AP Psychology Unit 3 Flashcards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
1
New cards
Biological Psychology
The scientific study of how the links between biological and psychological processes.
- brain, nerves, genes, hormones
- brain, nerves, genes, hormones
2
New cards
Nucleus
The brain of the cell, it's "command center"
3
New cards
Cell body
Surrounds the nucleus, holds cell's life support systems
4
New cards
Dendrite
Bushy fibers that receive information and sends it to the cells body
5
New cards
Axon
Passes messages to it's terminal branches, then into muscles and glands
6
New cards
Axon terminal branches
Form junctions with other neurons or cells
7
New cards
Myelin Sheath
A layer of fatty tissue that insulates the axon, they increase the speed of neurotransmission
- Develops until the age of 25
- Grows neural efficiency, judgment, and self-control
- Develops until the age of 25
- Grows neural efficiency, judgment, and self-control
8
New cards
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
The deterioration of the myelin sheath, will eventually shut down muscle control
9
New cards
Neuron
A nerve cell, the basic building block of the nervous system
10
New cards
Action potential + Speed of A.P.
A brief electrical charge that travels down the axon
- slowest = 2 mph, fastest = 180 mph
- Reaction time in humans is measured in milliseconds (thousandths of a sec.)
- Reaction time in computers is measured in nanoseconds (billionths of a sec.)
- chemical signals.
- like a battery. neurons let in positive ions that travel down the neuron
- slowest = 2 mph, fastest = 180 mph
- Reaction time in humans is measured in milliseconds (thousandths of a sec.)
- Reaction time in computers is measured in nanoseconds (billionths of a sec.)
- chemical signals.
- like a battery. neurons let in positive ions that travel down the neuron
11
New cards
Refractory period
A period of inactivity after a neuron has fired
- when it has to "recharge"
- POST NUT CLARITY
- when it has to "recharge"
- POST NUT CLARITY
12
New cards
Excitory signals
Seek to trigger a cell to fire
13
New cards
Inhibitory signals
Seek to keep a cell from firing
- Cells will fire when E > I
- Cells will fire when E > I
14
New cards
All or none response
A neurons reaction of firing 100% or NOT firing at all, no middle ground
15
New cards
Threshold
The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
16
New cards
Synapse
The junction between the terminal branches of one neuron's axon and the dendrites of another neuron.
*information travels from the terminal branches into the dendrites
*information travels from the terminal branches into the dendrites
17
New cards
Synaptic Gap/Synaptic Cleft
The tiny gap at the junction of two neurons
*When the action potential reaches the terminal branches of an axon, it releases chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
*When the action potential reaches the terminal branches of an axon, it releases chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
18
New cards
Neurotransmitters
Chemical molecules that cross the synaptic gap.
- They are released from the terminal branches and move toward the dendrites.
*They also bind to neuro-receptors on the dendrite
- They are released from the terminal branches and move toward the dendrites.
