Psych 134K Midterm
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Psychosocial Deprivation
lack of adequate opportunity for social and intellectual stimulation aka nurture
ex: romanian orphanage, PIY, hospitalisim
Romanian Orphans
Previously Institutionalized Youth
Harry Harlow Monkey Experiment
Monkey prefers soft terry cloth mother without food over wire mesh mother with bottle. Monkey prefers to have close contact with "loving" caregiver over food
Tuberculosis Hospitalism effect
During tuberculosis outbreak, the children that were in the hospital were isolated and got worse due to lack of nurture
when the ones at home (although they don't have all the medical things) they got better
Stress: Portrait of a Killer
Research done on baboons which reflects the chronic stress within western human due to hierarchy
- subordinate baboons/people = more stress, less dopamine, shorter life span
- dominate baboons/people = less stress, happier
too much cortisol --> negative health outcomes, weight in abdomen, clogged arteries, shorter telomere length, shorter life span
Different types of stress
-Positive: job promotion, getting to class, a meeting
-Tolerable: a car accident, natural disaster, a death (species expectant: we expect it)
-Toxic: chronic illness, trauma, poverty
parasympathetic nervous system stops working and the habitual negative feedback loop starts
Bucharest Early Intervention Project
children were randomly assigned to foster care our to stay in institution
- the younger the child the better the outcome
- gains in cognitive functioning but not social emotional
- sensitive period for socio-emotional closed
Psychosocial Dwarfism
stunted growth due to lack of nurture, so body reallocates resources to survival functions. physical growth is not necessary for survival
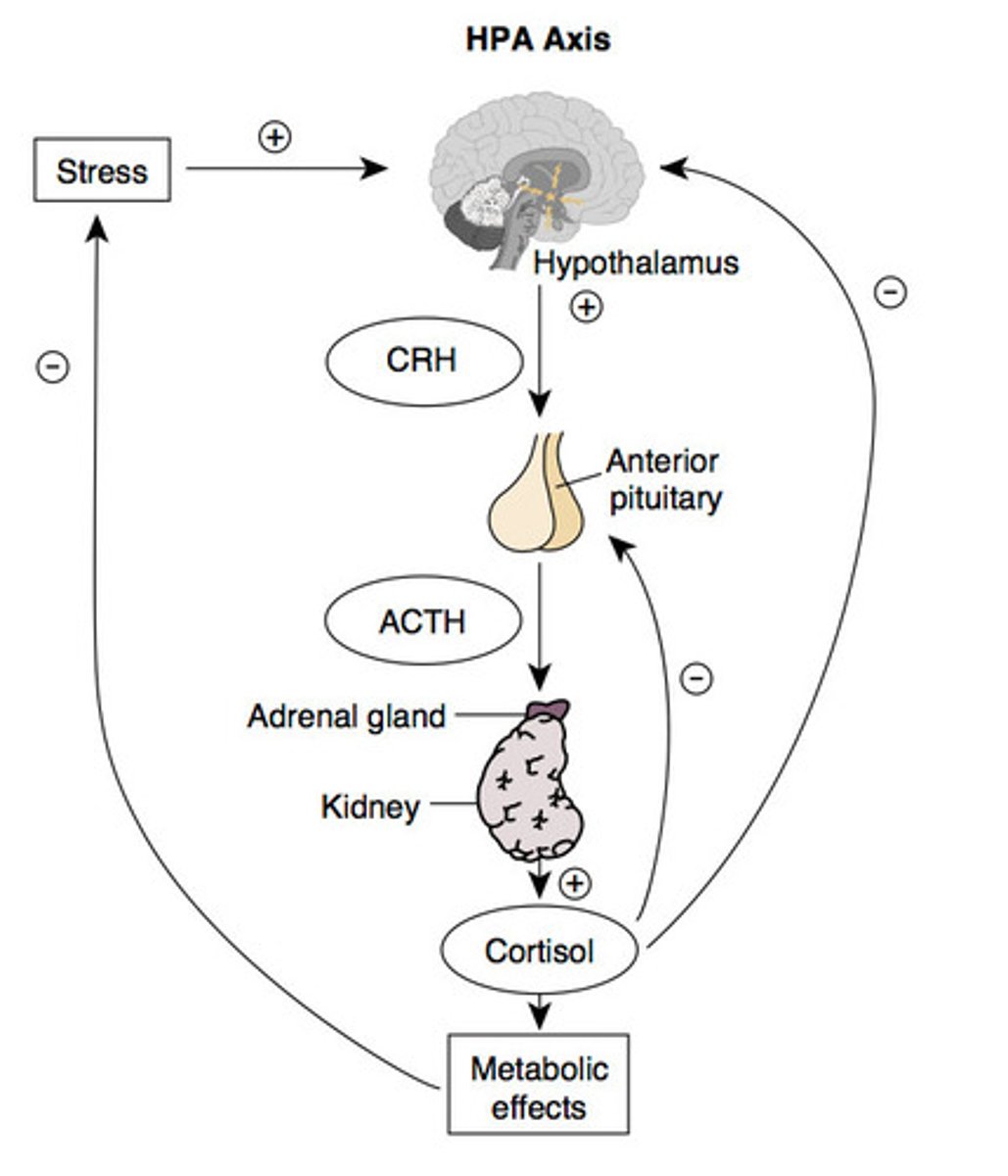
Function of HPA axis
The method for sustaining alert during threat:
- The amygdala activates the hypothalamus in response to stress
- the hypothalamus releases CRH into the anterior pituitary gland
- the anterior pituitary gland releases ACTH to the adrenal gland
- adrenal gland and kidney releases cortisol into the blood stream
- cortisol causes metabolic effects (suppresses sex drive, immunity, digestion, and growth)
