Genetics Chapter 8 and 19
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Chromosome Morphology
position of centromere on the chromosomes
metacentric (middle)
submetracentric (near middle)
acrocentric (near end)
telocentric (end)
p arm (short arm)
q arm (long arm)
Karyotype
a visual representation of an individual's complete set of chromosomes, organized by size, shape, and number.
Banding
Staining techniques help to distinguish among chromosomes of similar size and shape.
G Bands
Stain: Giemsa dye
Dark Bands Are: A–T rich DNA and heterochromatin
Q Bands
Stain: Quinacrine mustard
Visualization: UV fluorescence
Bright Bands: A–T rich regions
C Bands
Stain: Alkali treatment + Giemsa
Dark Region: Constitutive heterochromatin, especially centromeres
R Bands
Stain: Heat treatment + Giemsa
Shows: R bands (Reverse of G-bands)
Dark Bands Are: C–G rich regions
Use: Highlights gene-rich (active) chromosomal areas
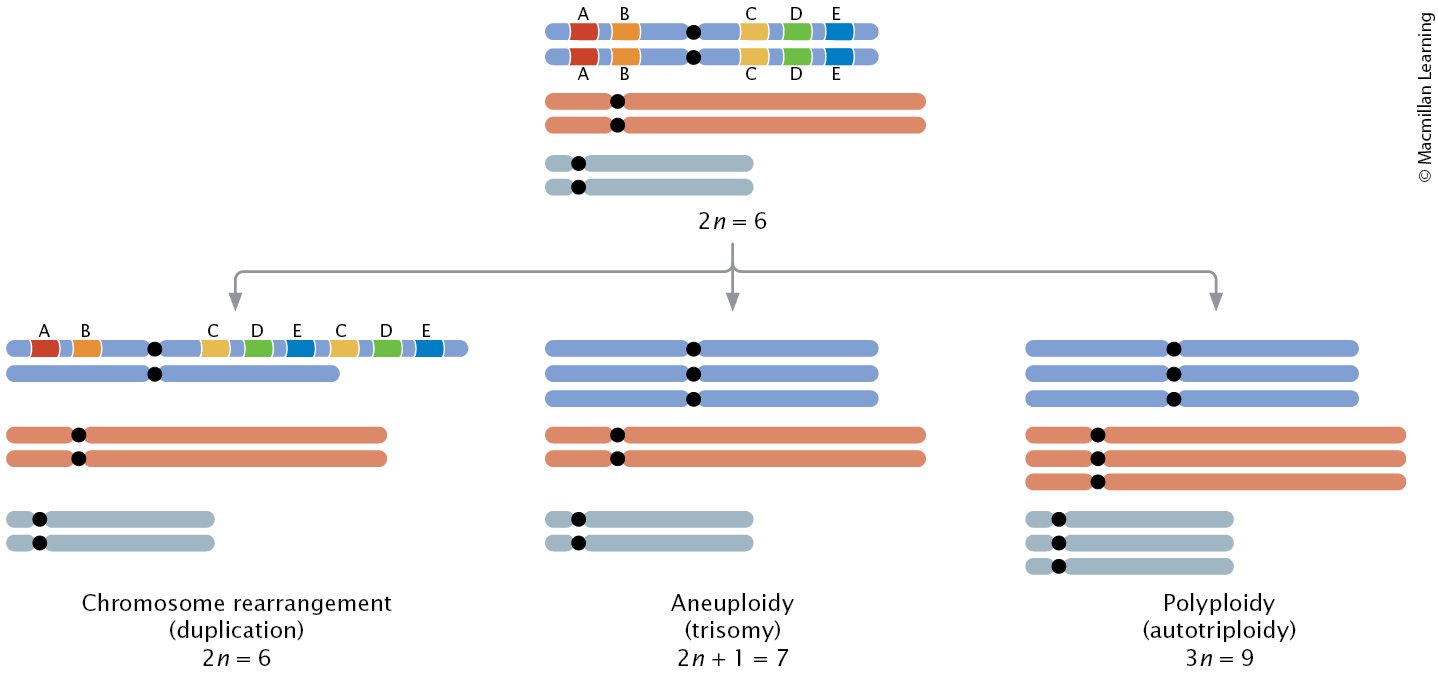
Types of chromosome mutations