*They also bind to neuro-receptors on the dendrite
19
New cards
Neuro-receptors
They receive neurotransmitters and then activate a neuro-transmission (action potential) in the receiving neuron
*Each neuro-receptor is specifically designed to receive unique neurotransmitters. This helps keep stuff separate
*Each neuro-receptor is specifically designed to receive unique neurotransmitters. This helps keep stuff separate
20
New cards
Synaptic vesicles
Produce + store the neurotransmitters
21
New cards
Re-uptake
When the sending neuron reabsorbs the neurotransmitters
*shortens the refractory period
*shortens the refractory period
22
New cards
Endorphins
Opiate like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure
- They dull/reduce pain, increase pleasure
- They dull/reduce pain, increase pleasure
23
New cards
How to generate endorphins
Exercise - "Runner's High", laughter, Drugs, Thrill rides, Horror movies
24
New cards
AceTylCholine (ACh)
- Helps with learning and memory
- The neurotransmitter at every junction between motor neurons and skeletal muscles
- When ACh is present, the muscle contracts
- When ACh is blocked, paralysis occurs (useful and anesthesia)
- When there is a deficiency, leads to Alzheimer's and dementia
- The neurotransmitter at every junction between motor neurons and skeletal muscles
- When ACh is present, the muscle contracts
- When ACh is blocked, paralysis occurs (useful and anesthesia)
- When there is a deficiency, leads to Alzheimer's and dementia
25
New cards
Dopamine
Influences:
- Movement, learning, attention, emotion
Oversupply: leads to schizophrenia
Undersupply: decreased mobility, Parkinson's
- Movement, learning, attention, emotion
Oversupply: leads to schizophrenia
Undersupply: decreased mobility, Parkinson's
26
New cards
Serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
Undersupply is linked to depression
*Some anti-depressants work to increase serotonin production or stimulate serotonin
Undersupply is linked to depression
*Some anti-depressants work to increase serotonin production or stimulate serotonin
27
New cards
Norepinephrine
Affects mood, alertness and arousal
Undersupply depresses mood
Undersupply depresses mood
28
New cards
GABA (Gammaamino butyic acid)
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter
Undersupply leads to seizures, tremors (ticks) and insomnia
Undersupply leads to seizures, tremors (ticks) and insomnia
29
New cards
Glutamate
A major excitory neurotransmitter
Oversupply leads to seizures, migraines, and overstimulation
Oversupply leads to seizures, migraines, and overstimulation
30
New cards
What neurotransmitters are in undersupply in someone who is depressed?
Serotonin and Norepinephrine
31
New cards
Morphine elevates mood and reduces pain, what category of neurotransmitter is it like?
Endorphins
32
New cards
What neurotransmitter inhibits central nervous system activity to calm a person during a stressful situation?
GABA
33
New cards
Agonist
A molecule that binds to a neuroreceptor and stimulates a response
- Some drugs cause a high by amplifying sensations of arousal or pleasure.
ex.) cocaine
- Some drugs cause a high by amplifying sensations of arousal or pleasure.
ex.) cocaine
34
New cards
Anatagonists
Molecules that bund to a neuroreceptor and inhibit a response
ex.) Bouttin, it's a type of poison that comes from improperly sealed canned foods
- Inhibits ACh
- Causes paralysis
ex.) Bouttin, it's a type of poison that comes from improperly sealed canned foods
- Inhibits ACh
- Causes paralysis
35
New cards
Nervous system
The body's speedy electro-chemical communication network
*To send information from brain to tissues, and from tissues to brain
*To send information from brain to tissues, and from tissues to brain
36
New cards
Parts of the Nervous System
1.) Nerve Cells
2.) Central nervous system (CNS)
3.) Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
2.) Central nervous system (CNS)
3.) Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
37
New cards
Sensory neurons
Carry "incoming information" from sensory receptors to the spinal cord + brain
*From tissue to brain
*From tissue to brain
38
New cards
Motor neurons
Carry "outgoing information" from brain or spinal cord to tissues + glands
*From brain to tissue
*From brain to tissue
39
New cards
Inter Neurons
Neurons within the brain + spinal cord that communicate between motor and sensory neurons, bridges the gap between them
40
New cards
Neuron numbers
- Few million sensory neurons
- Few million motor neurons
- Few billion inter-neurons
- Few million motor neurons
- Few billion inter-neurons
41
New cards
Nerves
Bundles of axons and different neurons that form "cables" connecting the central nervous system with organs and tissues
42
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Comprised of the brain and spinal cord
*The body's "decision makers"
*The body's "decision makers"
43
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The sensory + motor neurons that connect the central nervous system with the rest of the body
*Comprised of somatic and autonomic systems
*Comprised of somatic and autonomic systems
44
New cards
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
Enables the voluntary control of skeletal muscles
ex.) standing then the bell rings
- Arouses and expands energy
ex.) standing then the bell rings
- Arouses and expands energy
45
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Controls the muscles and glands of internal organs
*INVOLUNTARY*
*Comprised of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
*INVOLUNTARY*
*Comprised of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
46
New cards
Sympathetic Nervous System
The division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing it's energy in stressful situations
- If something alarms or challenges you, it will; accelerate heart beat, raise blood pressure, slow digestion, raise blood sugar, and cool the body with perspiration
- If something alarms or challenges you, it will; accelerate heart beat, raise blood pressure, slow digestion, raise blood sugar, and cool the body with perspiration
47
New cards
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving it's energy.
