EXSS 155. Lesson 8A, Part 2. Neurons and Synapses
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
neurons
functional unit of nervous system
form complex processing network in the brain
connect all regions of the body to the CNS
electrically excitable
responsible for
sensing
thinking
remembering
muscle control
gland regulation
neuroglia (glial cells)
smaller in size, greater in number
provide support to the neuron
-maintain homeostasis
-form myelin
motor neuron
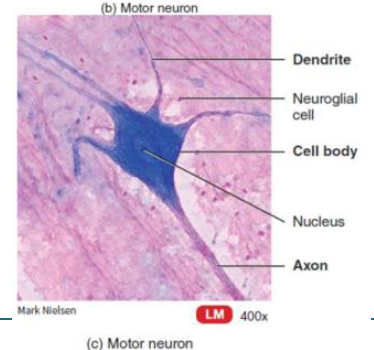
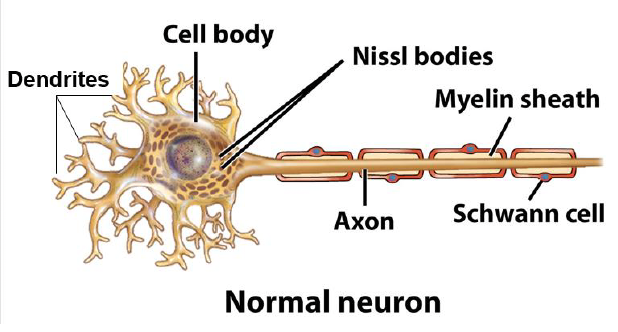
main components of neurons
dendrites
cell body (soma)
axon (many axons make up a nerve
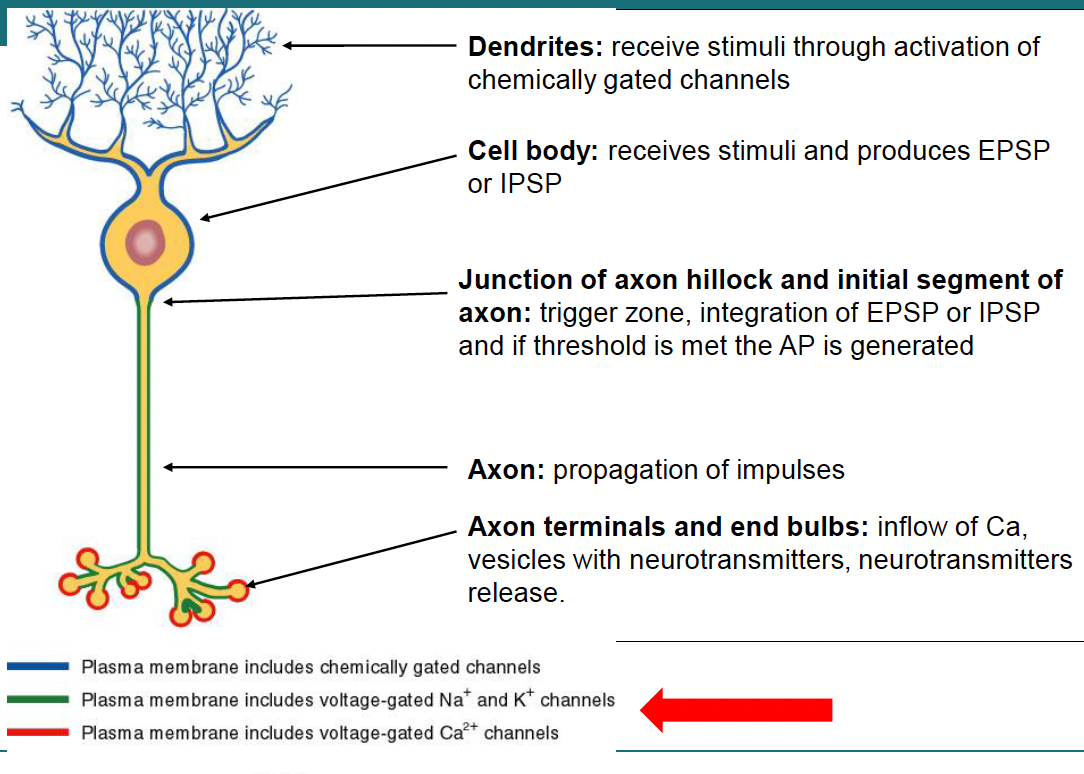
Neuron
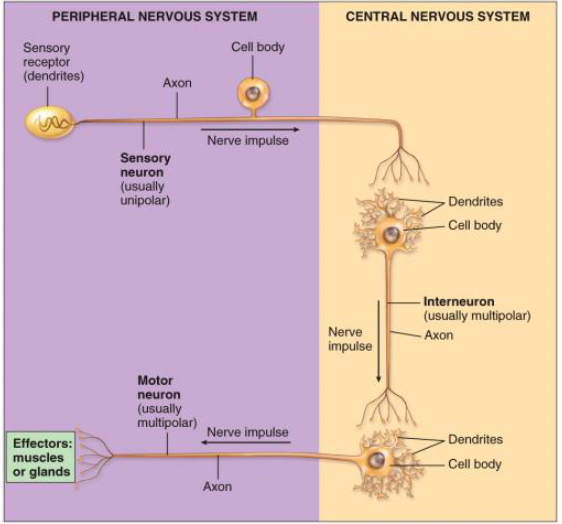
functional classification of neurons
neurons can be classified based on the direction of nerve impulse propagation:
sensory/afferent neurons (PNS)
motor/efferent neurons (PNS)
inter/association neurons (CNS)
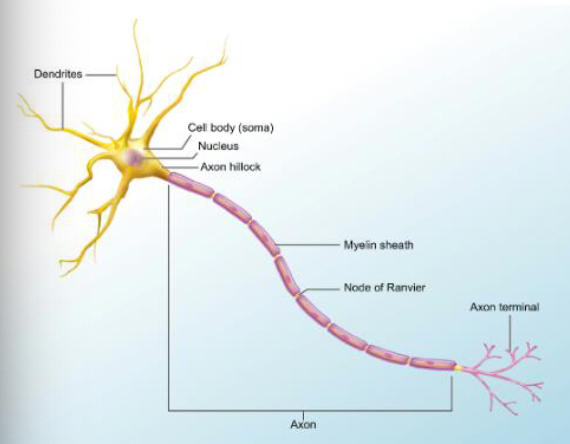
myelination
myelin sheath: multilayered lipid, insulates axon, increases nerve conduction velocity; nucleus = Schwann cells
Node of Ranvier
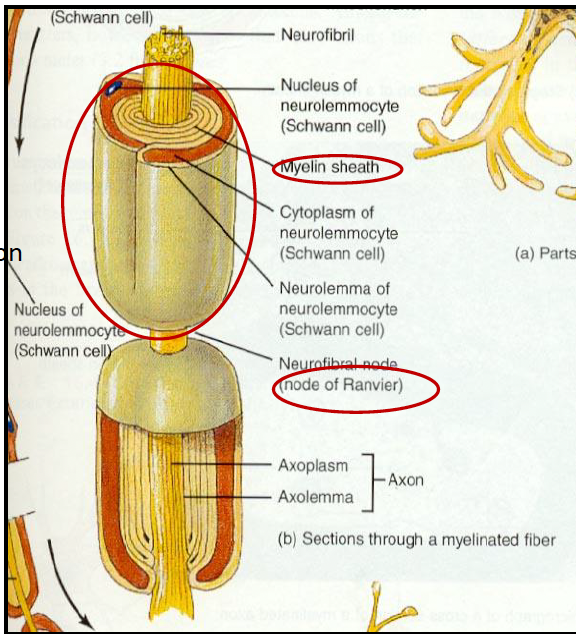
Myelin
lipid and protein covering
increases speed and efficiency of AP propagation
Schwann cells = act as insulator and prevent ion leakage
Nodes of Ranvier = gaps in myelin sheath
(Myelination of motor neurons to muscles controlling bladder not complete until age 3)
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
deterioration of myelin sheath
-sensory or motor neurons
-neurons become ineffective
-muscle atrophy
-decreased coordination
currently no cure
synapses
junctions between 2 neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell
