Unit 1 - Chemistry of Life
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Subatomic particles
protons, electrons and neutrons
Nucleus of an atom
made of protons and neutrons in an orbital
Valence shell
the last orbital in an atom
Valence electrons
electrons inside the last orbital
Atomic mass
the total number of protons and neutrons
Atomic number
the number of protons
O, C, H, and N
components of all living matter
Achieving stability
reason for chemical interactions
Covalent bonds
sharing electrons to achieve stability
Pure elements
substances consisting of only one type of atom. (H2 , O2)
Chemical compound
substances that are formed when two or more different elements chemically bond together
Electronegativity
the attraction of an atom to another in a covalent bond
Hydrogen bonds
attraction of a Hydrogen + Electronegative atom with another Hydrogen + Electronegative atom
Ionic bonds
when atom transfer electrons to satisfy their valence shells
Cation
a positively charged ion
Anion
a negatively charged ion
Adhesion
attraction between water and other molecules (xylem in plants)
Cohesion
attraction between water molecules (high surface tension, transpiration pull)
High heat capacity
ability to absorb and release large amounts of heat with only a slight change in temperature (how many C lost per 1 gram).
Crystalline lattice
structure that contains spaces between molecules.
Universal solvent
water dissolves all polar and ionic molecules, facilitating chemical reactions and processes in living organisms.
A mixture
a combination of two or more substances that are PHYSICALLY bonded together
Solutions
a uniform mixture of a solute and a solvent.
Solute
dissolvents that melt into the solution
Solvents
liquids in which solutes dissolve
Aqueous solution
a solution in which water is the solvent
Hydration shell
a layer of water molecules surrounding a solute particle, stabilizing it in solution and preventing it from interacting w/ other molecules
Hydrophilic substances
any substance with affinity (attraction) to water, usually polar or charged.
Hydrophobic substances
substances that repel water, are nonionic and non-polar, or cannot form hydrogen bonds.
Hydrophobic tail
made of non-polar fatty acid chain
Hydrophilic head
made of polar phosphate groups
pH (power of hydrogen)
measuring the concentration of H+ ions in a solution.
Buffer
helps maintain the internal pH of substances
Carbonic acid-Bicarbonate system
buffer system in blood that regulates pH using carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) and bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻)
pH of blood
7.4 (slightly basic)
4 bonds elements
carbon
2 bonds elements
oxygen and sulfer
Location of Sulfer
in proteins
Location of Oxygen and Hydrogen
in all types of macromolecules
3 bond elements
nitrogen and phosphate
Location of Nitrogen
in nucleic acids and proteins
Location of Phosphorus
in nucleic acids and some lipids
Single bond element
hydrogen
Hydrocarbons
organic molecules that consist of carbon and hydrogen atoms (fuel source in biological processes)
Isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangement of atoms
Structural isomers
same molecular formula but differ in the way atoms are connected or arranged (ex:- straight chain vs a branched chain)
Geometric isomers (trans-cis)
compounds with same atoms and same connectivity but have different arrangements
Cis isomers
isomers with similar groups on the same side of a double bond or ring.
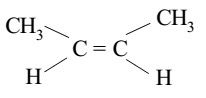
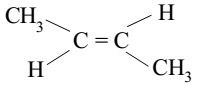
Trans isomers
isomers with similar groups on opposite sides of a double bond or ring.
Enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other, caused by a asymmetrical carbon atom that is 4 bonded.
Estradiol
type of estrogen found in females
Testosterone
the main sex hormone for males
Steroids
a carbon skeleton made up of four infused rings (ex:- estradiol and testosterone)
Chemical groups
groups of atoms that give specific properties and reactions to molecules, (ex:- hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino, and phosphate groups).