Human response to threat (snake example)
- visual input of snake goes through optic nerve
- image goes to thalamus where its detected as threat or not
- sends it to the amygdala if it is a threat (skips visual cortex)
- amygdala triggers sympathetic nervous system
- stress response activates
Habituated negative feedback loop
release of too much cortisol due to chronic stress
unregulated HPA axis response
sympathetic vs parasympathetic nervous system
-sympathetic: fight or flight, stress response
-parasympathetic: rest and digest, quiets the stress response, brings you back to resting state
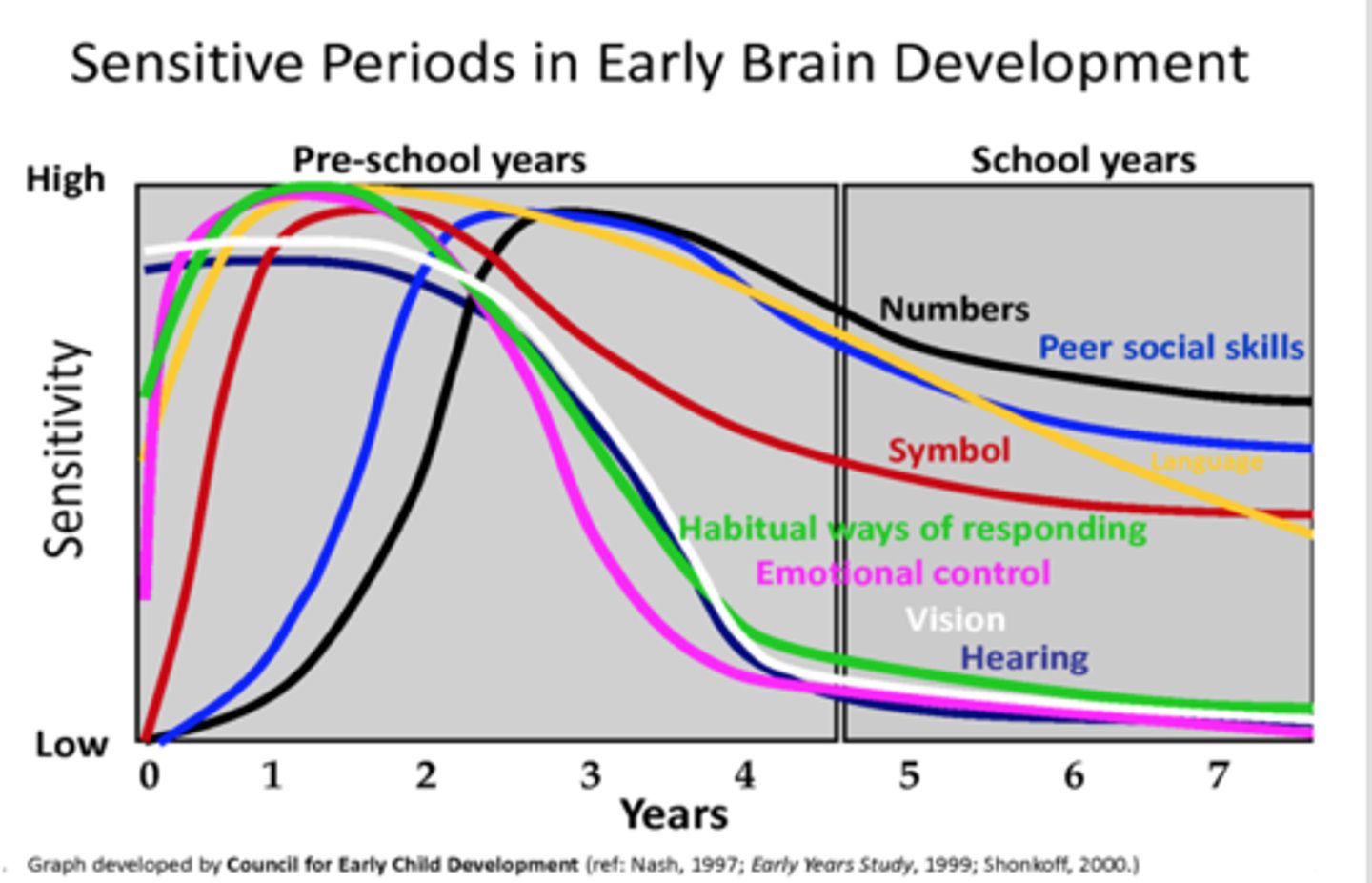
Sensitive vs. Critical Periods
What is negelct?
most common form of maltreatment
Different forms of abuse?
physical - most common
psychological (emotional)
sexual
The majority of perpetrators are parent
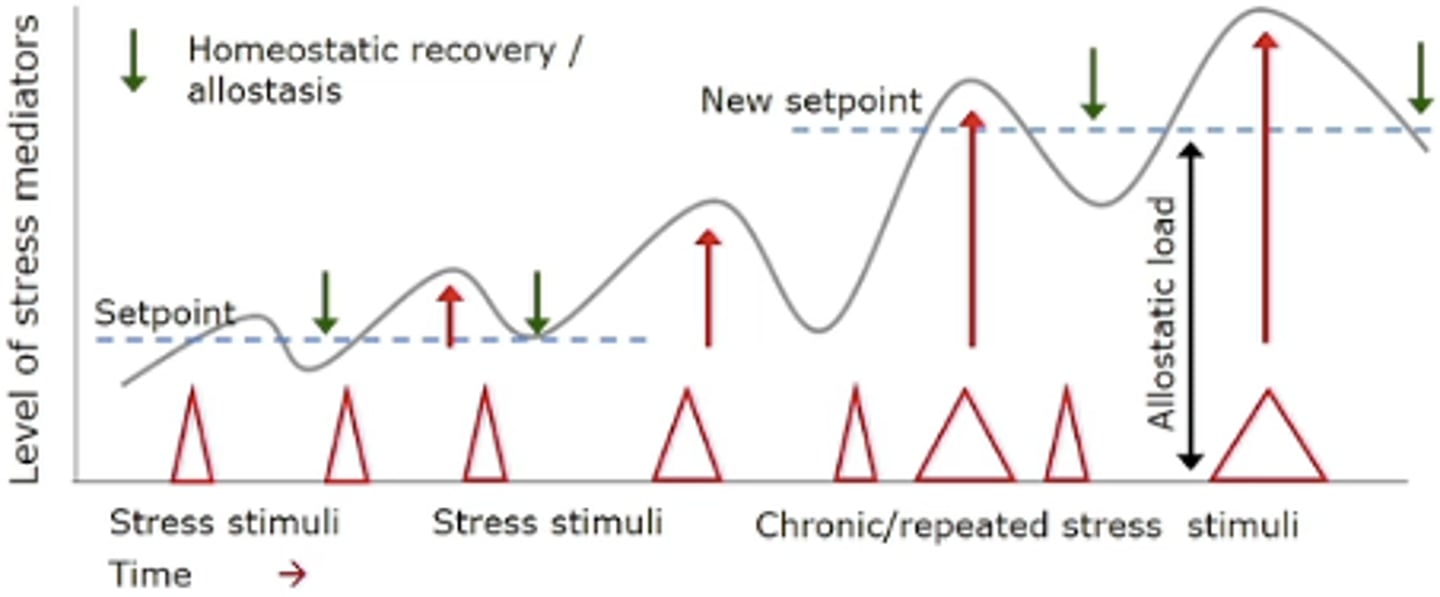
Allostatic load
Alters homeostasis so there is a new set point in response to constant or cumulative chronic stress
- change in set point in response to allostasis
*not tolerance, just more sensitized --> higher baseline*
What is adversity?
