Cardiac Physiology
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 1 Info
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Circulatory System purpose
transport O2 and nutrients to tissues
removal of CO2 wastes from tissues
regulation of body temperature
Circulatory system work with?
works with the pulmonary system: cardiopulmonary or cardiorespiratory system
Adjustments of blood flow during exercise of circulatory system
increased cardiac output
redistribution of blood flow from inactive organs to active muscle
Components of Circulatory System
heart, arteries/arterioles, capillaries, and veins/venules
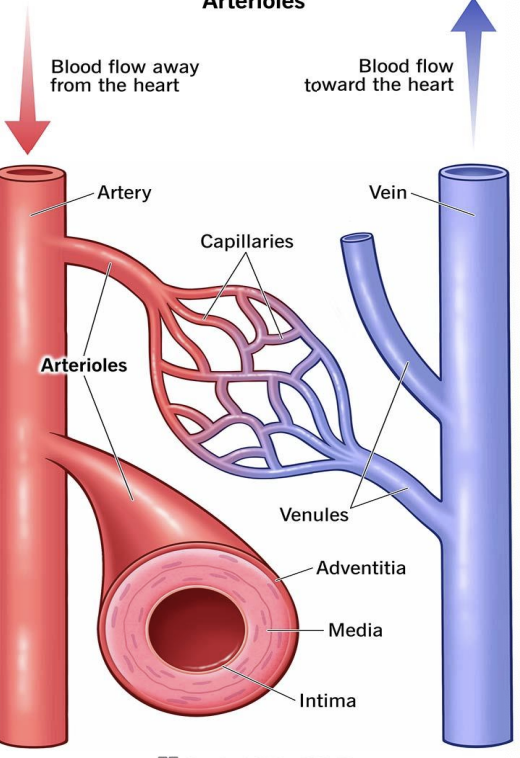
heart
creates pressure to pump blood
arteries and arterioles
carry blood away from the heart
capillaries
exchange of O2, CO2, and nutrients with tissues
veins and venules
carry blood toward the heart
Structure of the heart
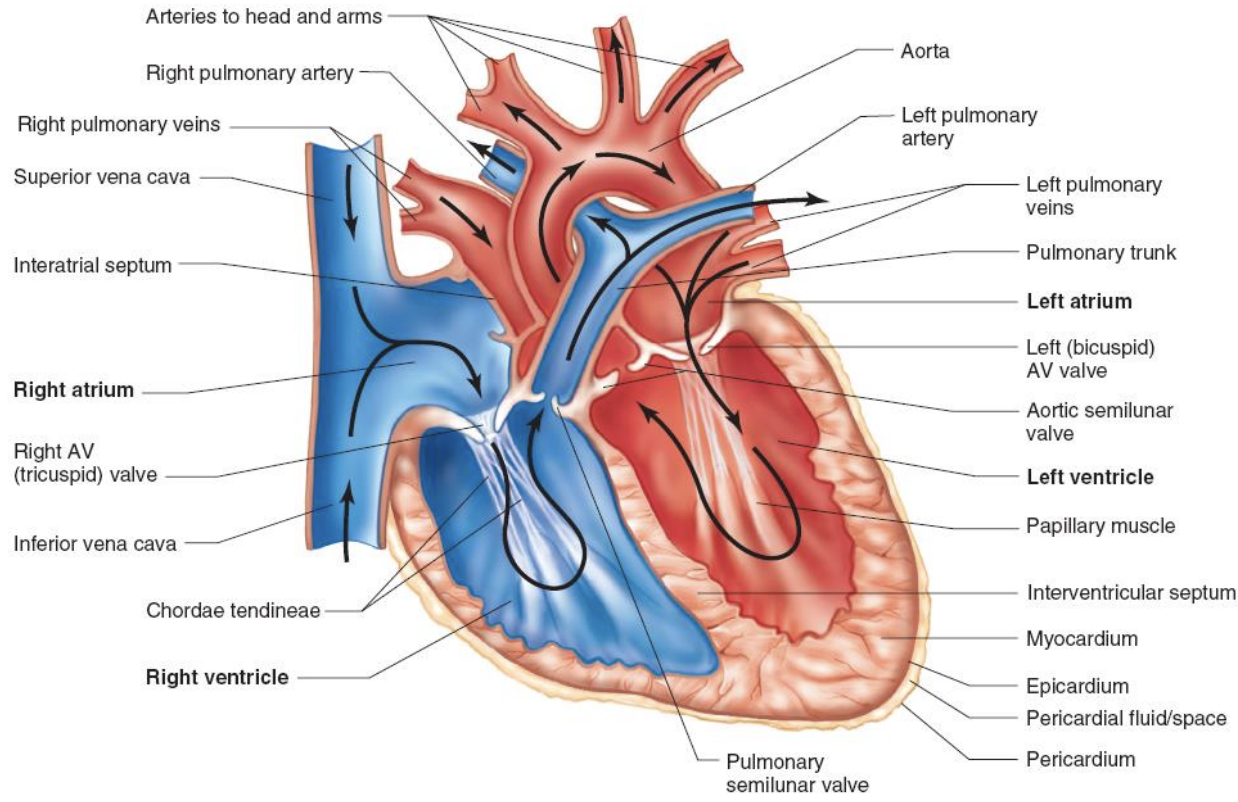
cardiac tissue
striated
branched
many mitochondria
involuntary control
connected through intercalated discs: purpose is to carry electrical signals
spiral orientation: purpose is to squeeze blood up and out of ventricles
Cardiac muscle structural comparison
contractile proteins: present
shape of muscle fibers: branching; shorter than muscle fibers
nuclei: single
Z discs: present
cellular junctions: intercalated discs
connective: endomysium
skeletal muscle structural comparison
contractile proteins: present
shape of muscle fibers: elongated
nuclei: multiple
Z discs: present
cellular junctions: no junctional complexes
connective: epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium
cardiac muscle functional comparison
energy production: primarily aerobic
calcium source: sacroplasmic and extracellular calcium
neural control: involuntary
regeneration potential: none; no satellite cells present
skeletal muscle functional comparison