Chromosome rearrangements (alter the structure of chromosomes)
Aneuploidy (alters the number of chromosomes)
Polyploidy (one or more complete sets of chromosomes are added)
Chromosomes rearrangments
Alter the structure of chromosomes
Four types: duplication, deletion, inversion, and translocation
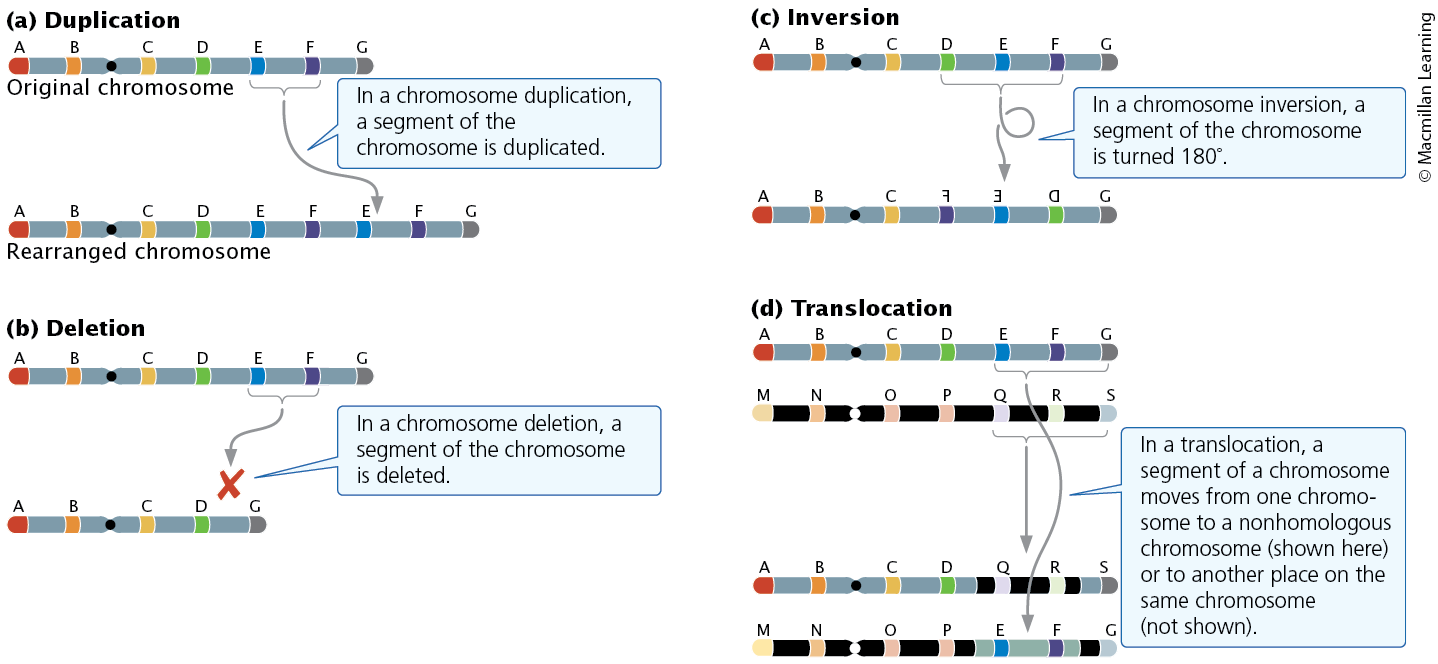
Duplication
Duplication of a chromosome segment
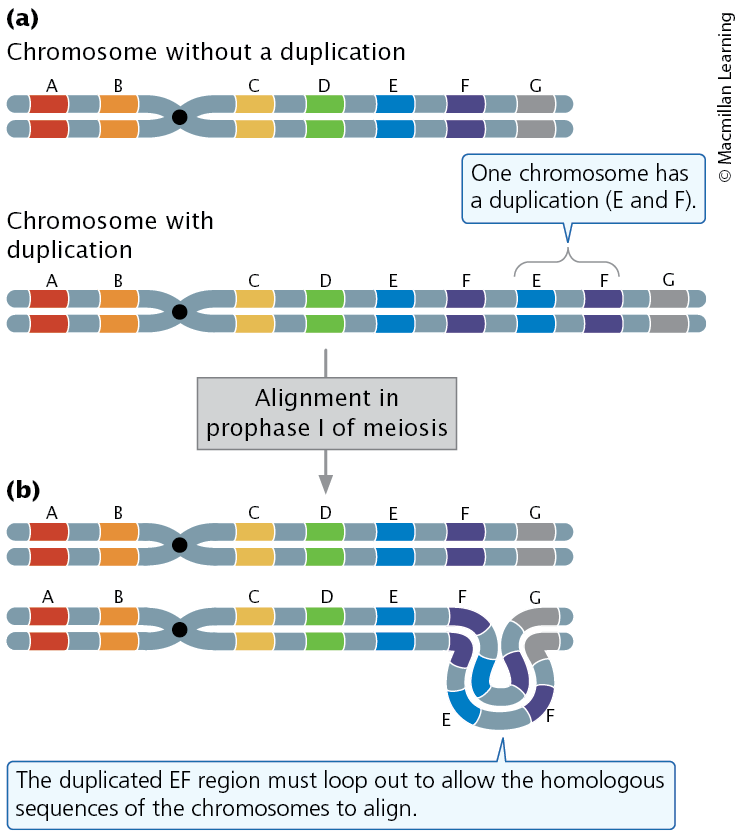
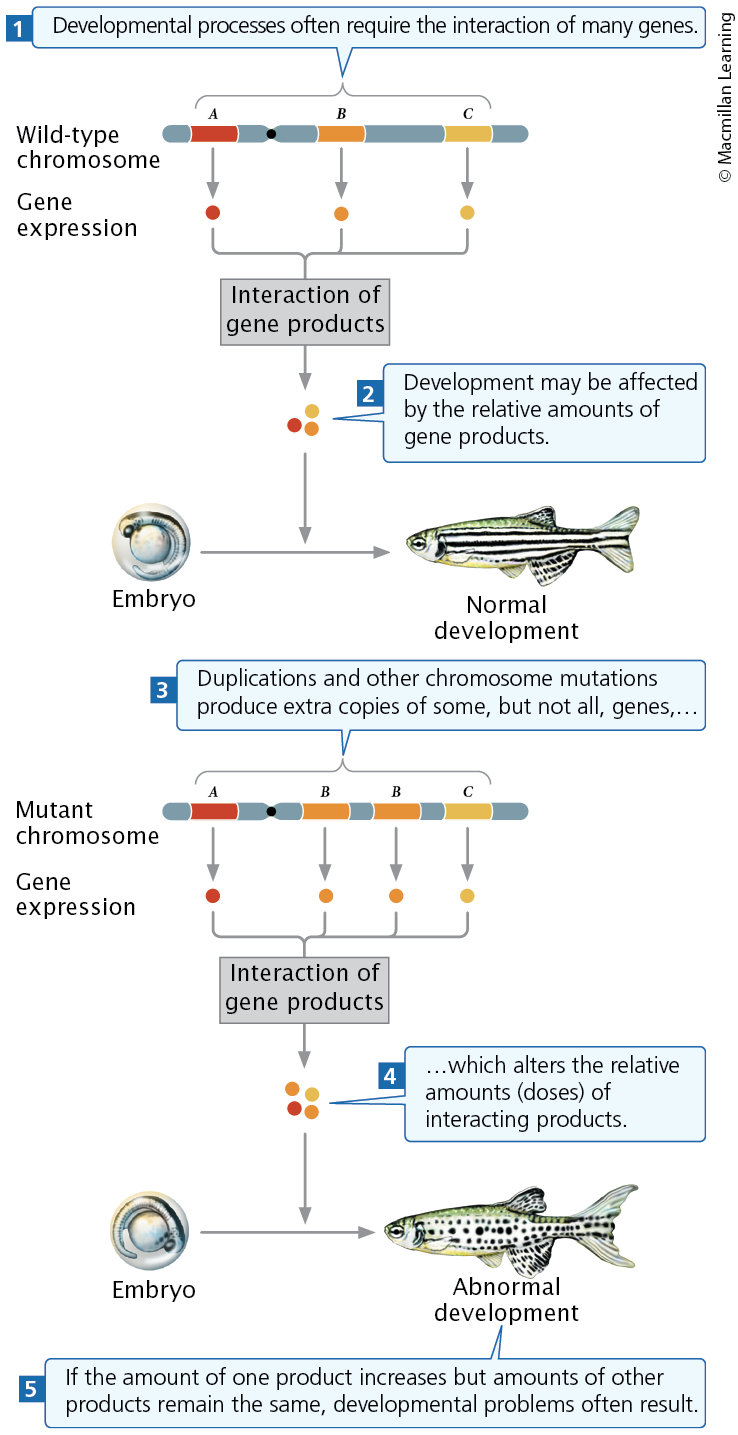
Effects of Chromosome Duplication (1)
In an individual heterozygous for a duplication, the duplicated region loops out during pairing in prophase
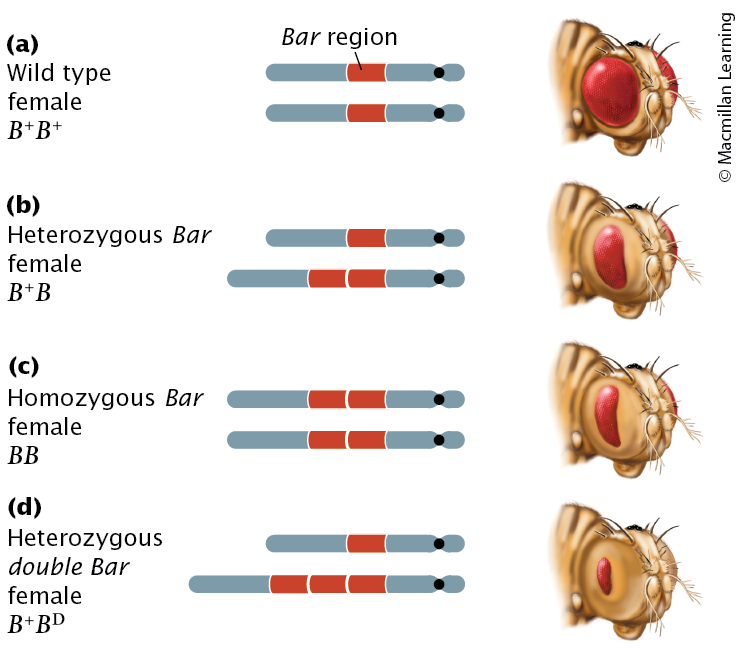
Effects of Chromosomes Duplication (2)
The Bar phenotype in Drosophila melanogaster results from an X-linked duplication.
(a) Wild-type fruit flies have full-sized eyes. (b) Flies that are heterozygous and (c) homozygous for the Bar mutation have smaller, bar-shaped eyes. (d) Flies with double Bar have three copies of the duplication and much smaller bar-shaped eyes.