It does the opposite of symp. because it lowers heart rate and blood pressure
It does the opposite of symp. because it lowers heart rate and blood pressure
48
New cards
Nervous system flow chart
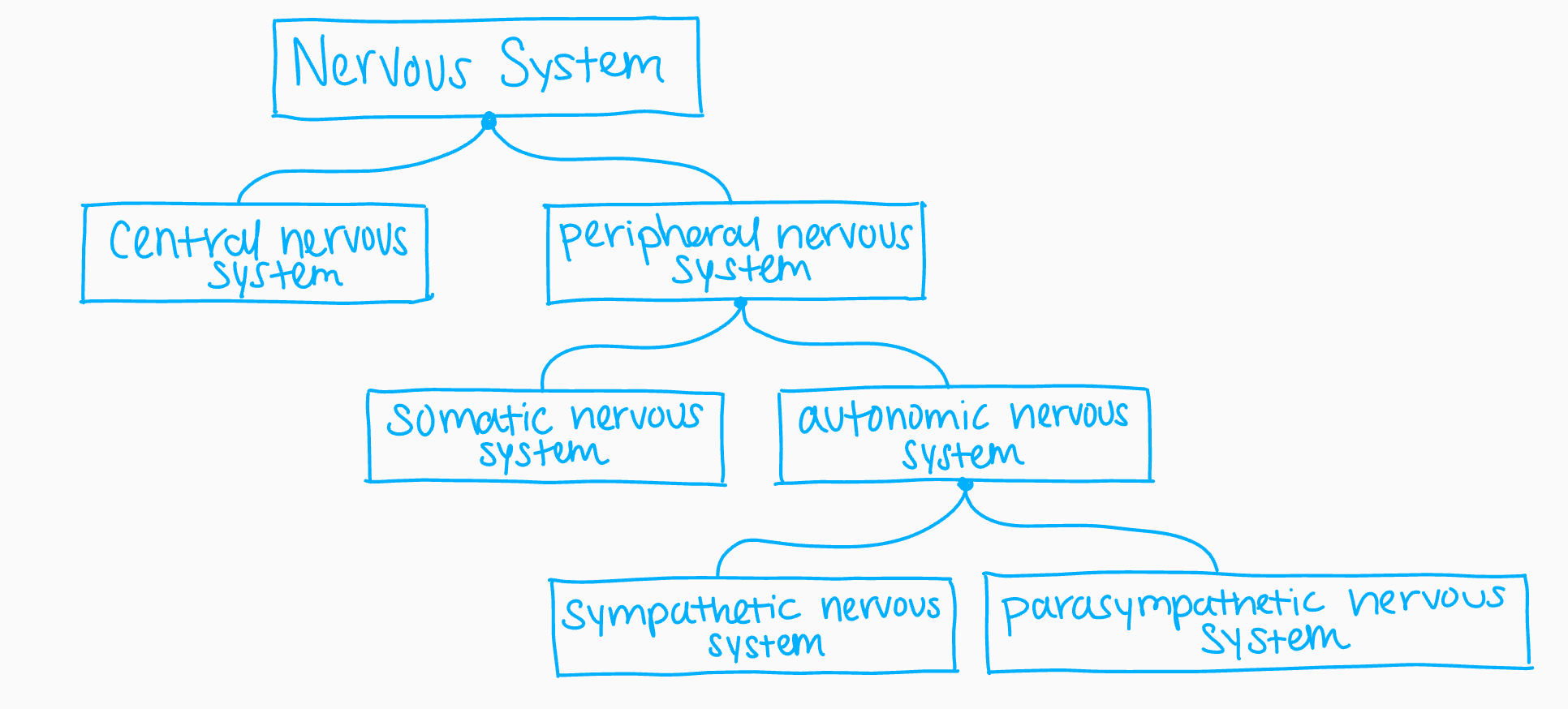
49
New cards
Reflexes
A simple autonomic response to a sensory stimulate (aka a knee-jerk response)
50
New cards
Endocrine system
A set of glands that secrete a form of chemical messengers called hormones
- These messengers travel through the blood stream to affect other tissues (including the brain)
- The slow communication system
- Influences interest in food and sex, and aggression
*Endocrine system messages tend to outlast neural messages
ex.) puberty, lasting anger
- These messengers travel through the blood stream to affect other tissues (including the brain)
- The slow communication system
- Influences interest in food and sex, and aggression
*Endocrine system messages tend to outlast neural messages
ex.) puberty, lasting anger
51
New cards
Hormones
Chemical messengers manufactured in the endocrine system
- Created in glands
- Through blood stream (like estrogen shots)
- To tissues
* Some hormones are identical to neurotransmitters
- Created in glands
- Through blood stream (like estrogen shots)
- To tissues
* Some hormones are identical to neurotransmitters
52
New cards
Endocrine System vs. Nervous System; Speed of action
Nervous system: Very fast
Endocrine system: Can be slow
Endocrine system: Can be slow
53
New cards
Endocrine System vs. Nervous System; Nature of response
Nervous system: Electrical impulses traveling on nerves
Endocrine system: Chemical messengers traveling through bloodstream
Endocrine system: Chemical messengers traveling through bloodstream
54
New cards
Endocrine System vs. Nervous System; Duration of response
Nervous system: Usually completed in seconds
Endocrine system: Can occur over years
Endocrine system: Can occur over years
55
New cards
Endocrine System vs. Nervous System; Area of response
Nervous system: Often confined to one area of the body
Endocrine system: Response is widespread and affects many different areas
Endocrine system: Response is widespread and affects many different areas
56
New cards
Endocrine System vs. Nervous System; Ex of controlled processes
Nervous system: Sensations, reflexes, movements
Endocrine system: Growth, development, reproduction
Endocrine system: Growth, development, reproduction
57
New cards
GLANDS IN THE BODY
58
New cards
Pituitary gland
- Located in the core of the brain
- The MOST influential component of the endocrine system, controls other glands in the body
Ex. of pituitary gland hormones
- growth hormone: used in physicals development
- oxytocin
- The MOST influential component of the endocrine system, controls other glands in the body
Ex. of pituitary gland hormones
- growth hormone: used in physicals development