energy production: aerobic and anaerobic
calcium source: sarcoplasmic retriculum
neural control: voluntary
regeneration potential: some possibility via satellite cells
epicardium/visceral pericardium characteristics
serous membrane including capillaries, lymph capillaries, nerve fibers
epicardium/visceral pericardium function
lubricating outer covering
myocardium characteristics
cardiac muscle tissue separated by connective tissues and including capillaries, lymph capillaries, nerve fibers
myocardium function
provides muscular contraction to eject blood from heart chambers
endocardium characteristics
endothelial tissue and thick subendothelial layer of elastic and collagenous fibers
endocardium function
serves as protective inner lining of chamber and values
myocardium
receives blood supply via coronary arteries
high demand for oxygen and nutrients
main coronary arteries (left and right)
left main coronary artery
left ventricle and left atrium
left anterior descending artery (LAD): front of left side of heart and septum
left circumflex artery: lateral and posterior heart wall
right coronary artery
right ventricle, right atrium, SA node, AV node
posterior descending artery: inferior aspect of the heart
acute marginal artery: lateral portion of right ventricle & septum of the heart
atherosclerosis
progressive condition resulting in narrowing of arteries due to fatty plaque build up in the inner wall of an artery
-decrease in radius of the vessel results in decrease in blood flow
—myocardial ischemia
Myocardial infarction (MI)
plaque in coronary artery ruptures
triggers a blood clot which blocks blood flow downstream
blockage in coronary blood flow results in cell damage
exercise is cardioprotective against MI
reduce incidence
improved survival
reduces the amount of myocardial damage from MI
-improvements in heart’s antioxidant capacity
