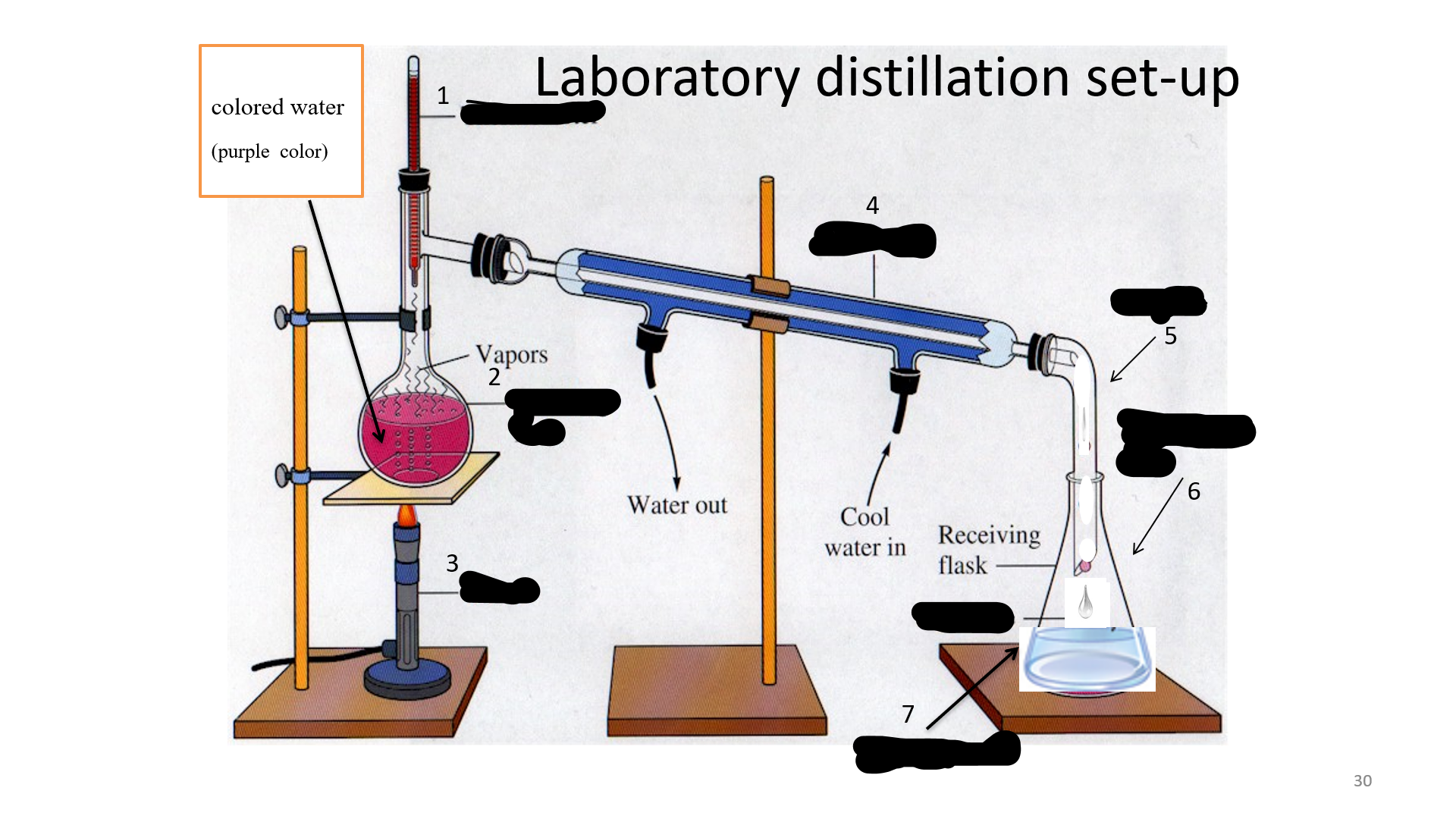
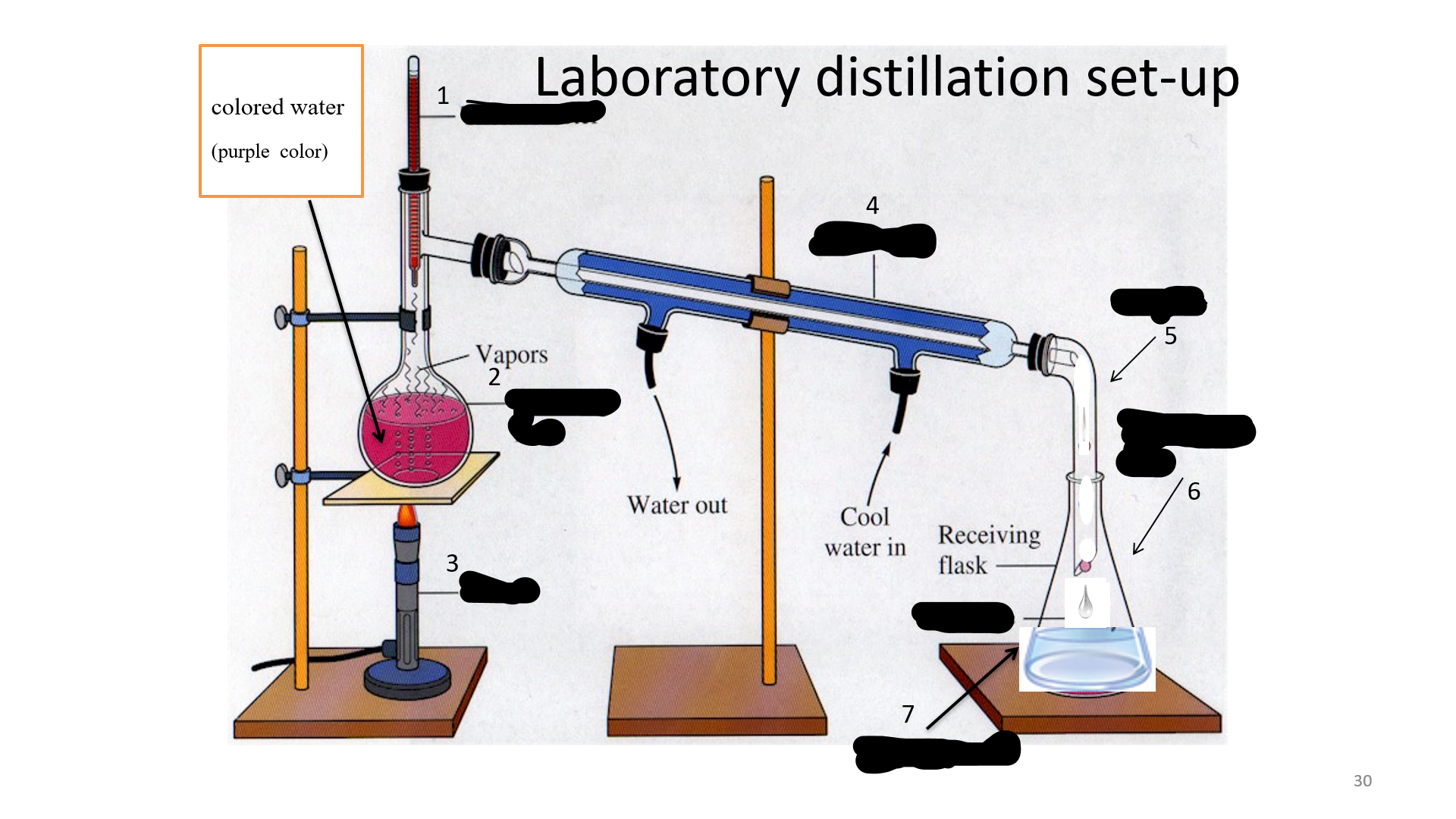
Distillation
is a process of purifying a substance; or a miscible liquid with different boiling temperature; or soluble mixture.
