CHAPTER 3 PART 3
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
what are the clinical manifestations of STIs (Skin Lesions)
Chancre
Chancroid
Genital Herpes
Granulomatous Reactions
Rashes
Warty Lesions
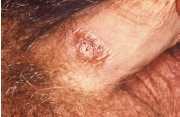
primary lesion of syphilis
painless
well-delineated
CHANCRE
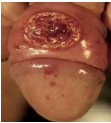
ulcer with ragged edges
painful
CHANCROID
start as a vehicle that becomes an ulcer after rapture
GENITAL HERPES
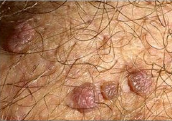
granuloma inguinale
GRANULOMATOUS REACTIONS
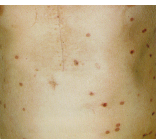
secondary syphilis
Gonorrhea
Candidiasis
RASHES
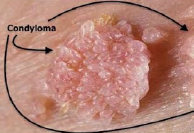
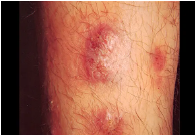
Condyloma acuminatum
Molluscum contagiosum
WARTY LESIONS
Clinical Manifestations of STIs (DISCHARGE)
Vaginal Discharge
Dysuria
Dyspareunia
Vulvar Irritation
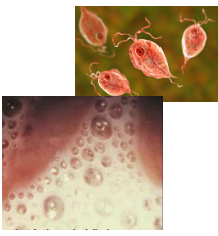
it is thin, foamy, and foul-smelling vaginal discharge
Trichomonas vaginalis
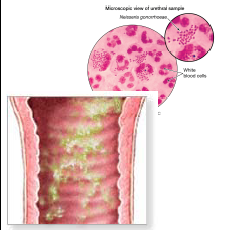
a greenish and purulent vaginal discharge
Neisseria gonorrhea
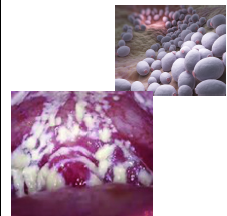
a thick, cheesy exudates (milk curd-like appearance) vaginal discharge
Candida albicans
Spirochete with fine regular coils with tapered ends
Strictly a human pathogen
Sensitive to oxygen
Cannot grow in cell-free culture medium
Treponema pallidum
clinical findings for Treponema pallidum
Adult Syphilis
Congenital Syphilis
Early Congenital Syphilis (right after birth)
Late Congenital Syphilis
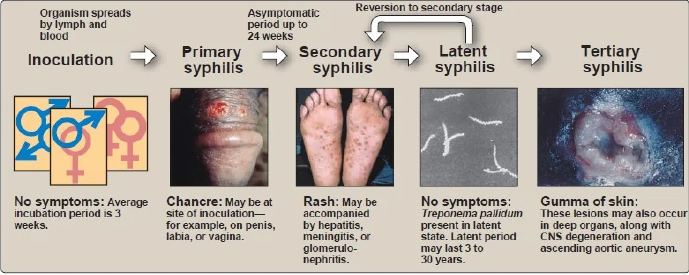
Adult Syphilis
right after birth
May be asymptomatic
Runny nose (snuffles), rash, condylomata, and hepatosplenomegaly
Early Congenital Syphilis
Manifested at 8th nerve deafness with bone and teeth deformities
saddle nose
saber shins
Hutchinson’s teeth, and
Mulberry or Moon’s molars
Late Congenital Syphilis
laboratory diagnosis for Treponema pallidum
Darkfield microscopy
Serology
Non-specific treponemal test – VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory) and RPR (Rapid Plasma Reagin)
Specific treponemal test – Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption (FTA-ABS)
treatment and prevention for Treponema pallidum
DOC: Penicillin
Alt.: Tetracycline and Doxycycline
“Gonococci”
Gram (-) diplococcus;
kidney bean-shaped (single) and coffee bean-shaped (pairs)
Virulence Factor: Pili
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
mode of transmission for Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Sexual contact
Gonorrhea in males
painful urination
a discharge of pus-containing material
80% —> after incubation period
most patients —> < a week
Gonorrhea in females
cervix (columnar epithelial cells)
most are asymptomatic
Complication —> Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (IPD)
Disseminated Gonorrhea
(1% - 3%) fever, migratory arthralgia, suppurative arthritis of the wrists, knees, and ankles, and pustules with erythematous base over the extremities
Other diseases associated:
Perhepatitis (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome)
Purulent conjunctivitis (adults)
Infected mother —> infant (Ophthalmia Neonaturum) —> Blindness
laboratory diagnosis for Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Culture (Thayer-Martin Medium)
treatment and prevention for Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Uncomplicated – Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Cefixime, or Ofloxacin