-improved function of ATP-sensitive potassium channels
Cardiac Cycle
Systole (contraction phase and ejection of blood), diastole (relaxation phase and filling with blood)
at rest, diastole longer than systole
during exercise, both systole and diastole are shorter
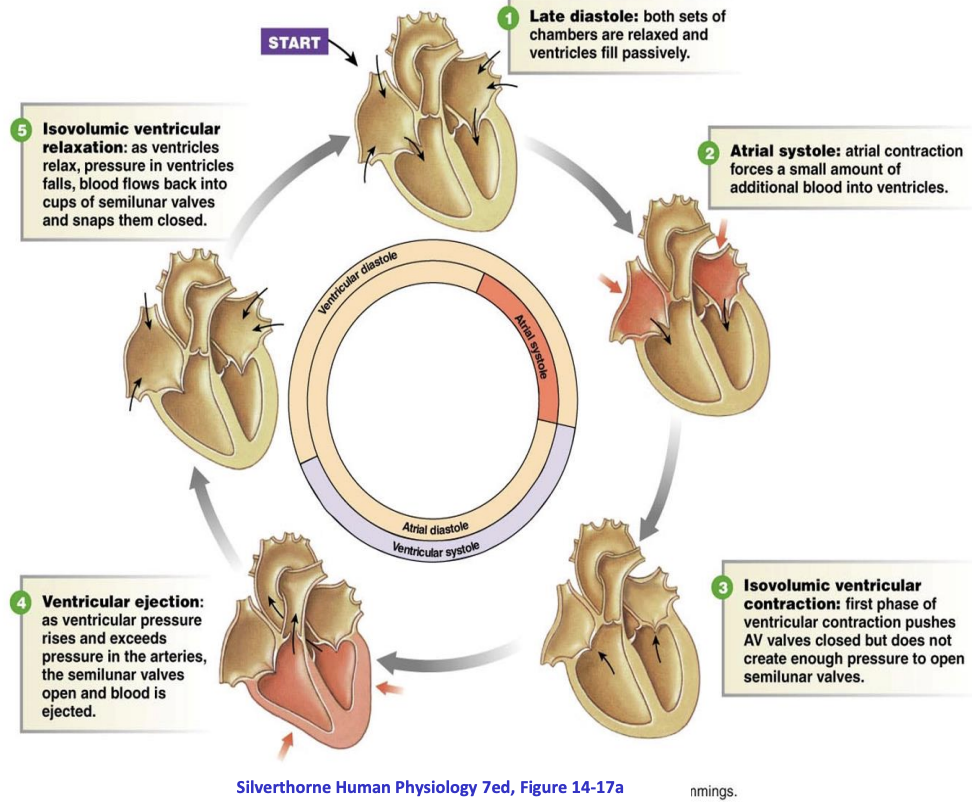
systole pressure changes
pressure in ventricles rises
blood ejected in pulmonary and systemic circulation
-semilunar valves open when ventricular P > aortic P
diastole pressure changes
pressure in ventricles is low
filling with blood from atria
-AV valves open when ventricular P < atrial P
heart sounds
First (S1): closing of AV valves
Second (S2): closing of aortic and pulmonary valves
Cardiac Cycle at Rest and During Exercise

electrical activity of the heart
contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium
conduction system
conduction system
SA node: pacemaker, initiates depolarization
AV node: passes depolarization to ventricles; brief delay to allow for ventricular filling
bundle branches: to left and right ventricle
punkinje fibers: throughout ventricle
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
records the electrical activity of the heart
-p wave: atrial depolarization
-QRS complex: ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
-T wave: ventricular repolarization
ECG abnormalities may indicate coronary heart disease (ST-segment depression can indicate MI)
Diagnostic Use of the ECG During exercise
-graded exercise test to evaluate cardiac function: observe ECG during exercise and also observe changes in blood pressure
-atherosclerosis
-ST segment depression or inverted T wave: suggests MI
atherosclerosis
fatty plaque that narrows coronary arteries
reduces blood flow to myocardium: (MI)
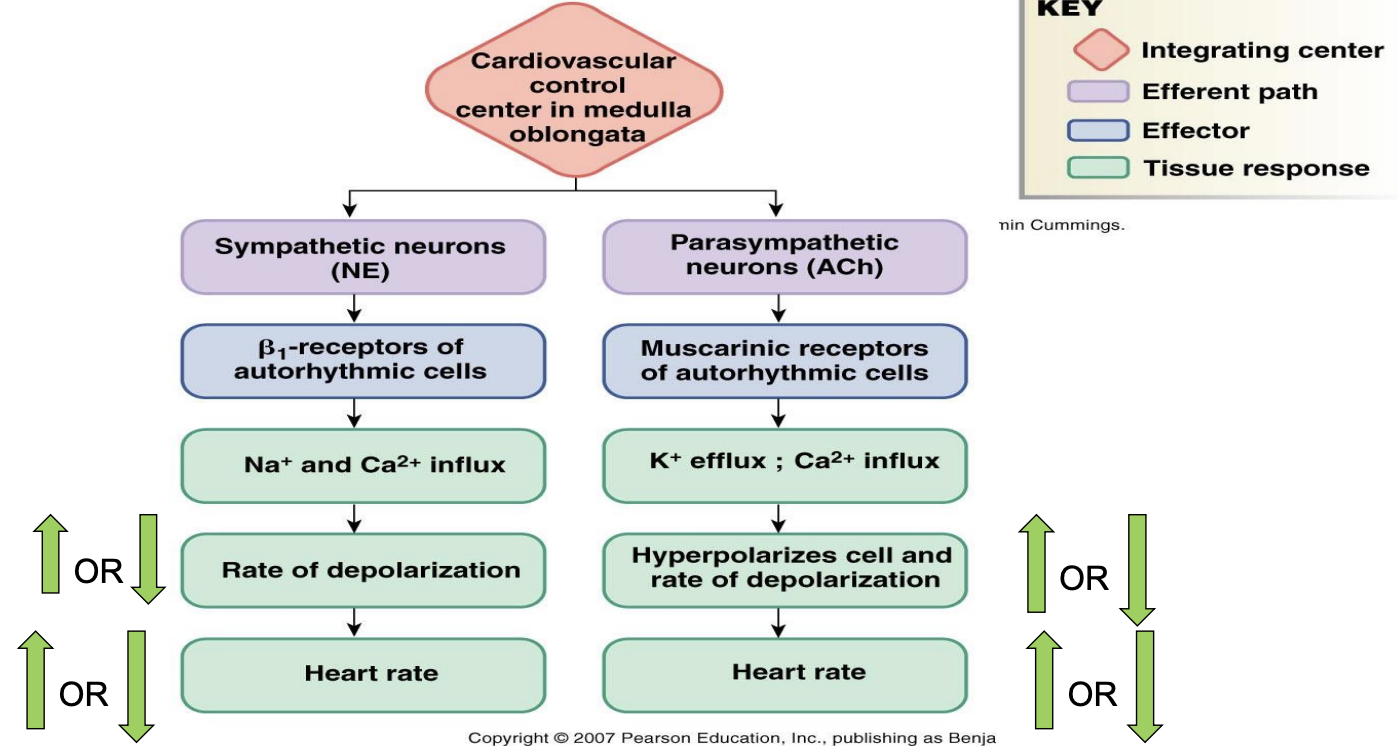
neural innervation of the heart