Effects of Chromosome Duplications (3)
Unequal crossing over produces duplications and deletions
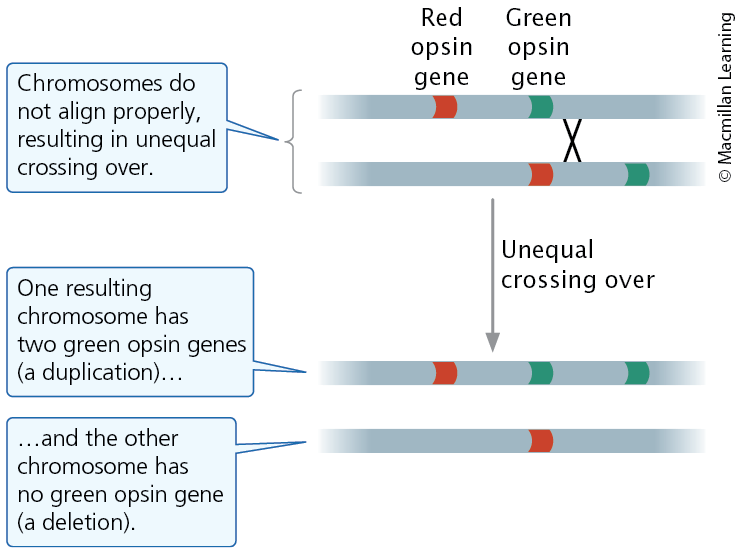
Unbalance Gene Dosage
There are too many or too few copies of a gene, which causes the cell to make too much or too little of its protein.
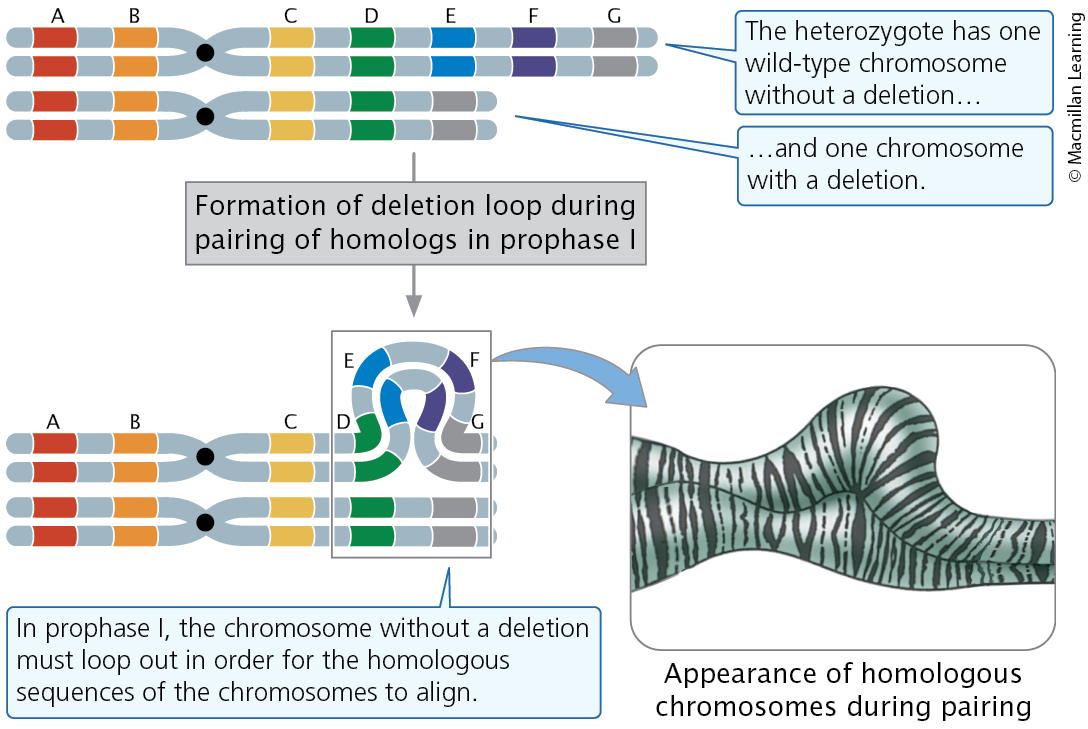
Deletions
loss of a chromosomal segment
Effect of Chromosome Deletion
Large deletions can be easily detected; during the pairing of homologs in prophase I of meiosis, normal chromosome loops out
Duplication on chromosome 4, short arm
Symptoms: Small head, short neck, low hairline, reduced growth, intellectual disability.
Duplication on chromosome 4, long arm
Symptoms: Small head, sloping forehead, hand abnormalities.
Duplication on chromosome 7, long arm
Symptoms: Delayed development, head asymmetry, fuzzy scalp, small nose, low-set ears.
Duplication on chromosome 9, short arm
Symptoms: Characteristic facial features, variable intellectual disability, high/broad forehead, hand abnormalities.
Deletion on chromosome 5, short arm
Cri-du-chat syndrome
Small head, distinctive cat-like cry, wide-set eyes, round face, intellectual disability.
Deletion on chromosome 4, short arm
Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome
Small head with high forehead, wide nose, cleft lip/palate, severe intellectual disability.
Deletion on chromosome 4, long arm
Small head, mild–moderate intellectual disability, cleft lip/palate, hand/foot abnormalities.
Deletion on chromosome 7, long arm
Williams–Beuren syndrome
Distinct facial features, heart defects, and cognitive impairment.
Deletion on chromosome 15, long arm
Prader–Willi syndrome
Poor feeding early → later obesity, mild–moderate intellectual disability.
Deletion on chromosome 18, short arm
Round face, large/low-set ears, mild–moderate intellectual disabilit
Deletion on chromosome 18, long arm
Distinctive mouth shape, small hands, small head, intellectual disability
Inversion
chromosome segment inverted 180 degrees
paracentric and pericentric
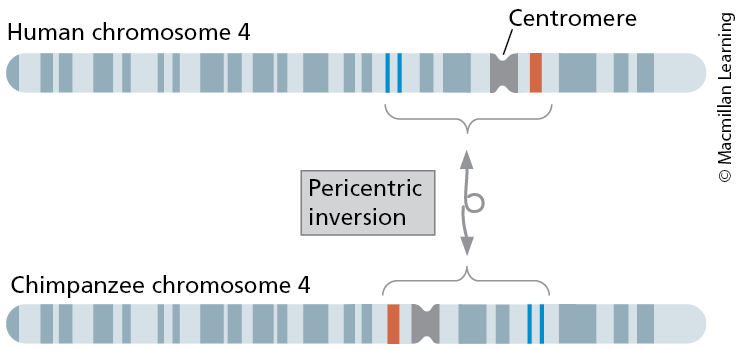
Pericentric Inversion
Chromosome inversion that includes the centromere in the inverted region
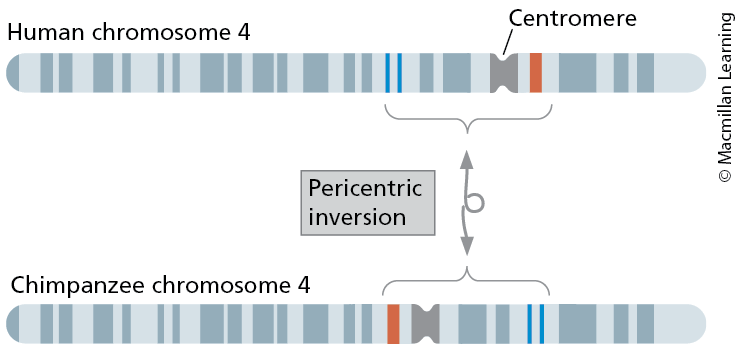
Paracentric Inversion
Inversions that do not include the centromere
Effect of Inversions (1)
Inversions in Meiosis
Individuals homozygous: no problems arise during meiosis
Heterozygous individuals
Homologous sequences align only if the two
chromosomes form an inversion loopDemonstrate reduced recombination in a paracentric
Inversion, as gametes are formed results in nonviable offspringHave abnormal gametes formed in a pericentric inversion
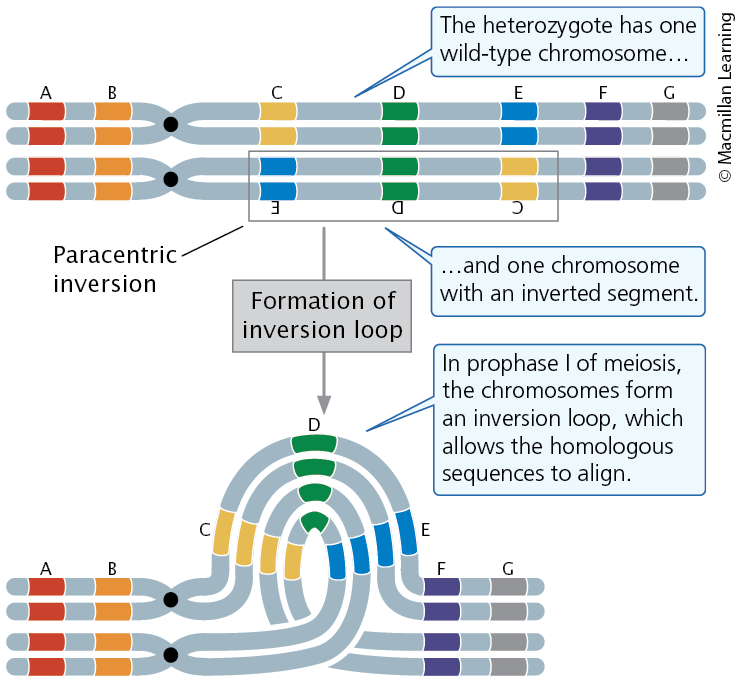
Effect of Inversions (2)
In a heterozygous individual, a single crossover within a paracentric inversion leads to abnormal gametes.