A negative violation of the expectable environment
includes malnutrition, chronic illness, maltreatment
What is stress?
the physiological results of a perceived as threatening or harmful
- all adversity is a form of stress
Gene driven brain development
-genes provide the blueprint for basic brain architecture
-prenatal environment is important
ex: cortisol passing to baby bloodstream and can activate amygdala
Synapse formation vs Synaptic pruning
formation: cells begin to connect to each other creating synapses (connections) overproduction
pruning: brain becomes specializes and prunes unnecessary synapse and strengthens necessary ones
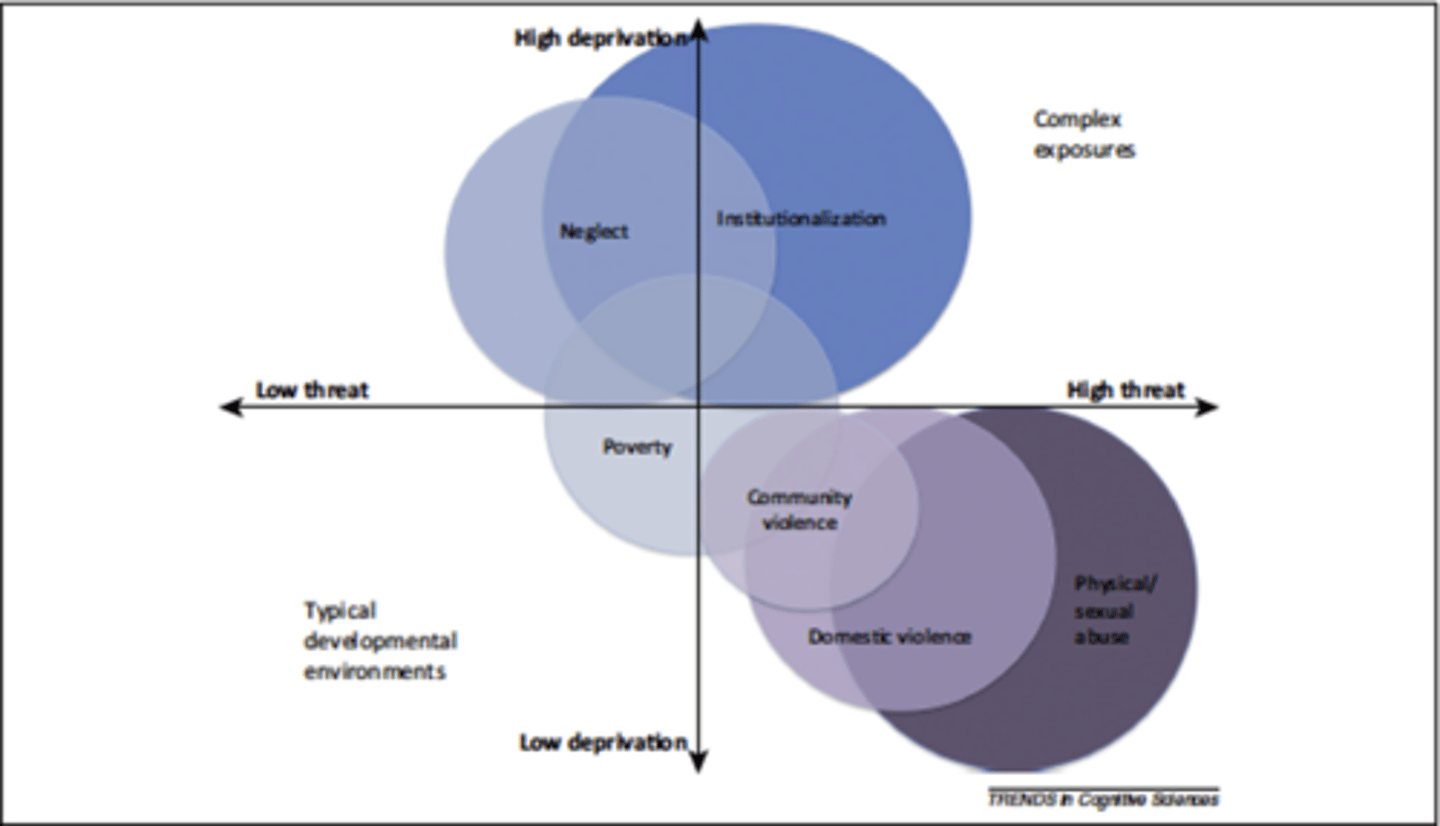
Deprivation vs Threat
neglect is deprivation
abuse is threat
Dimensional model
We can split different forms of adversity into two types:
Deprivation: the absence of something that should be there
Threat: when something is there that shouldn't be
Neglect: high in deprivation, we are missing a dedicated caregiver to nurture us
Abuse: high in threat
Amygdala Dependent Learning
stage 1-3: early infancy, infancy, attachment learning, Weaning
stage 2: adolscence, adulthood
What is attachment learning?
rats/people are attached to mother regardless if if they are abusive or not. you will always form an attachment
Consequences of attachment learning in early infancy
no short term
long term: appetitive behavior (attraction) towards stimuli regardless of their valence
- people that were abused are attracted to abusers/become abusive
Consequences of attachment learning in early infancy
short term: consequences only during high stress situations
- strange situation/attachment style
Consequences of attachment learning in weaning
decreases social exploration
Consequences of attachment learning in adolescence and adulthood
adolescence: depressive behavior (continues into adulthood)
adulthood: enhanced aggression, aberrant threat response, approaches threat, poor maternal protection
Lab abuse paradigm (in rats)
mother has insufficient nest, resources taken away -->> caused stress/abusive behavior --> releases cortisol --> transferred to pups through milk
Attachment learning in rats
Stage 1: Sensitive period: amygdala off because they rely on mother to protect from threat. No differences.
Stage 2: Transitional sensitive period: where we see a change in rats with/without abusive mother. Good mother: amygdala turns on when separate and still don't detect threat, and off if mother in present. Abusive mother: amygdala on regardless
Stage 3: Post-sensitive period: Amygdala on regardless of mother's presence for both rats (aversion learning). No difference
Attention vs aversion learning
attention: good mothers act as buffers, rat does not have to pay attention to threat
aversion: abusive mothers lead to rats having an on amygdala regardless of mothers presences because she is a threat
Maternal buffering
Primary caregivers buffer the activation of the amygdala
What are ACEs?