parasympathetic nervous system: vagus nerve; slow HR by inhibiting SA and AV node
sympathetic nervous system: cardiac accelerator nerves, increases HR by stimulating SA node and AV node, innervates the ventricles
Regulation of Heart Rate
low resting HR due to parasympathetic tone
increase in HR at onset of exercise
initial increase up to ~100 beats/min due to parasympathetic withdrawal - “ease off the brake”
later increase >100 beats/min due to increased sympathetic outflow - “press on the gas”
Beta Blockers
beta-adrenergic blocking drugs
complete with epinephrine and norepinephrine for beta adrenergic receptors in the heart (block)
reduce heart rate and contractility (lower the myocardial oxygen demand)
prescribed for patients with coronary artery disease and hypertension
will lower HR during submaximal and maximal exercise
important for exercise prescription
Heart rate variability (HRV)
time between heart beats (standard deviation of R-R interval; measured by ECG or specialized equipment)
indicator of sympathovagal balance: balance between SNS and PNS (factors affecting HRV: age and conditions affecting ANS
interpretation: wide variation in HRV is considered health; low HRV is a predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with existing CVD
aerobic exercise can improve HRV
Cardiac output
amount of blood pumped by the heart each minute
product of heart rate and stroke volume (HR and SV)
CO = HR x SV
depends on training state and sex
Regulation of stroke volume
end-diastolic volume (EDV): volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole (preload)
average aortic blood pressure: pressure the heart must pump against to eject blood (afterload); mean arterial pressure
strength of the ventricular contraction (contractility)
End-diastolic volume
cardiovascular system is a closed system, how would EDV change to meet metabolic demand?