Functional group
a specific group of hydrophilic atoms in a molecule that determines its chemical properties and reactions
Hydroxyl group
(-OH) Alcohol, polar
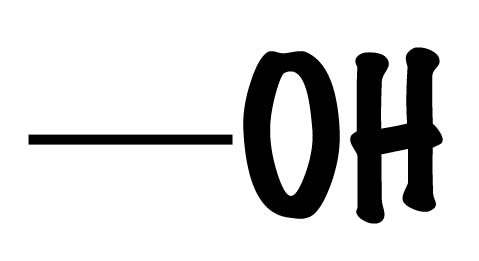
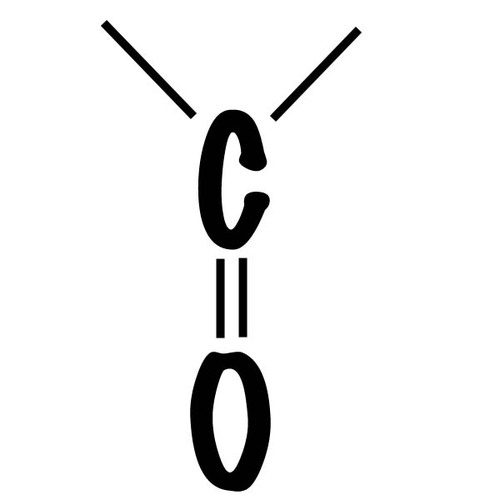
Carbonyl group
(>C=O) Ketone aldehyde, polar
Carboxyl group
(-COOH) Carboxylic acid, or organic acid, polar
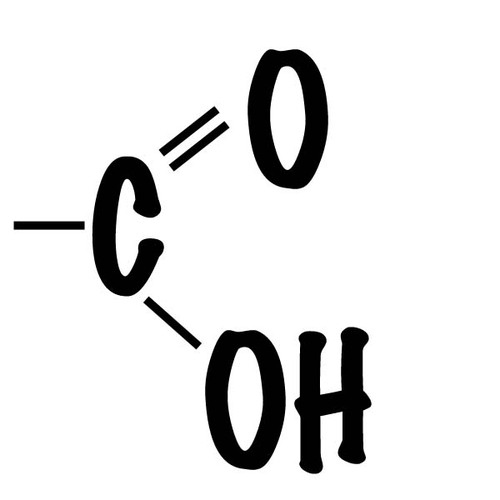
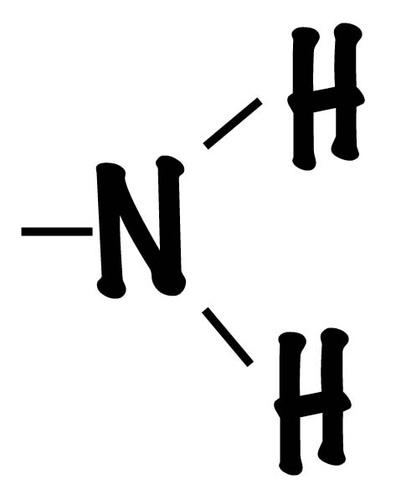
Amino group
(-NH2) Amine, polar
Sulfhydryl group
(-SH) Thiol, polar
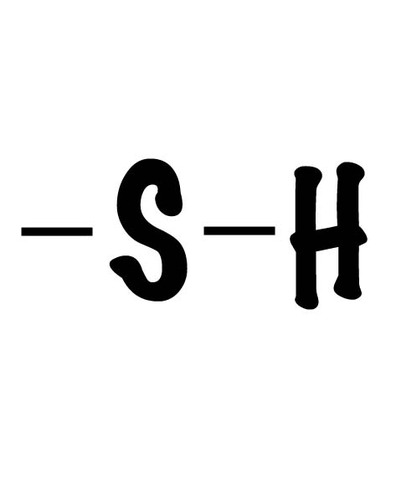
Phosphate group
(-OPO3²-) Organic phosphate, polar
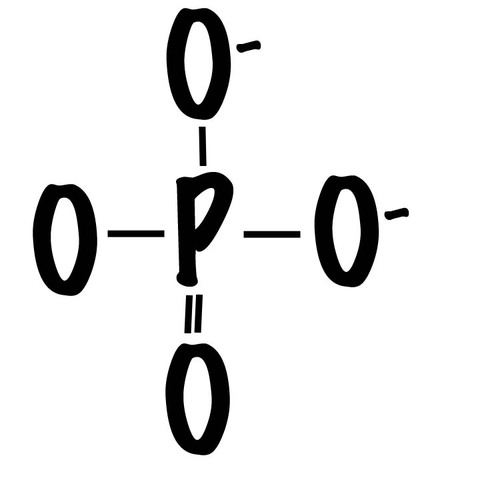
Methyl group
(-CH3) Methylated compound, non-polar
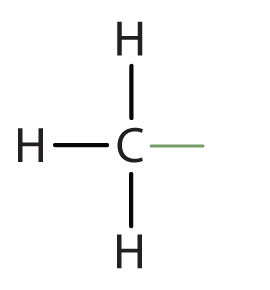
ATP
the energy currency in cells
ADP
an energy molecule that converts to ATP
Polymer
a long molecule made up many monomers (bonded by covalent bonds)
Carbohydrates
made from monosaccharides
Proteins
made from amino acids
Nucleic acids
made from nucleotides
Lipids
made from fatty acids and glycerol
Condensation reaction
a reaction where monomers combine to form polymers, releasing a molecule.