Dicentric
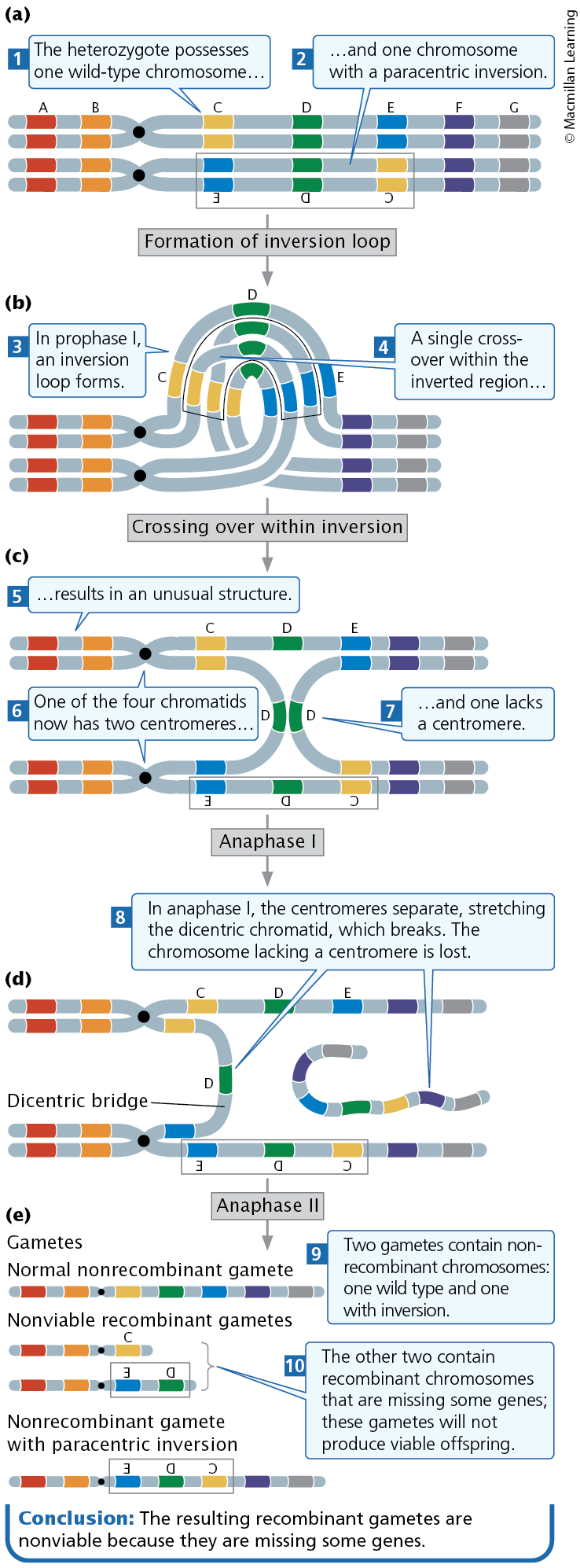
Effect of Inversions (3)
In a heterozygous individual, a single crossover within a pericentric inversion leads to abnormal gametes
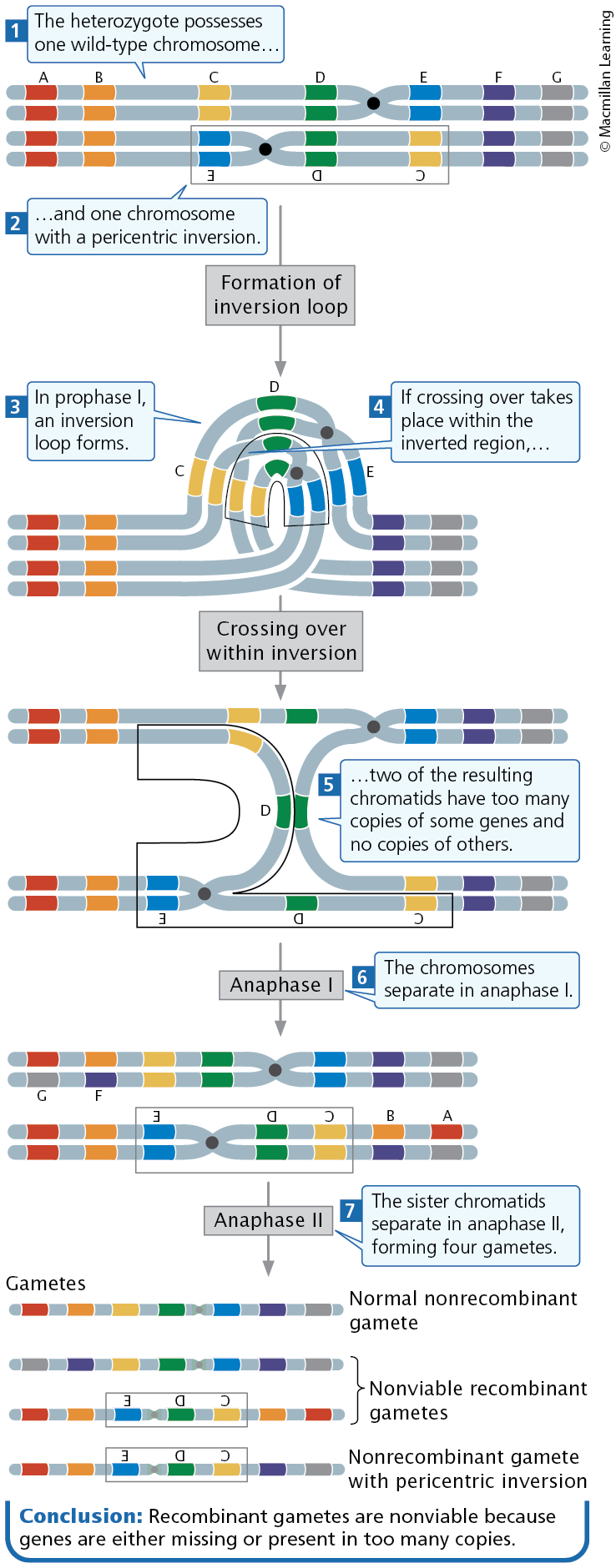
Translocations
Movement of a chromosome segment to a non-homologous chromosome or to another region of the same chromosome without reciprocal exchange
nonreciprocal, reciprocal, robertsonian,
Nonreciprocal Translocation
Movement of a chromosome segment to a nonhomologous chromosome or to another region of the same chromosome without reciprocal exchange
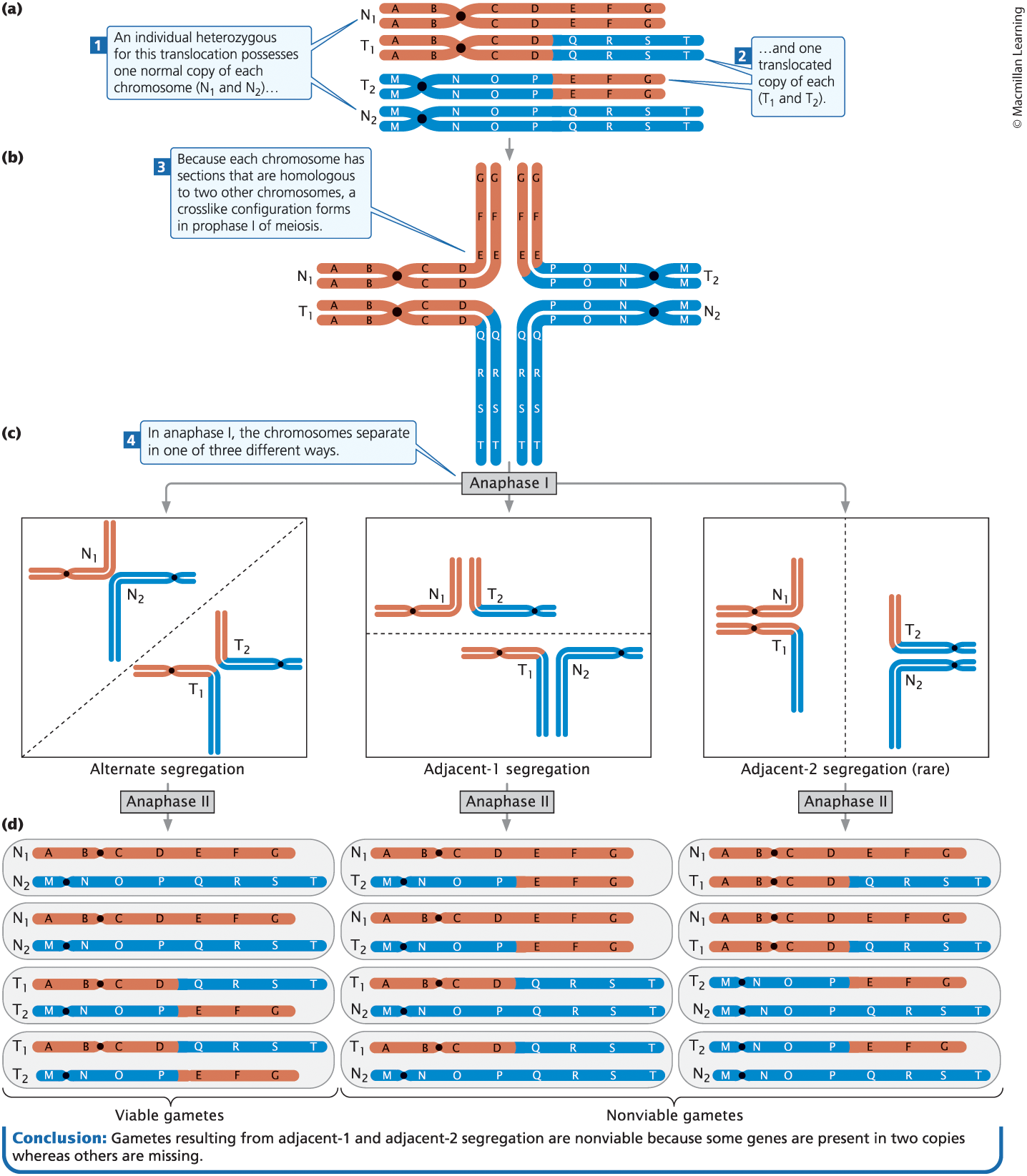
Reciprocal Translocation
Exchange between segments of a nonhomologous chromosome or to another region of the same chromosome
Robertsonian Translocation