Mixed Infection with Chlamydia – uncomplicated med + Doxycycline or Azithromycin
Ophthalmia neonatorum – Prevention: 1% AgNO3 or 5% Erythromycin or Tetracycline ointment
Obligate intracellular bacteria
Process of development (2 forms)
Elementary bodies – metabolically inactive infectious
Reticulate bodies – metabolically-active noninfectious
Serotypes D-K: non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU), cervicitis, and PID
Serotypes L1, L2, and L3: lymphogranuloma venereum
Chlamydia trachomatis
clinical findings for Chlamydia trachomatis
Urogenital Tract Infections
Lymphogranuloma Venereum (LGV)
Most are asymptomatic
Symptomatic:
cervicitis
endometritis
urethritis
salpingitis
bartholinitis
perihepatitis, and
mucopurulent discharge
Urogenital Tract Infections
Primary stage: a lesion appears at the site of infection, either a papule or ulcer, which is small, painless, and heals rapidly
Secondary stage: enlarged lymph nodes that are painful (buboes) and ruptures to form draining fistulas
Lymphogranuloma Venereum (LGV)
Laboratory Diagnosis for Chlamydia trachomatis
Giemsa staining (using scrapings from the lesion —> inclusion bodies)
treatment and prevention for Chlamydia trachomatis
Azithromycin
Doxycycline or
Erythromycin
Gram (-) coccobacillus
Only requires hemin (X factor) for growth (from blood)
Virulence Factor: Pili
Haemophilus ducreyi
clinical findings for Haemophilus ducreyi
Chancroid
A soft, painful papule with an erythematous base that develops into an ulcer with ragged edges associated with inguinal lymphadenopathy
Chancroid
Laboratory Diagnosis for Haemophilus ducreyi
Culture (in at least kinds of enriched media with VANCOMYCIN)
treatment and prevention for Haemophilus ducreyi
Cephalosporins
Azithromycin
Erythromycin or
Ciprofloxacin
what are the symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Community-acquired UTI
Nosocomial UTI
symptoms of UTI where:
More common in women —>(shorter urethra and proximity of anal opening to the urethral orifice)
Mostly uncomplicated
Community-acquired UTI
symptoms of UTI where:
Complications of prolonged urethral catheterization (most are resistant to various antibiotics)
Nosocomial UTI
What are the predisposing factors of UTI?
Gender - UTI is more common in females especially school-aged girls and those above 60 years of age.
Mechanical factors - catheterization, sexual intercourse, kidney stones, and improper use of tampons and douches.
Metabolic disorders - increased sugar content of urine, due to diabetes, for instance, is conducive to bacterial growth.
Anatomic abnormalities of the urinary tract - can lead to obstruction or incomplete voiding of urine or reflux of urine.
causative agents of UTI
Escherichia coli
Proteus mirabilis
Serratia spp.
Enterococcus faecalis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
it is the causative agent of UTI where:
G (-) bacillus
Part of the normal flora (colon)
The most common cause of community-acquired UTIs
Improper washing after defecation
Escherichia coli
causative agent of UTI where:
G (-) bacillus
Urease (+) –> alkalinization of the urine
Major cause of nosocomial UTIs
2nd most common cause of community-acquired UTIs
Proteus mirabilis
causative agent of UTI where:
Serratia marcescens
Prodigosin (imparts red color)
G (-) bacillus
Infections are associated with underlying disease, changing physiological patterns, immunosuppressive therapy, mechanical manipulation of patients
Serratia spp.