Adverse Childhood Experiences
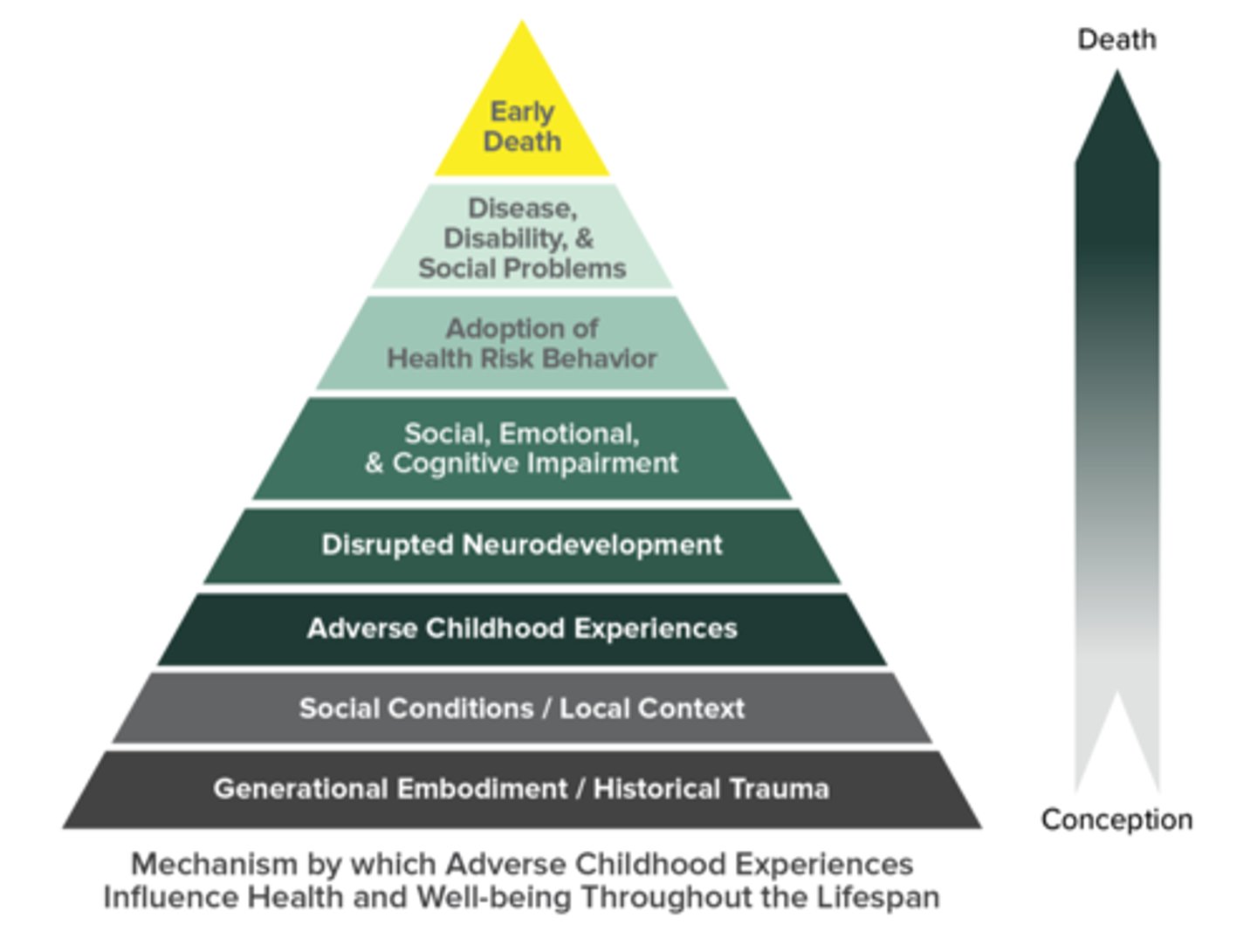
ACEs pyramid
added disrupted neurodevelopment and prenatal environment, then added generational embodiment/historical trauma and social conditions/local contexts
PFC-amygdala connectivity
Neglect: Connectivity comes on too early to make up for lack of adult presence
Abuse: connectivity doesn't come early but comes too strong and the amygdala overpowers the PFC. Exaggerated negative connectivity in adolescence
Aberrant threat response
altered functioning in social complex environments
dominance hierarchies
Failure to show subordination
increased aggression
When rats of abusive mothers become mothers, they too become poor caregivers
Anehodia
inability to feel positive emotions ( not sadness or feeling bad)
Inverted U of stress
-if stress is too low you're under-motivated/ low moral
-if stress is too high there will be burnout/overload
-optimal stress in the middle keeps you motivated
Allostasis
any stimuli that alters homeostasis in adaption to the environment
Experiment Expectant
we dont know what were being born to --> brain structure changes based on our unique experiences
Deprivation v Threat
-deprivation: absence of expected cognitive or social input (lack of nurture)
-threat: events that involve actual or threatened death, injury, or harm
Secondary altriciality
long period of dependency that human children have to their mother for survival
- babies need more than just food, water, clothing they also need nurture
Outcomes of social deprivation (social and physical)
-disturbances in social relatedness
-inc risk for externalizing disorders (adhd, odd, cd)
-inc risk for internalizing disorder (depression and anxiety)
-IQ deficits
-language deficits
-symptom mimicking autism
-psychosocial dwarfism
Outcomes of social deprivation (survival and adaptations)
-indescreminant friendliness (overly friendly to get social interaction)
-decreased response to sensory stimuli (dont cry)
-reduced chance of becoming overstimulated
-inc reactivity and sensitivity to emotional stimuli (others emotions, threats, avoid danger and better understand other behaviors)
Amygdala of PIY
-inc volume and reactivity
-dose-response (later child was adopted --> larger amygdala)
-inc response to stress (no parents so they have to be the adult)
-early maturation of pre-frontal cortex and amygdala connectivity (adult like PFC)
epigenetic changes in PIY
-diminished telomere length
-accelerated death
-accelerated aging
long term effects of PIY
- atypical emotional reactivity
- odd social behavior
- inc stress
-fearfull behavior
- limited relationships
*persist into adulthood*
Depression vs Anxiety in Previously Institutionalized Youth
higher depressive scores
no anxiety
high positive and negative until adolescence, then low positive valence because thats when the sensitive period for the ventral striatum
activation of nucleus accumbent doesn't fire how it should
Stress Acceleration Hypothesis
