B1.1 Carbohydrates and lipids
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
what are the functions of carbohydrates?
energy source, energy store and structural
what is a monosaccharide?
a single sugar
what are the properties of a monosaccharide?
soluble in water, sweet tasting, form crystals, chemically stable, yields high levels of energy when broken down
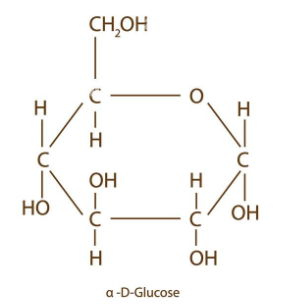
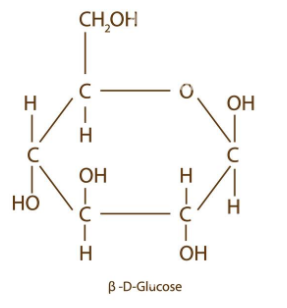
what is different between an alpha and beta glucose?
on C1, alpha glucose has H on top whereas beta has OH on top
draw alpha glucose
draw beta glucose
what is a disaccharide?
2 monosaccharides joined together
what is the carbon , hydrogen, oxygen ration for disaccharodes?
Cn (H2O)n-1
what are 3 examples of disaccharides?
maltose
sucrose
lactose
what are 3 examples of monosaccharides?
glucose
fructose
galactose
what type of reaction joins monosaccharides together?
condensation
draw a disaccharide
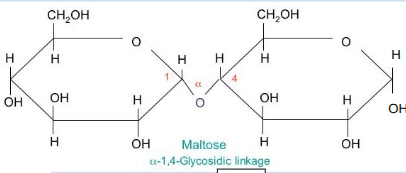
what 2 carbons join together when 2 monosaccharides join?
1 and 4
what is the bond between 2 monosaccharides called?
glycosidic bond
what carbons is a glycosidic bond formed between when there is a branch in the chain?
1 and 6
what is amylose found in, what bonds does it have and what is its function?
found in plants as starch grains
has 1,4 glycosidic bonds so is a straight chain
function is storing energy
what is amylopectin found in, what bonds does it have and what is its function?
found in plants as starch grains
has 1,6 and 1,4 bonds so is branched
function is storing energy
what is glycogen found in, what bonds does it have and what is its function?
found in animals as glycogen granules
has 1,6 and 1,4 bonds, has lots of branches
function is energy storage and can be hydrolysed into glucose
what is cellulose found in, what bonds does it have and what is its function? why is it different?
found in plants as long fibres
has 1,4 glycosidic bonds so is very straight and long
function is structure
different because it is made of beta glucose which flip every other one to allow hydroxyl groups to join.
what is a glycoprotein?
a protein with a carbohydrate chain attached
where are glycoproteins found? what is its role?
plasma membranes
allows cells to recognise each other
what are the roles of lipids?
energy source
store of energy
insoluble
insulation
protection around organs
waterproofing
buoyancy
cell membranes
what is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
C2 has 2 hydrogens on deoxyribose, and on ribose C2 has a hydrogen and a hydroxide
what does glycogen’s highly branched structure allow?
Rapid release of glucose, fast hydrolysis - important for quick bursts of energy in animals
what are the 3 main types of lipids?
triglyceride, phospholipids and steroids and waxes
draw a triglyceride
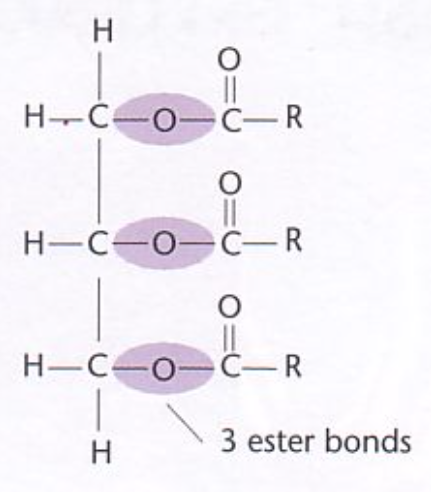
what bonds form between glycerol and fatty acids?
ester
define a saturated fatty acid
no double bonds, tend to be solid at room temperature
define a mono-saturated bond
one double bond
define a poly-saturated bond
multiple double bonds
what is the difference between cis and trans unsaturated fatty acid?
cis have the hydrogens on the same aide at the double bond, creating a kink, trans have the hydrogen on opposite sides at the double bond, so there is no kink.
which unsaturated fat is healthier?
cis
which unsaturated fatty acid has a lower melting point?
cis, usually liquid at room temp
what are triglycerides used for?
energy storage
where is adipose tissue found in animals?
around organs and under skin
what are the properties of triclygerides?
chemically stable
Immiscible with water
Release twice as much energy per gram in respiration as carbohydrate
Poor conductors of heat - thermal insulator
are steroids polar or non polar?
non polar
what are the common features of steroids?
Four fused rings of carbon atoms
17 carbon atoms in total
Varied positions of the carbon
Non-polar nature - pass through the phospholipid bilayer.