31
New cards
Thermometer
Name that thing (No. 1)
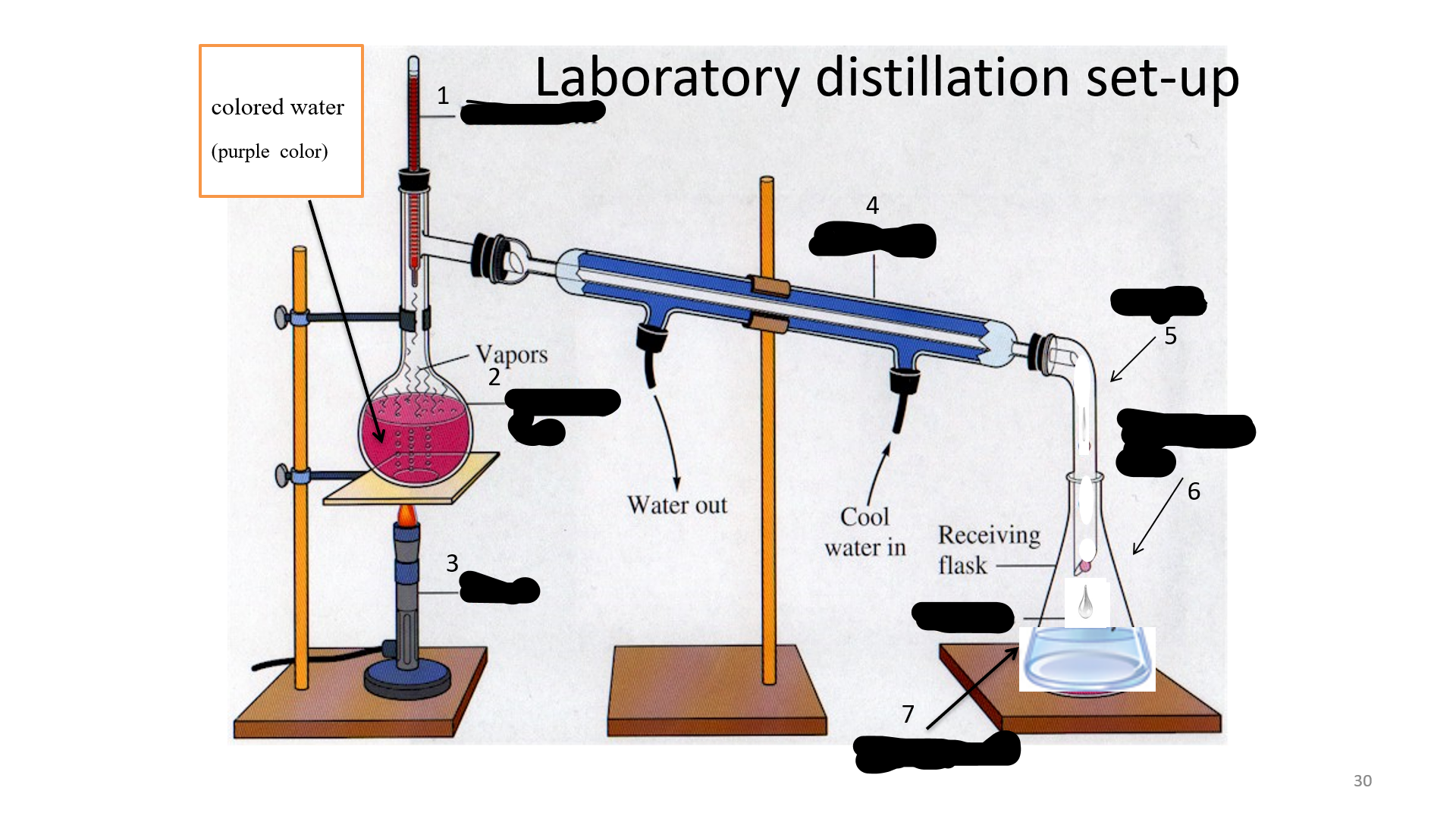
32
New cards
Distilling Flask
Name that thing (No. 2)
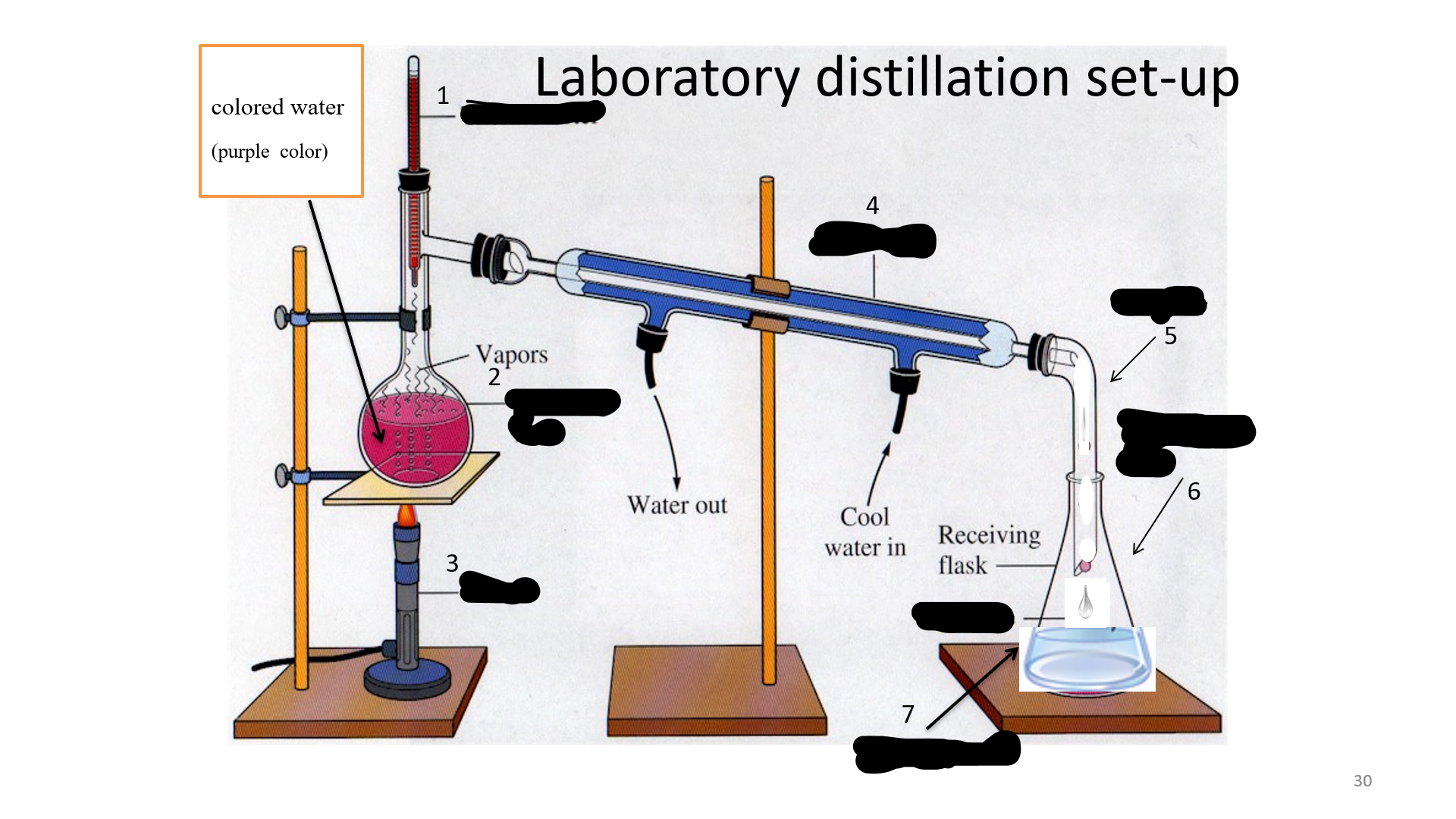
33
New cards
Bunsen burner
Name that thing (No. 3)
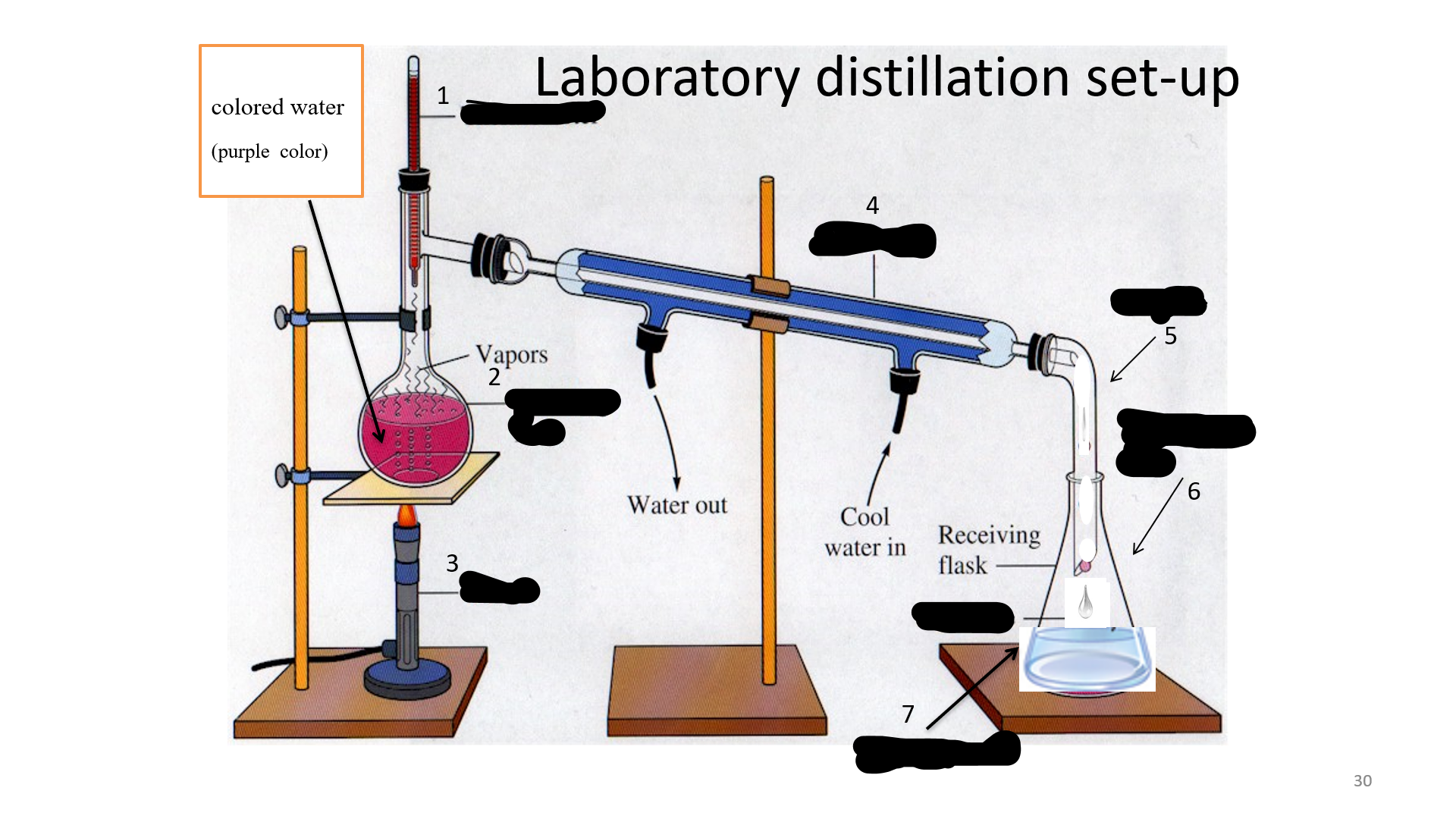
34
New cards
Condenser
Name that thing (No. 4)
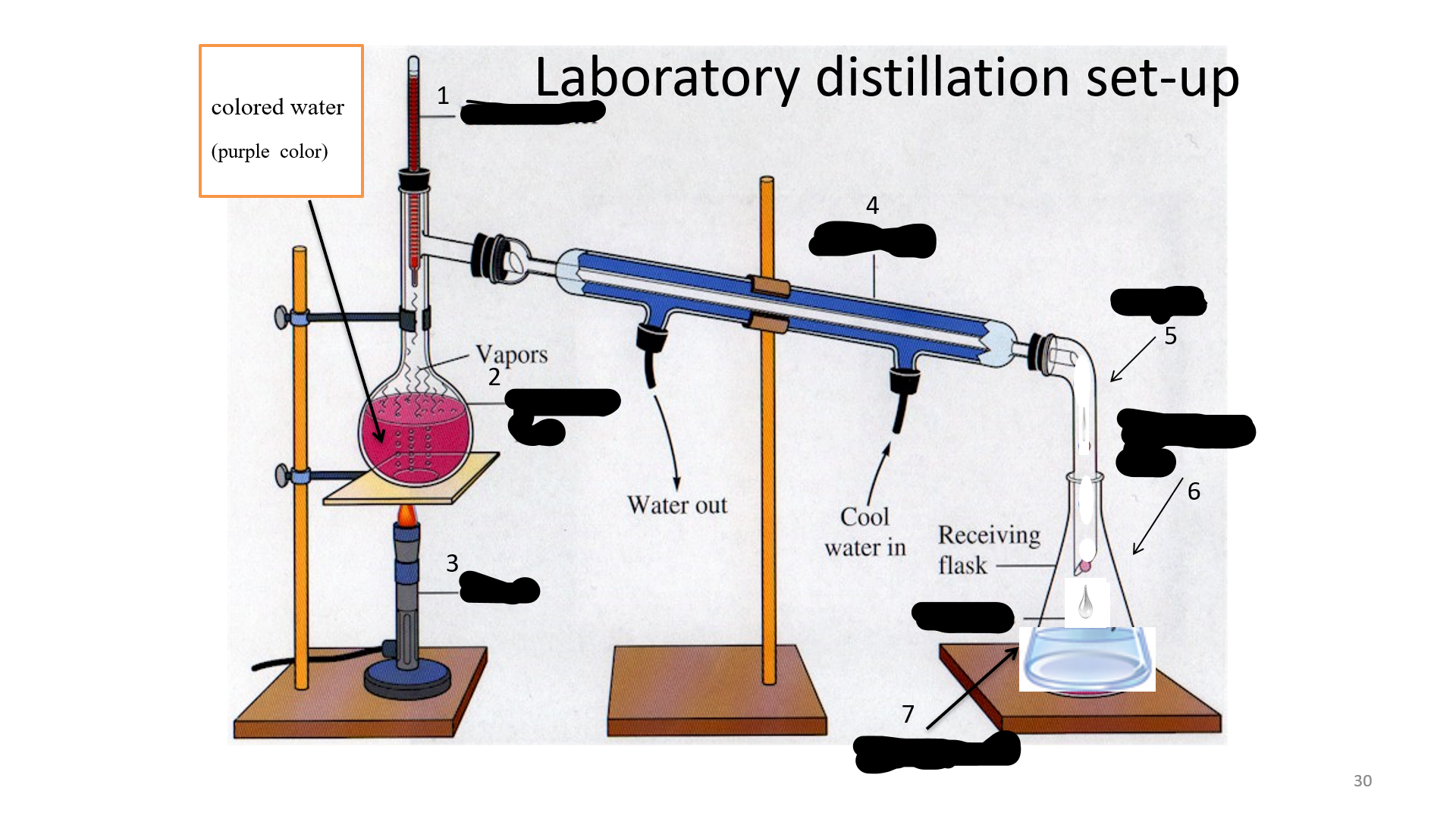
35
New cards
adapter
Name that thing (No. 5)
36
New cards
Erlenmeyer flask