dependent on venous return
venous return increased by: venoconstriction, skeletal muscle pump, and respiratory pump
Frank-starling mechanism
venoconstriction
SNS
skeletal muscle pump
rhythmic skeletal muscle contractions force blood in the extremities toward the heart re
respiratory pump
changes in thoracic pressure pull blood toward heart
frank-starling mechanism
greater EDV results in a more forceful contraction
due to stretch of ventricles
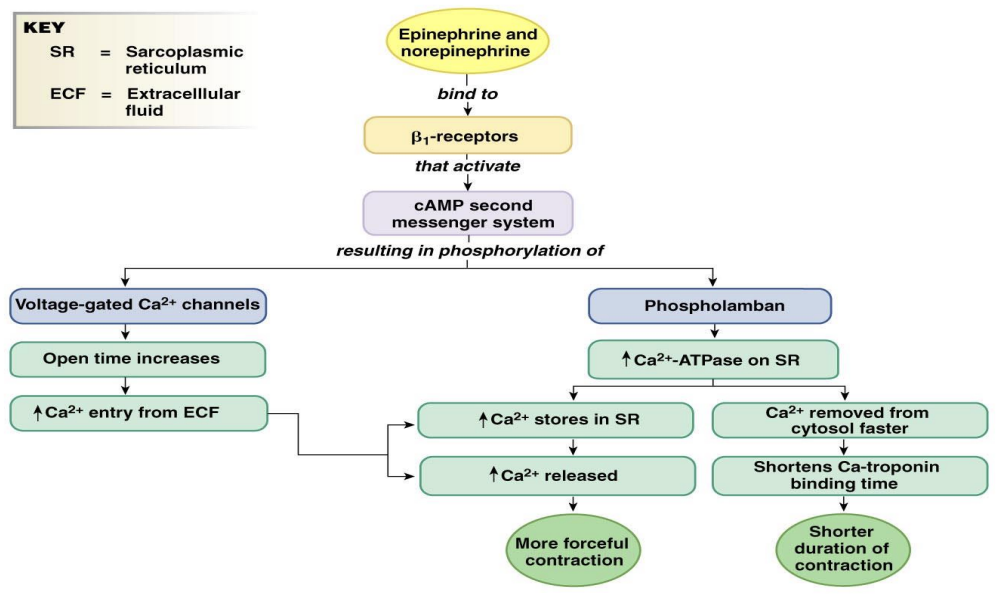
effects of sympathetics stimulation on stroke volume
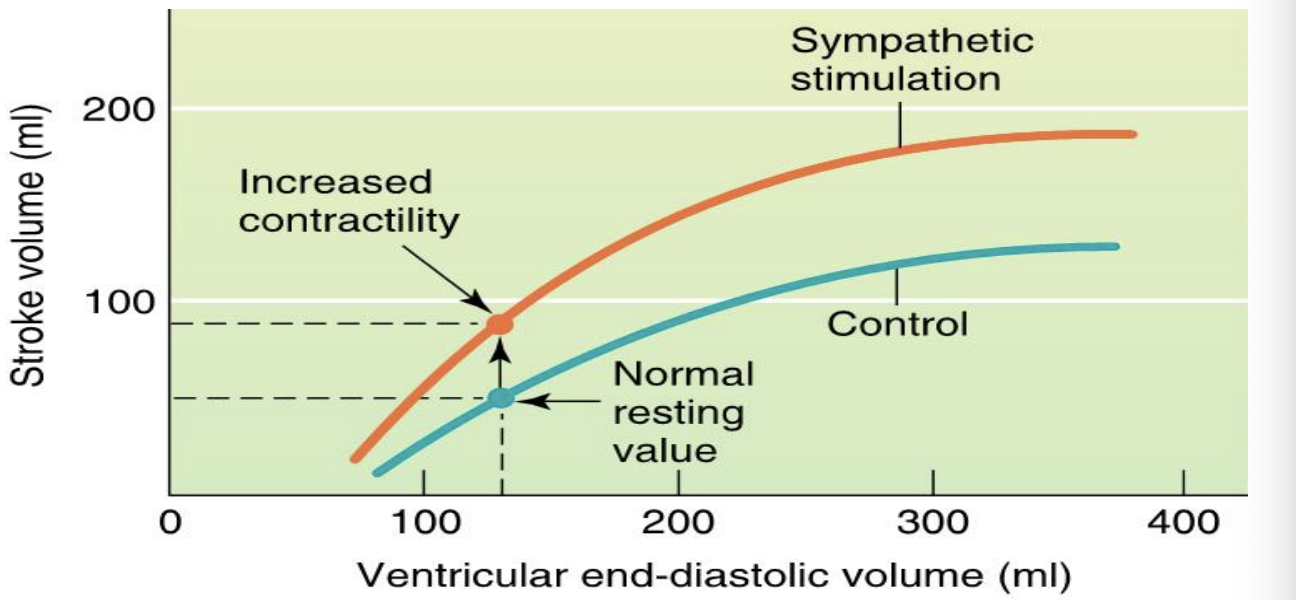
Cardiac Ca2+ Handling with Sympathetic Stimulation
Factors that regulate cardiac output
Cardiac Rate: parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves
Stroke Volume: sympathetic nerves (contractions strength); Frank-starling (stretch → contraction strength), end-diastolic volume and means arterial pressure