- oxytocin
59
New cards
Oxytocin
- Enables contractions during childbirth
- Enables milk flow during nursing
- Orgasm
- Promotes group cohesion and trust
- Enables milk flow during nursing
- Orgasm
- Promotes group cohesion and trust
60
New cards
Pituitary gland feedback loop
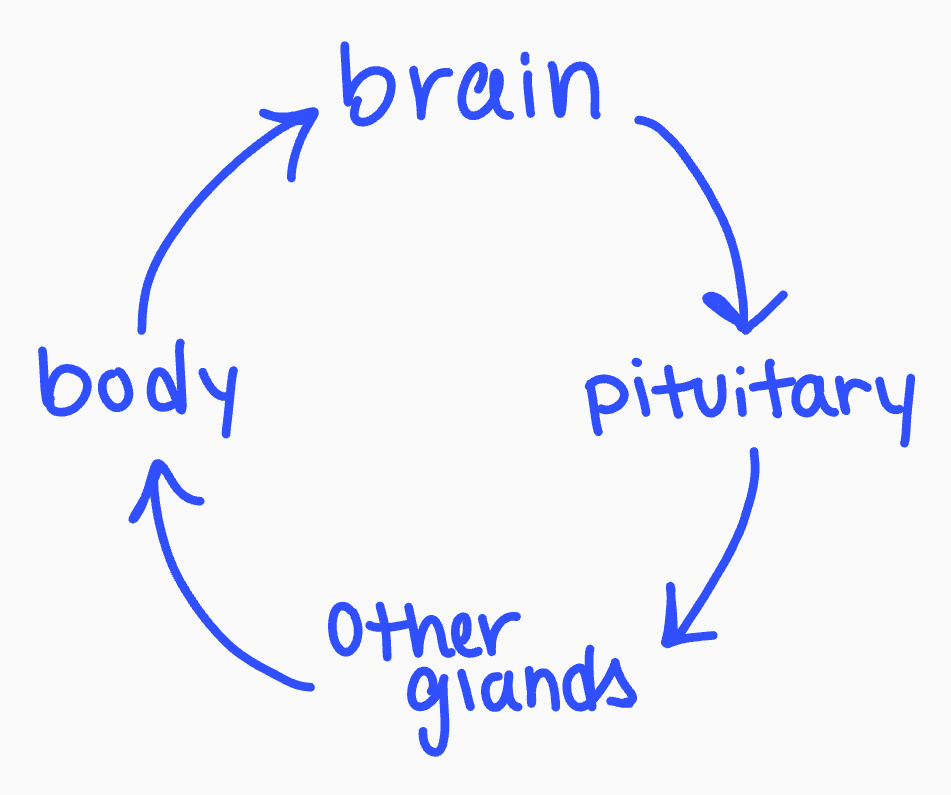
61
New cards
Hypothalamus
Brain region controlled by the pituitary gland
*Not a gland*
*Not a gland*
62
New cards
Thyroid gland
Metabolism (weight gain or loss)
- Energy
- Energy
63
New cards
Parathyroid gland
Regulates the level of calcium in the blood
64
New cards
Adrenal gland
Sit directly above each kidney
*Release 2 different hormones; epinephrine (Adrenaline) and norepinephrine (Non-adrenaline)
- These hormones aid in fight or flight
- Raise blood pressure
- Raising blood sugar
- Giving surge of energy
*Release 2 different hormones; epinephrine (Adrenaline) and norepinephrine (Non-adrenaline)
- These hormones aid in fight or flight
- Raise blood pressure
- Raising blood sugar
- Giving surge of energy
65
New cards
Pancreas
Regulates blood sugar
66
New cards
Ovaries
Secret female sex hormones
67
New cards
Testes
Secret male sex hormones
68
New cards
Lesion
Tissue destruction (cuts)
*Can be done accidentally or as part of experimentation
- Scientists selectively lesion the brain and leave all surrounding tissue unharmed
*Can be done accidentally or as part of experimentation
- Scientists selectively lesion the brain and leave all surrounding tissue unharmed
69
New cards
EEG - Electro encephalogram
Measures the surface electricity in the brain
70
New cards
CT or CAT Scan (computed tomography)
A series of x-rays taken at different angles and positions, then copositied together to form a single "slice" of tissue
- Photograph = doesn't show movement or changes
- Photograph = doesn't show movement or changes
71
New cards
PET Scan (position emission tomography)
Will inject a colored or radioactive amount of glucose into the brain and then follow it as a brain performs a given task
- Only lets us see one part of the brain at a time
- Only lets us see one part of the brain at a time
72
New cards
MRI - Magnetic resonance imaging
A technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer generated images of soft tissue
- Can show brain anatomy
- Can show brain anatomy
73
New cards
FMRI
Functioning, shows functions as well as structures
74
New cards
Older Brain Structures
- In primitive animals, only regulate basic survival
- In lower mammals, more complex brains; allow for simple thinking, emotion and memory
- In most advanced mammals (humans); process info, and use foresight + hindsight
- In lower mammals, more complex brains; allow for simple thinking, emotion and memory
- In most advanced mammals (humans); process info, and use foresight + hindsight
75
New cards
The brain stem