The long arms of two acrocentric chromosomes become joined to a common centromere, generating a metacentric chromosome with two long arms and another chromosome with two very short arms
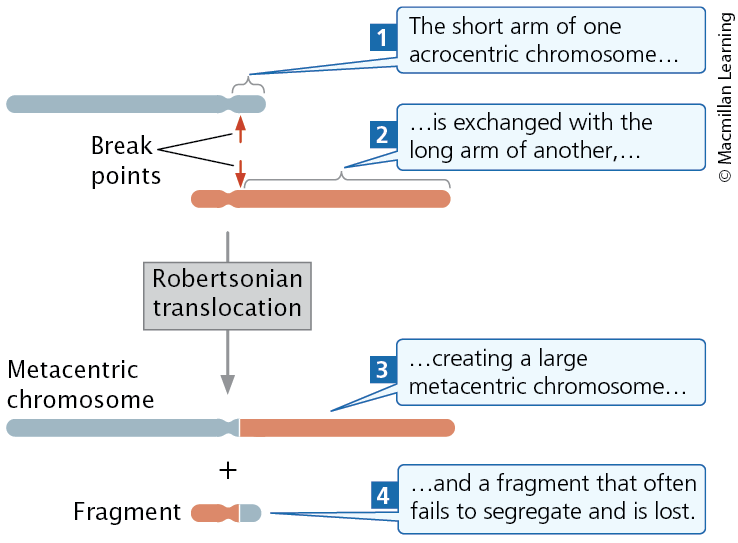
Effects of translocation
In an individual heterozygous for a reciprocal translocation, crosslike structures form in homologous pairing
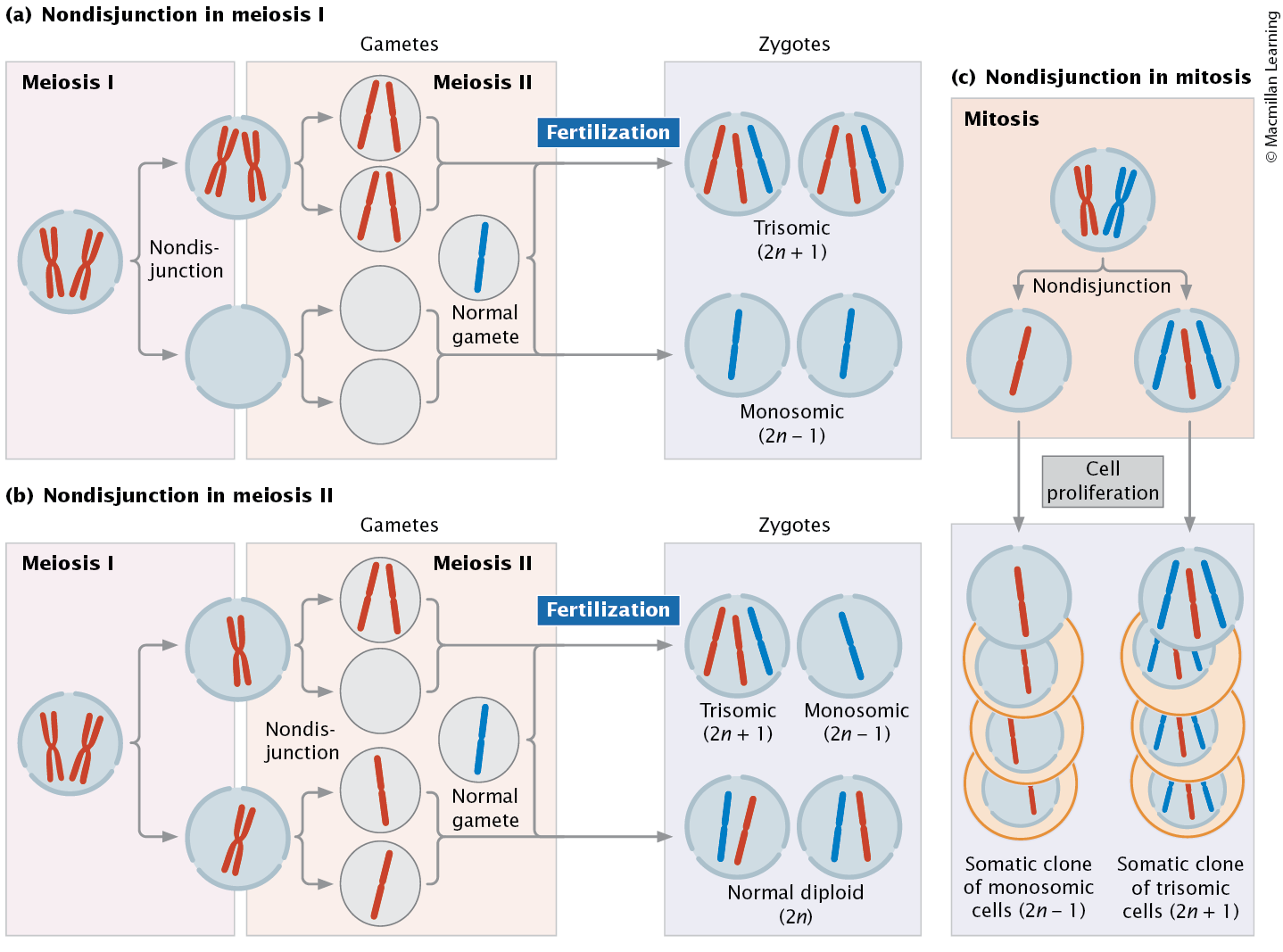
Aneuploidy
change in number of individual chromosomes
caused by:
deletion of centromere during mitosis and meiosis
robertsonian translocation
nondisjunction during meiosis
types: monosomy, trisomy, tetrasomy, nullisomy
Types of Aneuploidy
Nullisomy: loss of both members of a homologous pair (2n-2)
Monosomy: loss of a single chromosome (2n-1)
Trisomy: gain of a single chromosome (2n+1)