Dehydration reaction
When the condensation reaction releases water
Hydrolysis
Breaking down of polymers by adding water
Enzymes
reusable proteins that speed up chemical reactions.
Defensive proteins
protects against disease
Storage Proteins
stores amino acids
Casein
the protein of milk
Ovalbumin
the protein of the egg white
Transport proteins
transport of substances
Hemoglobin
iron-containing protein in blood
Hormonal proteins
coordinates an organism’s activity
Insulin
a hormone secreted by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar by forcing tissues to absorb glucose.
Receptor protein
responds to the cell by chemical stimuli
Contractile and motor proteins
for movement (actin, myosin, cilia and flagella)
Structural proteins
gives support and shape to cells and tissues
Keratin
the protein of hair, horns, feathers and skin appendages
Collagen and elastin
a fibrous framework in connective tissue
Protein structure
amino group, carboxyl group and side chain
Peptide bonds
covalent bonds that link together amino acids, forms when a carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with an amino group of another
Polypeptides
a chain of amino acids liked together by peptide bonds
Amino acid - Nonpolar
side chains are hydrophobic
Amino acid - Polar neutral
side chains are hydrophilic (slightly charged)
Amino acid - Polar acidic
side chains are hydrophilic (negatively charged, presence of carboxyl group)
Amino acid - Polar basic
side chains are hydrophilic (positively charged, presence of amino group)
Protein - Primary structure
linear sequence liked by peptide bonds
Protein - Secondary structure
parts of the polypeptide chain interact together through hydrogen bonds between atoms of the backbone
Protein - Tertiary structure
the overall 3D shape of a polypeptide
Protein - Quaternary structure
a protein chain made up of two or more polypeptide chain
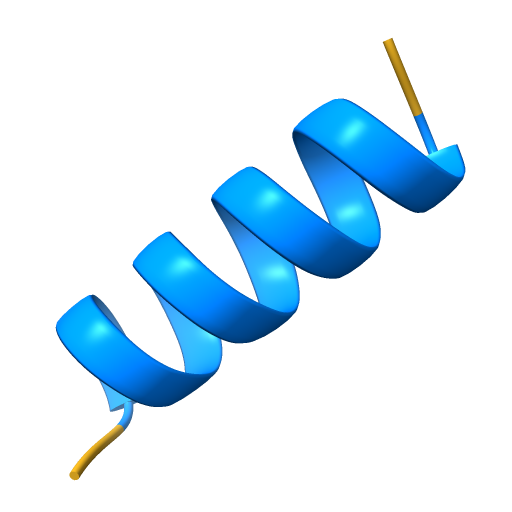
Alpha helix
a coiled structure held together by hydrogen bonds
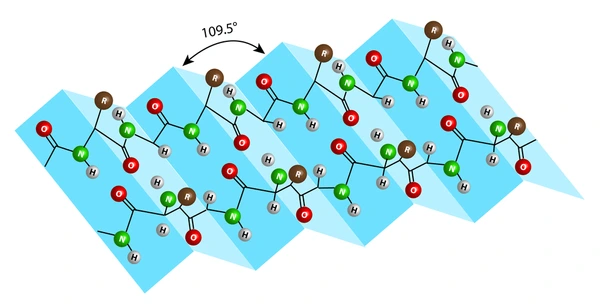
Beta-pleated sheet
flat structure where the segments of the chain line side by side, held together by hydrogen bonds
Denaturation
when the weak bonds holding the protein together is disturbed, causing it to unravel and lose it shape, therefore its function