The brain's oldest and innermost system where the spinal cord swells after entering the skull
- Responsible for automatic survival functions
- Made up of the medulla and pons
- Responsible for automatic survival functions
- Made up of the medulla and pons
76
New cards
Medulla
- Located at the base of the brain stem
- Responsible for most basic functions; heart beat, breathing
*Most essential tasks
- Responsible for most basic functions; heart beat, breathing
*Most essential tasks
77
New cards
The Pons
- Located just above the Medulla
- It helps with coordinating movements
- It helps with coordinating movements
78
New cards
Thalamus
- A pair of "egg" shaped structures above the pons
*The brains sensory control center*
- Receives info from brain and spinal cord
Re: Sight, hearing, touch, taste (no smell) and sends it to higher parts of the brain
*Directs responses from higher regions of brain to the body
*The brains sensory control center*
- Receives info from brain and spinal cord
Re: Sight, hearing, touch, taste (no smell) and sends it to higher parts of the brain
*Directs responses from higher regions of brain to the body
79
New cards
The Reticular Formation
- A net like set of neural fibers that extends from spinal cord through the thalamus
--> Info to thalamus
--> Info from thalamus
together work like a filter
--> Info to thalamus
--> Info from thalamus
together work like a filter
80
New cards
Cerebellum "little brain"
- Extends from the rear of the spinal cord
- Processes sensory input, manages balance, coordinates movements, and helps with non verbal learning
- Alcohol disrupts the cerebellum
- Processes sensory input, manages balance, coordinates movements, and helps with non verbal learning
- Alcohol disrupts the cerebellum
81
New cards
The Limbic System
Composed of the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus
- Controls emotions like fear + anger and basic motives; ie. food, sex, etc.
- Lies between old Brain structures and our highest brain systems
- Controls emotions like fear + anger and basic motives; ie. food, sex, etc.
- Lies between old Brain structures and our highest brain systems
82
New cards
Amygdala
2 lima bean sized clusters linked to the emotions aggression and fear
In the temporal lobe in front of the hippocampus
In the temporal lobe in front of the hippocampus
83
New cards
Hypothalamus
BELOW the thalamus
- Is important link in the command chain governing body maintenance (endocrine system)
- Maintaining a steady internal state (homeostasis)
- Responding to hunger, thirst, body temp. and sexual behavior
- Is important link in the command chain governing body maintenance (endocrine system)
- Maintaining a steady internal state (homeostasis)
- Responding to hunger, thirst, body temp. and sexual behavior
84
New cards
Hypothalamus Feedback loop
Cerebral cortex is thinking about sex