Tetrasomy: gain of two homologous chromosomes (2n+2)
Effects of Aneuploidy (1)
In plants:
Trisomics deviate from wild type
In humans: Sex-chromosome aneuploids:
Turner Syndrome: XO
Klinefelter Syndrome: XXY
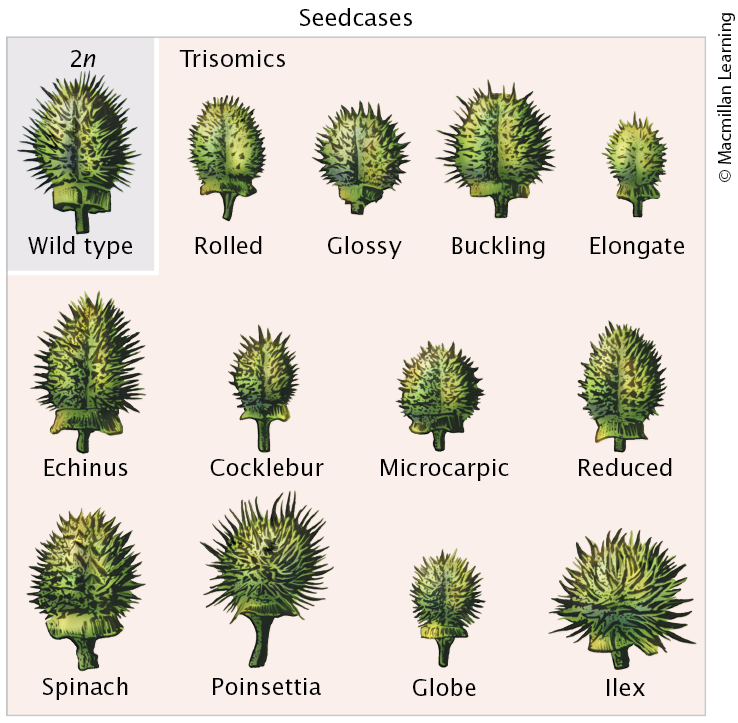
Effects of Aneuploidy (2)
Trisomy 21: Down Syndrome
Primary Down Syndrome: 75% random nondisjunction in egg formation
Familial Down Syndrome: Robertsonian translocation between chromosomes 14 and 21
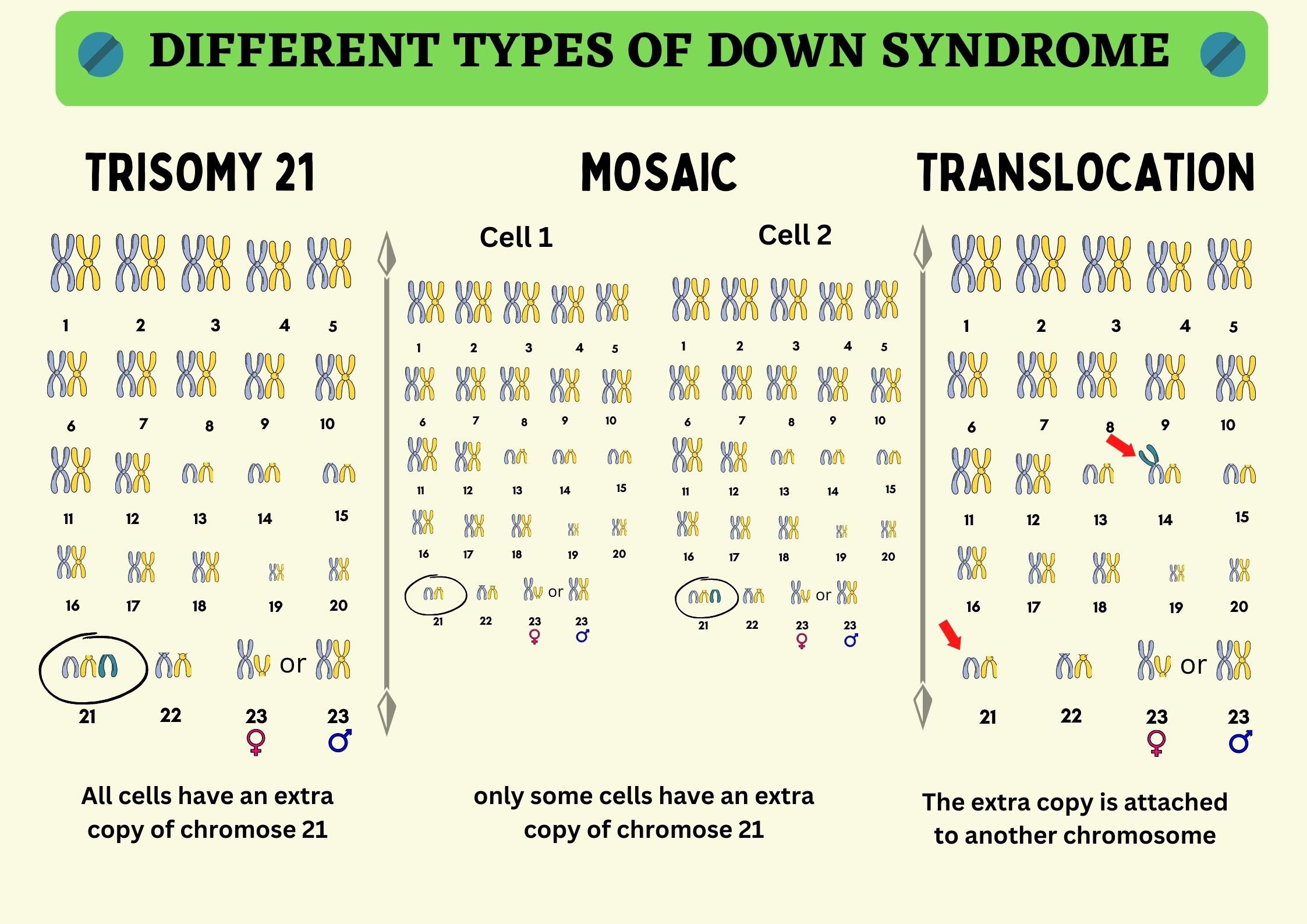
Effects of Aneuploidy (3)
Autosomal Aneuploids:
Trisomy 18: Edward syndrome, 1/8000 live births
Trisomy 13: Patau syndrome, 1/15,000 live births
Trisomy 8: 1/25,000 ~ 1/50,000 live births
Why is there a drastic decrease in frequency of this
trisomic syndrome from chromosome 18 to
chromosome 8?
