Chapter 21 Materials
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
3D arrangement of atoms
in solid materials, is critical to understanding a wide array of properties
regular
Most engineering materials are crystalline — the arrangement is _________, not random. Can predict where atoms should be based on small section
lattices
there are 14 distinguishable crystalline arrangements; but most engineering materials fall into only a handful of simpler types
face-centered cubic (FCC)
atoms at every corner; atoms touch along face diagonals that go through the center of the atom on the face. Close-packed planes are stacked ABCABC…
4 atoms total, efficiency factor: 0.74
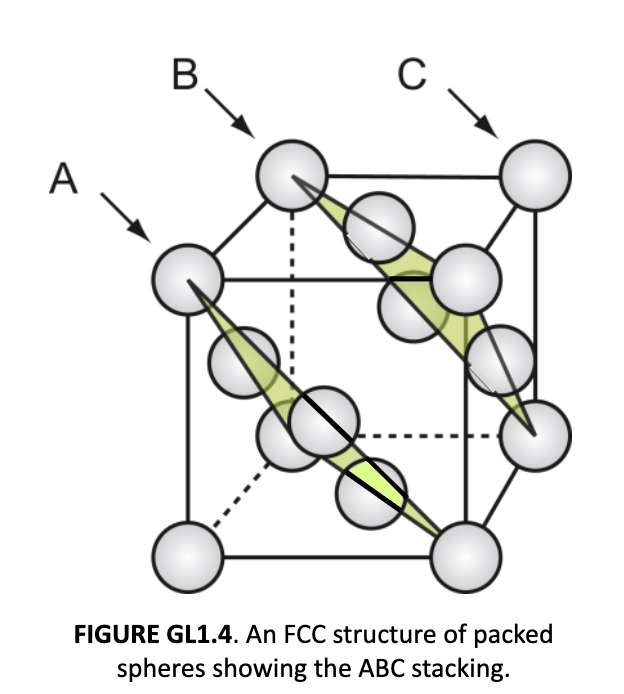
FCC edge length
a = 4r/√2
examples of face-centered cubic metals
aluminum, copper, silver, gold, nickel, platinum, lead, austenitic stainless steel, calcium, strontium, rhodium, palladium, ytterbium, iridium, achnium, thorium, einsteinium (17 metals)
characteristics of face-centered cubic metals
very ductile when pure. work harden rapidly, but soften when annealed, amenable to deformation process, generally tough and resistant to crack propagation, retain ducility and toughness at very low temperatures (unusual)
body-centered cubic (BCC)
atoms at every corner and at the center of the cube. Atoms touch along body diagonals (4). Not a close-packed structure. Lower packing efficiency at 0.68. Two atoms per unit cell
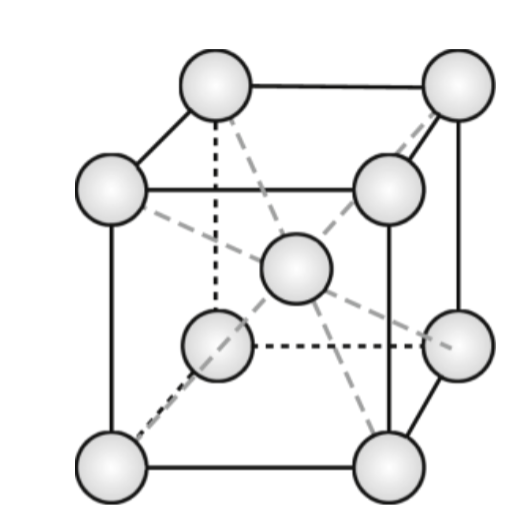
BCC edge length
a = 4r/√3
examples of body-centered cubic metals
iron, chromium, manganese, molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium, niobium, lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, barium, europium, tantalum, and radium (16 metals)
characteristics of BCC metals
ductile, especially when hot. Stronger than FCC. Generally tough and resistant to crack propagation, except at low temperatures (become brittle). Brittle at low temperatures (ductile-to-brittle transition). Strength depends on temperature, even at low temperature
hexagonal close-packed (HCP)
hexagonal unit cell with atoms at each corner, one at the center of the hexagon, and three in the middle. Close-packed with ABABAB… sequence. Sometimes called CPH. 6 atoms, not cubic. Packing efficiency same as FCC (0.74), but less symmetrical
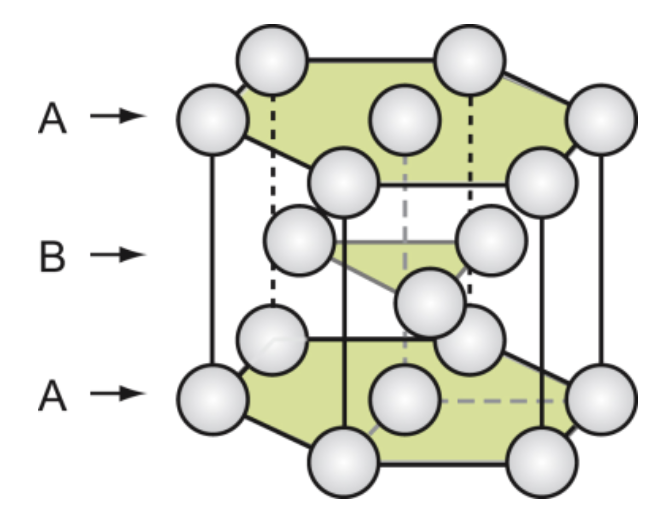
examples of HCP metals
beryllium, magnesium, titanium, cobalt, zinc, zirconium, ruthenium, cadmium, tellurium, lutetium, hafnium, rhenium, osmium, thalium, 11 lanthanide metals, 4 trans-uranium metals (33 metals - ½ of all metals)
characteristics of HCP metals
ductile, but more limited than FCC. More anisotropic than FCC or BCC