Hypothalamus recognizes that C.C is thinking
Sends messages to pituitary gland
Pituitary gland sends hormones to ovaries/testes
Testes/Ovaries release sex hormones
Cerebral cortex is stimulated by sex hormones
Hypothalamus recognizes that C.C is thinking
Sends messages to pituitary gland
Pituitary gland sends hormones to ovaries/testes
Testes/Ovaries release sex hormones
Cerebral cortex is stimulated by sex hormones
85
New cards
Hippocampus
A neural center in the limbic system that helps process + store EXPLICIT MEMORIES
ex. names, places, events, numbers, etc
- In the middle of the temporal lobe
ex. names, places, events, numbers, etc
- In the middle of the temporal lobe
86
New cards
Cortex
a subsection
87
New cards
Pleasure cortex (PC)
Somewhere in the limbic system
- When triggered in humans, it produced mild calming effects
- Triggered through electrical stimulation
- When triggered in humans, it produced mild calming effects
- Triggered through electrical stimulation
88
New cards
The Cerebral Cortex
Cerebrum: "Newer" neural networks
--> Made up of specialized areas that aid in our perceiving, thinking, speaking, and learning
--> Makes up most of the brian, 85% brain mass
--> THE WRINKLY PART (more surface area
Cerebral Cortex: like the bark on a tree - the thin surface layer of interconnected neural cells surrounding the cerebrum
--> The brain's ultimate info processing center
--> Cerebral cortex increases with evolutionary complexity
--> 20-23 billion nerve cells + 300 trillion synapses
--> Made up of specialized areas that aid in our perceiving, thinking, speaking, and learning
--> Makes up most of the brian, 85% brain mass
--> THE WRINKLY PART (more surface area
Cerebral Cortex: like the bark on a tree - the thin surface layer of interconnected neural cells surrounding the cerebrum
--> The brain's ultimate info processing center
--> Cerebral cortex increases with evolutionary complexity
--> 20-23 billion nerve cells + 300 trillion synapses
89
New cards
Glial Cells (G.C)
METAPHOR
*Neurons are like queen bees; they cannot feed or protect themselves
G.C: Cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
- They provide nutrients to make neurotransmitters
- Provide myelin (lipids and fatty tissue) for the myelin sheath
- May also play a role in learning + thinking (einstein)
*Neurons are like queen bees; they cannot feed or protect themselves
G.C: Cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
- They provide nutrients to make neurotransmitters
- Provide myelin (lipids and fatty tissue) for the myelin sheath
- May also play a role in learning + thinking (einstein)
90
New cards
Cerebral Cortex
2 hemispheres; Right and left from brain holders view (think of the paper behind you, so as opposites on paper)
91
New cards
Cerebral Cortex Lobes
(in no particular order)
1. Frontal lobe
2. Parietal lobe