Adversity may lead to a reprioritization of developmental strategy away from a juvenile state (favoring a slow developmental pace and prolonged childhood) towards more adult-like functioning within fear/stress-related domains
- Resources need to be redirected towards survival
- later in life, the PFC is actually smaller because all the resources were used in childhood
- Molars come in sooner and teeth loss later in life
Life History Theory
fMRI / facial go/nogo task
people were given different facial expressions and told not to press for fearful face
- people were better at withholding response to positive v negative face
- PIY are especially bad at withholding response to fearful face --> due to larger amygdala sending stronger signal
-neglect: higher stress reactivity, inc fearful behavior, inc sensitivity to neg info, inc anxious behavior --> persists into adulthood - larger amygdala = inc anxiety
anxiety (dsm V def)
persistant worry about everyday challenges out of proportion to the perceived threat --> often associated with depression
RDoC framework
biopsychosocial model of looking at mental illness, looking at the holistic picture rather than just checking off a list of symptoms
nucleus accumbens
- deals with stress
- sensitive to stress
ventral striatum
- pleasure center
- sensitive to stress
- adolescence is the sensitive period
- adolescence is the most pleasure we will ever feel
How early life adversity causes adolescence emergent depression
early life adversity --> HPA axis dysregulation --> altered BDNF secretion --> dysregualted mesolimbic dopamine --> ventral striatic hypoactivation --> adolescence depression
Life history theory
Exposure to abuse favors traits consistent with faster maturation while exposure to neglect should favor traits that conserve resources
Contradicts the Stress Acceleration Hypothesis, MUST differentiate between abuse and neglect
Abuse: expectation to have shorter life span → quickens reproductive process. faster cell death
Neglect: I need more time to mature → pushes back reproductive process. normal cell death
Adverse Childhood Experiences Study
asked people 10 most common adversity questions about: Abuse: to emotional, physical, sexual
Household challenges: mother violence, substance abuse, mental illness, separation/divorce, incarcerated household member
Neglect: physical, and emotional
Odds of having ACEs
once you one have, the odds you have another are high, once you have two etc...
dose response relationship until you have 6, then it levels off
6+ ACES = die 20 years earlier
psychological maltreatment
repeated pattern of behavior conveyed to children that they are worthless, flawed, unloved, unwanted, endangered, or only of value in meeting another needs
- attacks childrens basic developing development need for love and affection
neglect definition
failure to provide basic physical and social are that is considered, based on community standards, the minimal necessary for children to thrive