Anaerobic and aerobic respiration
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
anaerobic (definition)
does not require oxygen
aerobic (definition)
requires oxygen
glycolysis
1st step of cellular respiration that does not require oxygen to produce 2 ATP
Cell
Place where 1st step of cellular respiration (glycolysis) occurs
mitochondria
Where cellular respiration occurs
anaerobic respiration (ATP)
Type of respiration that produces 2 ATP
Lactic acid fermentation
A type of anaerobic respiration, undergone by humans and animals
aerobic respiration (ATP)
Type of respiration that produces 32-34 ATP
ethanol (alcohol)
Product of alcohol fermentation that would be used to create adult beverages
Lactic acid
Product of lactic acid fermentation
glucose
Type of sugar needed for aerobic and anaerobic respiration
What process does glycolysis happen in?
occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration
alcohol fermentation (equation)
C6H12O6 → 6CO2 + alcohol + ATP
aerobic respiration (equation)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
anaerobic respiration (alcohol fermentation) (real life connection)
Process that causes grapes to ferment in a sealed barrel to create wine or alcohol
Aerobic respiration (real life connection)
Process that causes humans to breath heavily during exercise.
Glycolysis, the 1st step of cellular respiration does not need oxygen to produce 2 ATP
Reason why anaerobic respiration can produce ATP
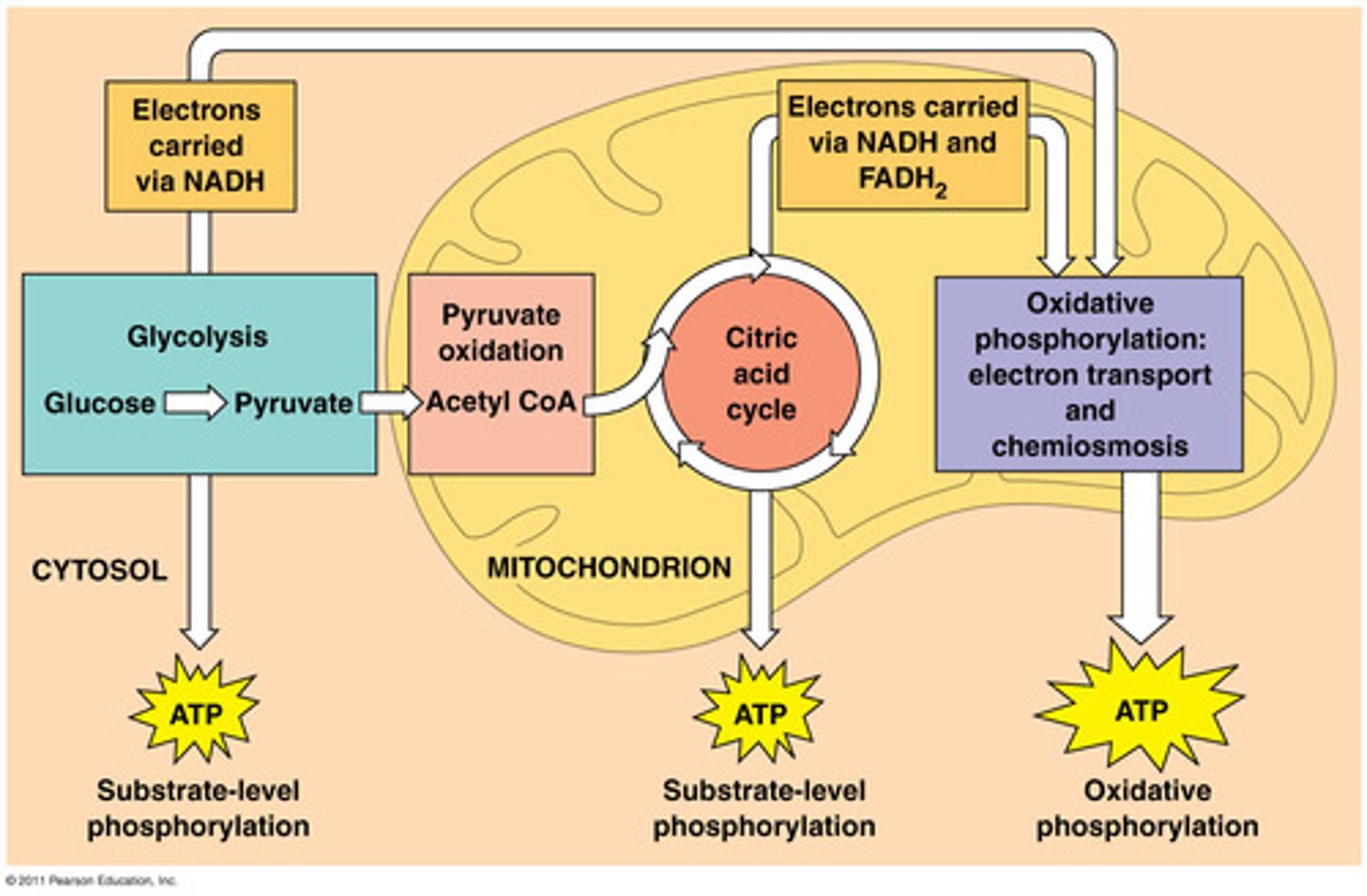
lactic acid fermentation (what happens to body)
Process that causes muscles to burn after overworking/fatigue.
Alcoholic fermentation (definition)
A type of anaerobic respiration, undergone by plants/fungus/bacteria
Carbon Dioxide
A product of anaerobic respiration that was used to raise the bags of yeast.
Digestion
The process in which the body breaks down food into monomers that can be used to make ATP
ATP
Energy source for the cells
Monomer
The smallest form of a macromolecule, like glucose
Small intestine
Place where macromolecules are broken down into monomers, the monomers are absorbed into the blood
Esophagus
Food is transported through this from the mouth to the stomach
Mouth
Chemical and mechanical reactions occur here to help break down the food into digestible and swallowable chunks
Saliva
A chemical reaction in the mouth that helps to break down food
Large Intestine
Absorbs water and transports waste
Stomach
Uses chemical and mechanical processes to break down food into macromolecules which are then transported to the small intenstine
Enzymes
Help to speed up reactions and the breakdown of food in the stomach, mouth and small intestine
Water
A by-product of cellular respiration that is replaced by alcohol in anaerobic respiration processes
Chemical Energy
The type of energy plants and trees convert sunlight into
Mechanical Energy
The type of energy that allows us to move!