Autoimmunity and Vaccinations
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:45 PM on 2/6/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
What is an *autoimmune disease*?
When the body attacks itself, the immune system damages body cells as a result
2
New cards
What cells are attacked, and by what?
Self-antigens are attacked by antibodies, T-cells and B-cells
3
New cards
What are self-antigens?
the antigens present on the organism’s own cells
4
New cards
What does self-antigens being attacked cause?
Self-antigens are treated as foreign antigens and launches an immune response on the body’s own tissue
5
New cards
Name 2 examples of autoimmune responses
Lupus
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
6
New cards
What forms the surface antigen and what does it do?
Glycoproteins and glycolipids form surface antigens that enable the immune system to determine whether the cell belongs to the body or if it is foreign
7
New cards
What is active immunity
Long term circulation in blood
8
New cards
What is passive immunity
Temporary circulation in blood
9
New cards
What is natural active immunity?
Immunity that is caused by an infection – antibodies remain in the blood permanently
10
New cards
What is natural passive immunity?
Anti-bodies are provided to a baby across placenta pre-birth, and in breast milk in colostrum – anti-bodies only last a few months
11
New cards
What is artificial active immunity?
Immunity that is cause by vaccination / immunisation – antibodies remain in the blood permanently
12
New cards
What is artificial passive immunity?
Anti-bodies are injected in to a person while they have an infection – they only last a few months
13
New cards
What differentiates between the different types of immunity?
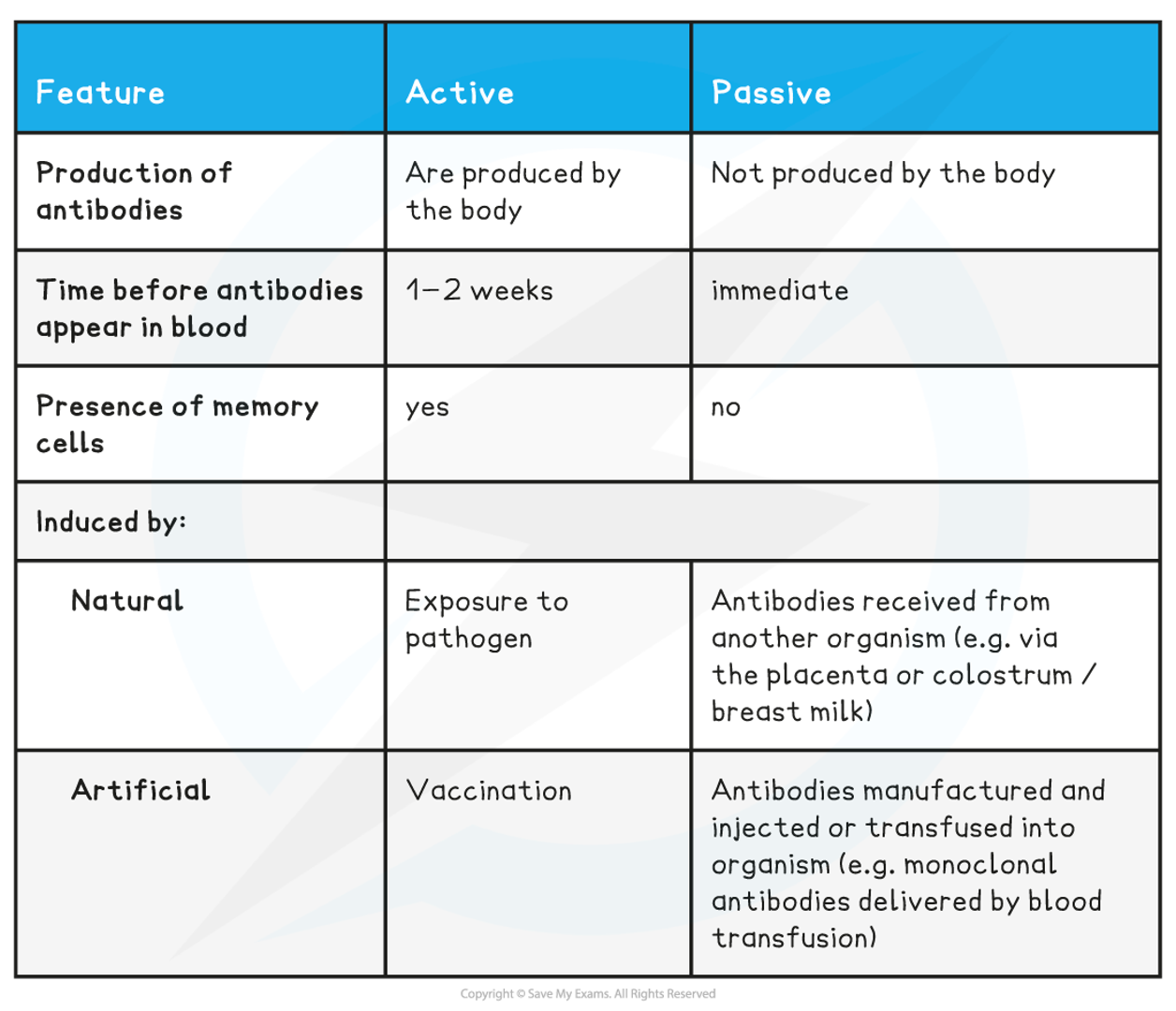
14
New cards
Define *vaccine*
a ^^suspension of **antigens**^^ that are intentionally put into the body to ^^induce **artificial active immunity**^^
15
New cards
Name the 3 types of vaccine
1. Inactivated
2. Live attenuated
3. Subunit
16
New cards
What is inactivated vaccine
The whole pathogen is given but it cannot reproduce, DNA is not able to replicate and its metabolic processes are stopped
17
New cards
What is live attenuated vaccine?
This only stops the reproduction of the pathogen
18
New cards
What is subunit vaccine?
Only a part of the antigen is given
19
New cards
What are 3 challenges of vaccines
1. Antigenic variation
2. Poor response
3. Adjuvants reaction
20
New cards
What is antigenic variation?
A variation in the antigens of pathogens causes the vaccine to not be able to trigger an immune response.
\
Diseases caused by eukaryotes can have too many antigens on their cell surface membrane, which makes it difficult to produce vaccines which prompt a quick immune response
\
Diseases caused by eukaryotes can have too many antigens on their cell surface membrane, which makes it difficult to produce vaccines which prompt a quick immune response
21
New cards
Why could people have a poor response to vaccines
People could be malnourished and this not produce the antibodies or proteins
Or their immune system could be defective
Or their immune system could be defective
22
New cards
What are adjuvants?
Other things in vaccines. eg aluminium
23
New cards
What is herd immunity?
**Herd immunity** arises when a ^^**sufficiently large proportion of the population has been vaccinated (and are therefore immune)**^^ which ^^makes it difficult for a pathogen to spread within that population^^