The larger the chromosome, the lower the frequency of live-born trisomic syndromes, because extra copies of many genes are usually lethal.
Effect of Aneuploidy (3)
Aneuploidy and Maternal Age
Nondisjunction happens more often as mothers get older, leading to a higher chance of giving birth to a child with down syndrome
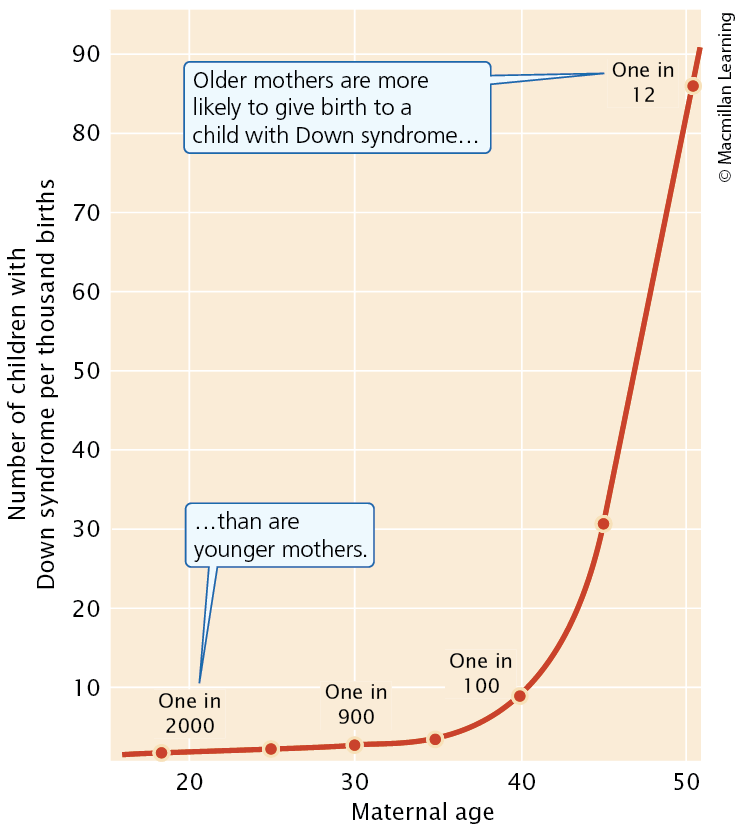
Why sex-chromosome aneuploids are more common than autosomal aneuploids in humans and mammals?
Sex chromosomes tolerate dosage changes better, so their aneuploidies are more likely to survive to birth
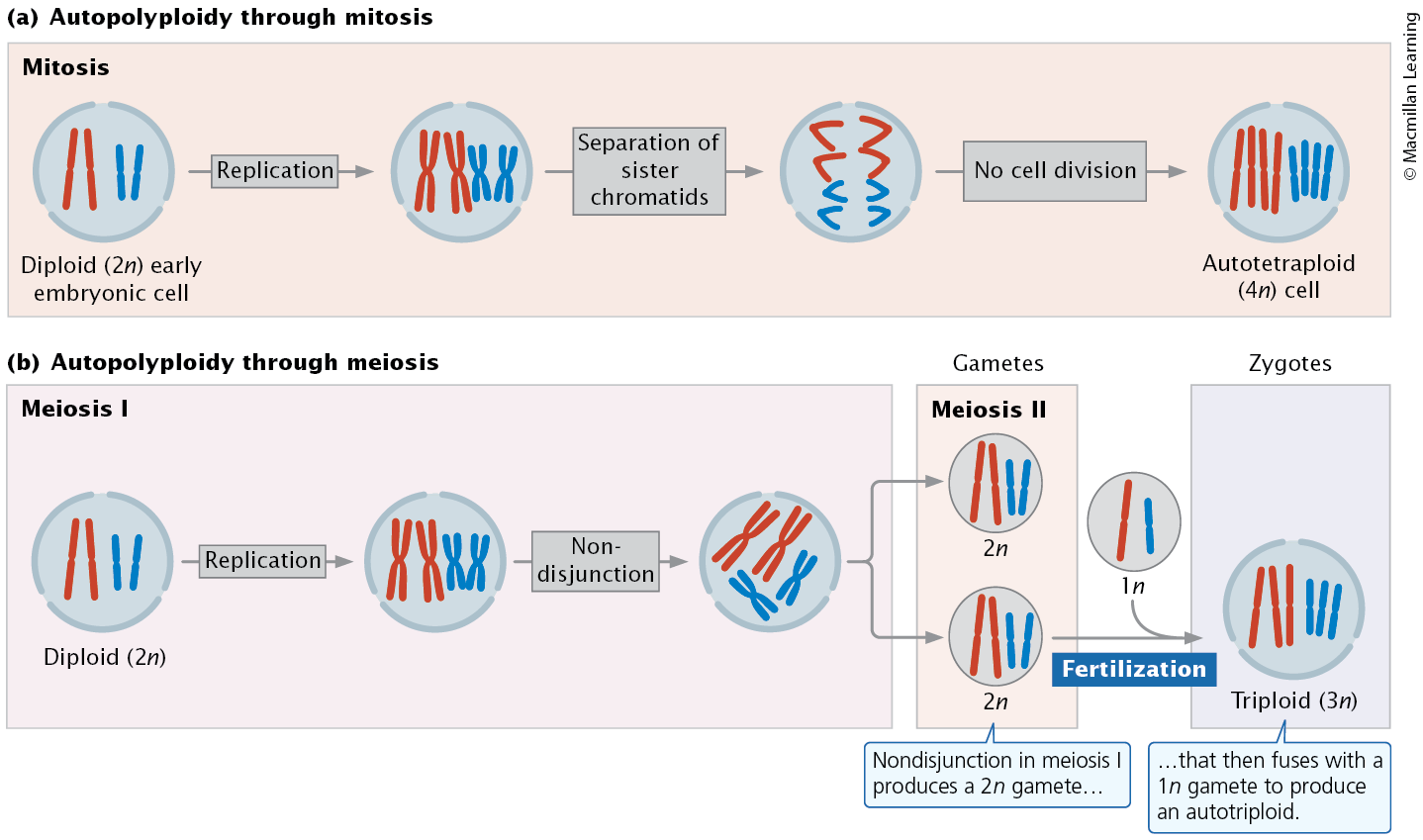