the causative agent of UTI where:
G (+) coccus
Part of the enteric flora
Grows in 6.5% NaCl
Causes nosocomial UTIs
Enterococcus faecalis
causative agent of UTI where:
G (+) coccus
Common cause of UTI in sexually active young women
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
clinical findings for UTI
Cystitis
Urethritis
Pyelonephritis
Urethrocystitis
inflammation of the urinary bladder
suprapubic pain and tenderness, frequency of urination, and occasional hematuria
Cystitis
inflammation of the urethra
dysuria, frequency, and urgency of urination
Urethritis
inflammation of the kidneys
flank pain, fever, chills, hematuria, kidney punch
Pyelonephritis
malodorous urine, especially in women, incontinence
Urethrocystitis
laboratory diagnosis for UTI
Urinalysis
Urine Culture
treatment and prevention for UTI
Uncomplicated Infection (E. coli) – Co-trimoxazole
Proteus and Pseudomonas – DOC: Fluoroquinolones
Acute Pyelonephritis – Fluoroquinolones or 3rd Generation cephalosporins
Susceptibility testing
All transmitted by the bite of arthropods except Q fever (inhalation)
All are zoonotic except Endemic Typhus (which occurs only in humans)
Groups:
Typhus Group – Epidemic, Murine (Endemic), Scrub
Spotted Fever Group – Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Traditional Group – Rickettsialpox
Q Fever
Trench Fever
Ehrlichiosis
Rickettsial Infections
Gram (-) pleomorphic
Obligate intracellular parasite
Stain well using Giemsa or Gimenez Stain
Growth enhanced by sulfonamides
Rickettsial Infections
Diseases under Rickettsial Infections
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Rickettsialpox
Epidemic Typhus
Murine Typhus
Scrub Typhus
Q (Query) Fever
Ehrlichiosis
Human monocyte ehrlichiosis
Human granulocyte ehrlichiosis
Erwingii ehrlichiosis
Sennetsu Fever
Etiology: Rickettsia rickettsii
Vector: Tick
Reservoir: Ticks, Wild rodents
Manifestations: Maculopapular rashes appear on the hands and feet —> later in the trunk (2-6 days)
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Etiology: Rickettsia akari
Vector: Mite
Reservoir: Mites, Wild rodents
Manifestations:
A mild disease resembling varicella
Fever, headache, chills, myalgia, the appearance of a firm red macule at the bite site —> deep-seated vesicle that ruptures —> ESCHAR
Rickettsialpox
Etiology: Rickettsia prowazekii
Vector: Louse
Reservoir: Humans (primary reservoir), squirrel fleas, flying squirrels
Manifestations:
Maculopapular rashes (sparing palms and soles)
More severe systemic infection; more fatal
Associated with Brill-Zinsser Disease
Epidemic Typhus
Etiology: Rickettsia typhi
Vector: Flea
Reservoir: Wild rodents
Manifestations: Similar to Epidemic typhus but milder and rarely fatal except in the elderly
Murine Typhus
Etiology: Orientia/Rickettsia tsutsugamushi
Vector: Mite
Reservoir: Mites, Wild rodents
Manifestations:
Resembles Epidemic Typhus except for the Eschar
Generalized lymphadenopathy and lymphocytosis
May also involve severe cardiac and cerebral complications
Scrub Typhus
Etiology: Coxiella burnetti
Vector: None ( via inhalation of spores)
Reservoir: Cattle, Sheep, Goats, Cats
Manifestations:
Resembles influenza and non-bacterial pneumonia, hepatitis or encephalopathy
Does not present any rash or local lesion
Q (Query) Fever
Etiology:
Vector: Tick
Reservoir: Ticks
Manifestations:
Parasitize lymphocytes, neutrophils, and monocytes
Manifest non-specific symptoms with thrombocytopenia
Ehrlichiosis
Etiology of Human monocyte ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichia chaffeensis
Etiology of Human granulocyte ehrlichiosis
Anaplasma phagocytophilum
Etiology of Erwingii ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichia ewingii
Etiology of Sennetsu Fever
Ehrlichia sennetsu
Spirochete
Reservoir Host: Rats
excreted in the urine and contaminated soil and water
Leptospira interrogans
mode of transmission for Leptospira interrogans
The organism enters through breaks in the skin or mucous membranes
Ingestion of contaminated food and water
clinical findings of Leptospira interrogans
Leptospirosis
1st Stage: flu-like symptoms —> fever, severe headache, myalgia, and chills
2nd Stage: (immune period) —→ s/sx of meningitis
Severe cases: impaired renal function and liver damage (Weil’s Disease/Infective Jaundice)
laboratory diagnosis for Leptospira interrogans
Darkfield Microscopy
Increase in agglutinating antibodies
treatment and prevention for Leptospira interrogans
Recommended drug – Penicillin
Prophylaxis – Doxycycline
Preventive Measures:
Avoid wading in contaminated water
Avoid contact with contaminated soil
Rodent control
Spirochete with coarse, irregular coils
Reservoir: Wood Rat
Host: Mammals (Deer – where the tick completes its life cycle)
Borrelia burgdorferi
mode of transmission for Borrelia burgdorferi
Bite of a tick (Ixodes)
clinical findings for Borrelia burgdorferi
Lyme Disease (Lyme Borreliosis)
1st Stage: painless, circular red rash (erythema chronicum migrans) with a clear center at the site of the bite, athralgia, fever, headache, chills, and fatigue (with or without)
2nd Stage(after a few weeks/months): myocarditis/pericarditis, aseptic meningitis, Bell’s palsy, and neuropathies
Latent Period (several weeks or months)
3rd Stage: arthritis (large joints) and progressive chronic involvement of the CNS
laboratory diagnosis for Borrelia burgdorferi
Giemsa or Silver stains
Darkfield Microscopy
Serological tests (ELISA or Indirect immunofluorescence)
Confirmatory Test – Western Blot Assay or PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Treatment and Prevention for Borrelia burgdorferi
Mild Infections – Amoxicillin or Doxycycline
Late Stage – Pen G or Ceftriaxone
Spirochete; highly flexible and highly motile (rotatory and twitching)
Can survive at low temperature (4 degrees C) in blood or culture
Reservoir: Rodents
Borrelia recurrentis
mode of transmission for Borrelia recurrentis
Bite of a human body louse (Pediculus humanus) – Louse-borne relapsing fever
Bite of ticks (Ornithodorus) – Tick-borne relapsing fever
clinical findings for Borrelia recurrentis
Relapsing Fever
Fever, headache, and chills
The fever lasts for a few days and resolves but recurs after a week with associated multi-organ dysfunction.