Name that thing (No. 6)
37
New cards
Distillated water
Name that thing (No. 7)
38
New cards
carbonate, bicarbonates, chlorides and sulfates
Hardness in water is due to the present of mineral salts of _______, ______, ________, and __________ of Ca 2+, Mg 2+,
Fe +3
Fe +3
39
New cards
Least
Distilled water (standard soap sol, detergent sol, observation)
40
New cards
More
Tap water (standard soap sol, detergent sol, observation)
41
New cards
moderate
Boiled Water (standard soap sol, detergent sol, observation)
42
New cards
Temporary and permanent
Types of Hardness of Water
43
New cards
Temporary hardness
due to the presence of bicarbonate , HCO 3 – 1 & carbonate, CO 3 – 2 of
Ca 2+, Mg 2+, Fe +3 like calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate and ferric carbonate can be removed by boiling or distillation.
Ca 2+, Mg 2+, Fe +3 like calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate and ferric carbonate can be removed by boiling or distillation.
44
New cards
Permanent hardness
due to the presence of chlorides, Cl – 1 and sulfates, SO 4 – 2 of Ca 2+,
Mg 2+, Fe +3 and can be removed by cation and anion exchange.
Mg 2+, Fe +3 and can be removed by cation and anion exchange.
45
New cards
Soft water
treated water, absence of minerals and removal of permanent hardness