Autopolyploidy
All chromosome sets are from a single species
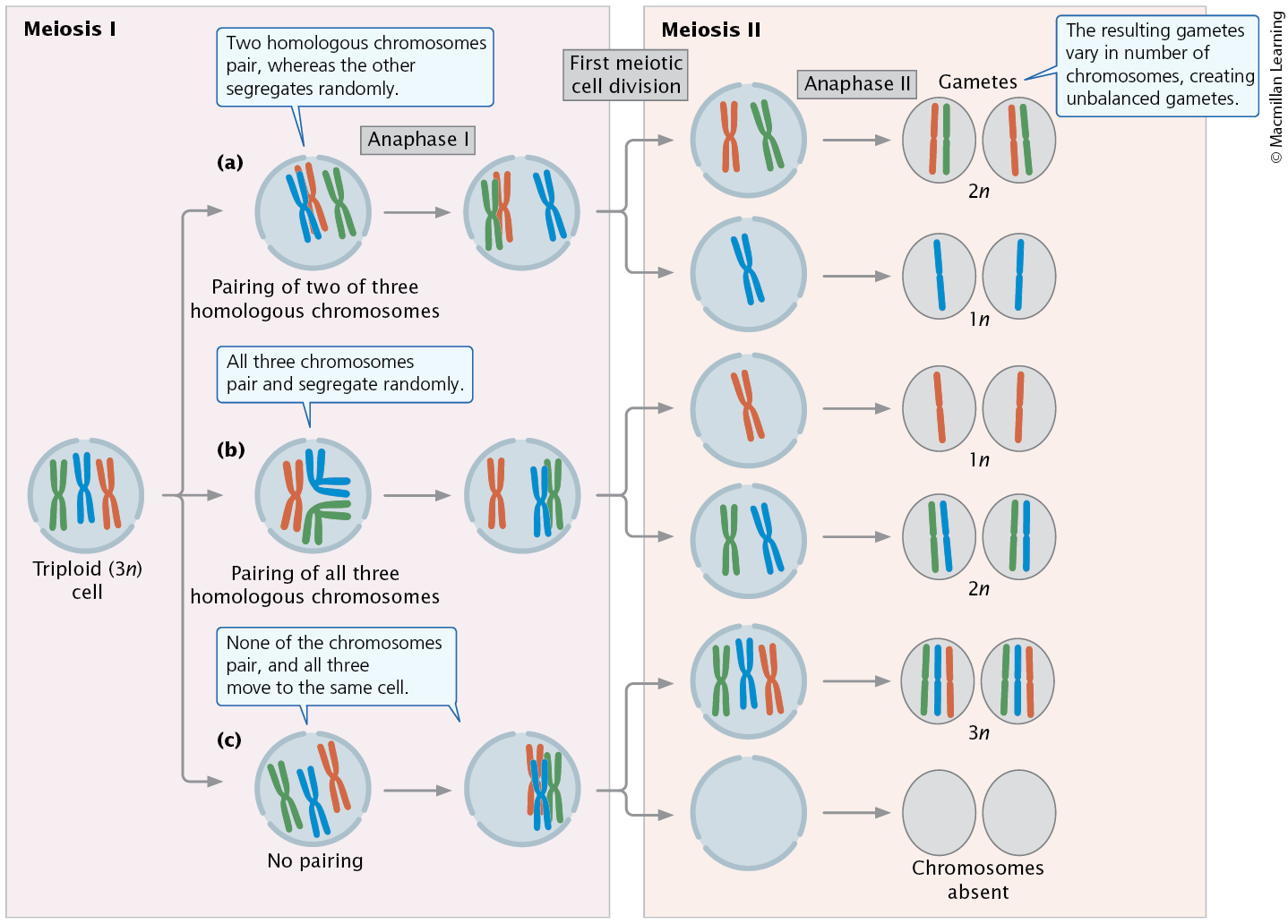
Meiosis in Autopolyploid
In meiosis in an autotriploid, homologous chromosomes can pair, or fail to pair, in three ways. This example illustrates the pairing and segregation of a single homologous set of chromosomes.
Allopolyploidy
The chromosome sets are from two or more species
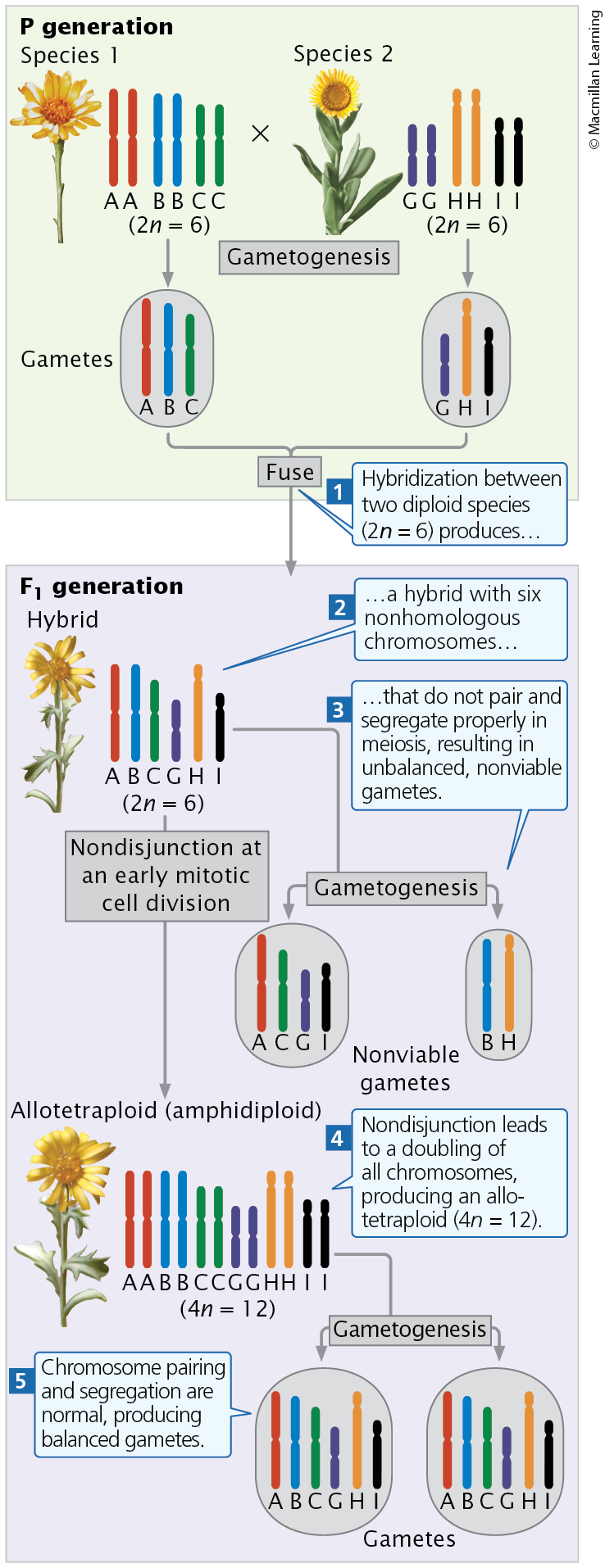
Species A has 2n=16 chromosomes and species B has 2n=14. How many chromosomes would be found in an allotriploid
16 + 7 = 23
14+ 8 = 22
22 or 23