presynaptic terminal (send the impulse)
postsynaptic terminal (receives the impulse)
gap junctions
electrical synapses
ionic current spreads to next cell
faster, 2-way transmission and capable of synchronizing neurons
synaptic clefts
chemical synapses
1-way information transfer from presynaptic to postsynaptic neuron
neurons/cells involved do not touch but are separated by a synaptic cleft
Botulinum toxin
blocks release of neurotransmitter at NMJ so muscle contraction cannot occur
bacteria found in improperly canned food
death occurs from paralysis of diaphragm
Curare
plant poison from poison arrows
causes muscle paralysis by blocking the ACh receptors
used to relax muscle during surgery
neurotransmitters
released from axon terminal into synaptic cleft in response to a nerve impulse
effects can be modified via:
-synthesis
-release
-removal
-receptor site (blocked or activated)
agonist
enhances effect of transmitter
antagonist
blocks action of neurotransmitter
common small-molecule neurotransmitters
ACh
Amino Acids: glutamate, aspartate, GABA
Amines: norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, serotonin
ATP
common neuropeptides
substance P
endorphins
hypothalamic hormones
CCK
Application of Neurotransmitters in Depression
anxiety disorders and depression often due to a GABA deficiency
drugs like diazepam (Valium) enhance the action of GABA
-can help slow down obsessive thinking
-can relieve muscle spasms
Application of Neurotransmitters in Parkinson’s Disease
degeneration of neurons that release dopamine
-plays a role in executive function, motor control, etc.
symptoms worsen as disease progresses
-shaking, stiffness, difficulty with balance and coordination