3-10 recurrences (with each recurrence manifestations become less severe)
laboratory diagnosis for Borrelia recurrentis
Giemsa or Wright Stain (the best time for sample collection is during the height of the fever)
Infections of the eyes
Conjunctivitis
Keratitis
Keratoconjunctivitis
Pink eye conjunctivitis
Highly contagious
Manifestations: eye irritation, reddening of the conjunctiva, swelling of the eyelids, mucopurulent discharge, and photophobia
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Etiologic Agents of Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Haemophilus influenzae
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Staphylococcus aureus
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Chlamydia trachomatis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Koch-Weeks bacillus
G(-) coccobacillus
Virulence Factor: Pili
Epidemics of acute, purulent conjunctivitis (summer months)
Transmission: Gnat Fly (mechanical vector)
Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius
most common cause of NGU
“swimming pool conjunctivitis”
inclusion conjunctivitis – newborn babies
Trachoma - chronic keratoconjunctivitis caused by serotypes A, B, Ba, and C
Symptoms: Eye pain, Swelling eyelids, and Eye irritation
Transmission:
eye-to-eye by droplets, fomites, flies, feces, and respiratory droplets
Chlamydia trachomatis
Ophthalmia Neonatorum
Neisseria gonorrhoea
Infections of the Nervous System
Encephalitis (brain parenchyma)
Encephalomyelitis (brain and spinal cord)
Meningitis (pia and arachnoid matter)
Meningism - symptoms that signifies the occurrence of meningitis
Meningoencephalitis (brain and meninges)
Myelitis (spinal cord)
TRIADS - fever, headache, and nuchal rigidity (stiff neck)
ETIOLOGIC AGENTS:
Escherichia coli - the most common cause of this disease in newborn
Haemophilus influenzae Type B (Hib) - Hib-caused meningitis occurs mostly in children under age 4, especially at about 6 months when antibody protection provided by the mother weakens.
Neisseria meningitidis (Meningococcus)
Listeria monocytogenes
Acute Bacterial Meningitis
G(-)
coffee-bean/kidney-shaped diplococcus
Transient flora of the nasopharynx (carriers)
Virulent Factor: Endotoxin
Neisseria meningitidis
mode of transmission for Neisseria meningitidis
Respiratory droplets (main mode)
Carriers
clinical findings for Neisseria meningitidis
Meningococcal Meningitis (Meningococcemia)
Under 2 years of age (residual damage – deafness)
Throat infection → bacteremia → meningitis
Rash: petechiae or purpuric skin lesions over the trunk and in lower extremities (does not fade when pressed)
Complication: Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome (destruction of the adrenal gland)
laboratory diagnosis for Neisseria meningitidis
Culture of the organism (Blood and CSF)
Gram-staining
Detection of polysaccharide antigen
treatment and prevention for Neisseria meningitidis
Penicillin -DOC
Chloramphenicol and 3rd gen cephalosporins - alternative
Minocycline and rifampicin - treatment of carriers
Sulfonamides and rifampicin - prophylaxis
Cold-loving (capable of growth at 1 degree C) but are also capable of growth at 45 degrees C and in high salt concentration
Tumbling motility
Mainly infects immunocompromised patients
Listeria monocytogenes
mode of transmission for Listeria monocytogenes
Ingestion of contaminated food products (primary source)
Transplacental transmission (during pregnancy/birth)
clinical findings for Listeria monocytogenes
Newborns
Early-onset Listeriosis – acquired during pregnancy
Granulomatous infantiseptica – severe form
Late-onset Listeriosis – acquired during or right after delivery
Meningitis or meningitis + encephalitis with septicemia
laboratory diagnosis for Listeria monocytogenes
Culture (blood, spinal fluid, or the placenta)
Cold enrichment media
Observation of tumbling end-to-end motility
treatment and prevention for Listeria monocytogenes
TOC: Penicillin or ampicillin either singly or combined with gentamicin
clinical findings for Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Tuberculosis Meningitis
Affects children younger than 6 years old
Usually appears 3-6 months after the initial infection
Accompanies Military Tuberculosis (50% cases)