Chapter 12: Conflict & Peacemaking
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
How does prejudice affect stigmatized group members?
Internalization of stereotypes
attritional ambiguity
Stereotype threat
How does prejudice affect stigmatized NON group members?
Self fulfilling prophecy
Shooter bias
Internalization of stereotypes
Privately accepting the descriptive stereotypes of one’s group as an accurate description of oneself
Attributional ambiguity
Difficulty interpreting feedback from others
E.g., Uncertain whether feedback reflects their own performance OR others’ biases
Negative feedback = “did I do poorly OR is the person giving the feedback prejudiced?”
Positive feedback = “did I do well OR is the person giving the feedback patronizing/compensating for their biases?”
Stereotype threat
Fears that one will confirm the stereotype about one’s group interferes with performance
Stereotype becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy
Stereotype threat experiment
Black and White Stanford students all took a test → difficult verbal passage from GRE
Half were told that the test was diagnostic of intellectual ability
*RESULTS = Black participants got lower scores compared to White participants → self-fulfilling property/stereotype threat
Half were told it was NOT diagnostic
RESULTS = scores were similar
How can we reduce the negative effects of stereotype threat?
Not emphasizing social category
Emphasizing incremental/growth models of ability (NOT fixed mindsets)
Self-affirmations
Simply learning about stereotype threat can reduce its affects
Labelling the situation can help to explain the anxiety is causes and reduce discomfort
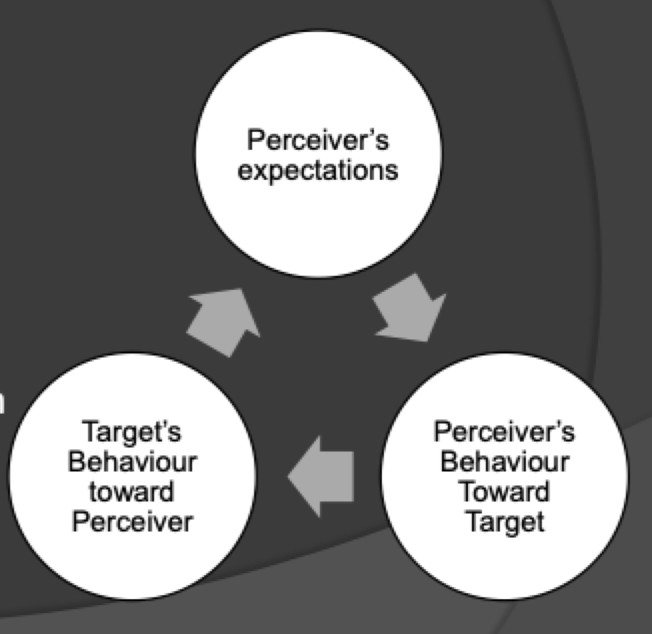
Self-fufilling prophecy
When your expectations about another person lead you to engage with them in ways that confirm those expectations
Shooter bias
The tendency among the police to shoot Black civilians rather than white → EVEN when they are unarmed…
Unarmed Black people = 3.5x more likely to be shot by police (as compared to unarmed white people)
What are 2 ways of reducing prejudice?
Contact hypothesis
Superordinate goals
Contact hypothesis
Increased contact between members of barriers social groups can be effective in reducing prejudice between them
Ex. military, socially assisted housing projects, roommates of different races
*BUT in the context of racial desegregation in American schools → this unfortunately did not reduce stereotypes and prejudice
Moderated version contact hypothesis
Status equivalence
Personal interaction
Multiple out-group members
Co-operative activities
Normalizing intergroup contact
Superordinate goals x jigsaw classroom (making a team)
A co-operative learning method where interracial groups work together
Social outcomes = more positive attitudes toward minority/outgroup members
Academic outcomes = improvement in academic performance for minority/outgroup members (*no change for majority)
Conflict
A perceived incompatibility of actions or goals
Peace
Low levels of hostility and aggression in mutually beneficial relationships
Peace = the outcome of managed conflict
Social trap
When conflicting parties become caught in mutually destructive behaviour → through rationally pursuing their own self-interest
Tragedy of the Commons
The “commons” = any shared resource
Ex. air, water, energy sources, and food supplies
The tragedy occurs when individuals consume more than their share → the cost of their doing so is dispersed among all
THUS causing the ultimate collapse!
Non-zero-sum games
Games in which outcomes need not sum to zero
With cooperation of both teams → both can win!
BUT with competition → both can lose…
*Mixed-motive situations
Equal-status contact
Contact on an equal basis
Just as a relationship between people of unequal status breeds attitudes consistent with their relationship, so do relationships between those of equal status…
THUS to reduce prejudice = interracial contact should ideally be between persons equal in status
Superordinate goals
Shared goals that require cooperative effort → unites group
Goals that override people’s differences
Bargaining
Seeking an agreement through direct negotiation between parties
Mediation
An attempt by a neutral 3rd party to resolve a conflict by facilitating communication and offering suggestions
Arbitration
Resolution of a conflict by a neutral 3rd party who studies both sides and imposes a settlement
GRIT
“Graduated and reciprocated initiatives in tension reduction”
A strategy designed to de-escalate international tensions
How do we avoid social traps?
Rules regulating self-serving behaviour
Keep social groups small so people feel responsible for one another
Enable communication → reduces mistrust
Changing payoffs to make cooperation more rewarding
Invoking altruistic norms