3. Occipital lobe
4. Temporal lobe
1. Frontal lobe
2. Parietal lobe
3. Occipital lobe
4. Temporal lobe
92
New cards
Frontal lobe
A portion of the cerebral cortex right behind the forehead
- Involved in speaking, muscle movements, making plans, and evaluating consequences
- Involved in speaking, muscle movements, making plans, and evaluating consequences
93
New cards
Motor Cortex
An area near the rear of the frontal lobe that controls voluntary movement
- Have mapped the entire thing
- Ear to ear section
- Have mapped the entire thing
- Ear to ear section
94
New cards
Parietal Lobe
The portion of the cerebral cortex lying near the top of the head (sensory, from thalamus)
- Receives info for touch and body position
- Receives info for touch and body position
95
New cards
Somatosensory Cortex
Part of the parietal lobe, furthermost front
- Registers body sensations for all body parts
- Well mapped
- The more sensitive the body part, the bigger the portion of the somatic sensory cortex devoted to it.
- Registers body sensations for all body parts
- Well mapped
- The more sensitive the body part, the bigger the portion of the somatic sensory cortex devoted to it.
96
New cards
Occipital Lobe
Portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head
- Receives information from the visual cortexes (EYES)
- Receives information from the visual cortexes (EYES)
97
New cards
Blindness and the Occipital Lobe
Someone can be blind because of damage to the occipital lobe and their eyes work fine, or vise versa - someone can be blind because of eye problems like degenerative disease and their occipital lobe works fine
- This applies to the temporal lobe and deafness too
- This applies to the temporal lobe and deafness too
98
New cards
Temporal Lobe
Portions of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears
- Receives auditory information from the ears
- Receives auditory information from the ears
99
New cards
Visual Cortex
Portion of the occipital lobe that processes visual sensations
- If you are blind because your eyes don't work, the visual cortex can be stimulated by electricity to "see"/process light and color
(you're seeing things IN YOUR BRAIN that the scientists are deciding to show you, lowkey gaslighting to be honest)
- Right vision is processed in the left visual cortex and vice versa
- If you are blind because your eyes don't work, the visual cortex can be stimulated by electricity to "see"/process light and color
(you're seeing things IN YOUR BRAIN that the scientists are deciding to show you, lowkey gaslighting to be honest)
- Right vision is processed in the left visual cortex and vice versa
100
New cards
Auditory cortex
Portion of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information received from the opposite ears (because the left brain controls the right side of the body and vise versa)