Invertebrate Biology: Phyla Overview and Characteristics
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What is the body plan of sponges in Phylum Porifera?
Sponges have no true tissue layers or organ systems, consisting only of a mesophyll layer and an epidermis.
How do sponges feed?
Sponges are filter feeders; they absorb nutrients from water that circulates through their bodies.
What specialized cell in sponges contains a flagella for water circulation?
Collar cells (choanocytes) contain a flagella that causes water to circulate through the sponge.

What are spicules in sponges?
Spicules are spike-shaped structures made of calcium carbonate or silica that provide structural support to the sponge.
What is the function of amoebocytes in sponges?
Amoebocytes (archaeocytes) can move within the mesophyll layer, make spicules, and digest food particles absorbed by collar cells.
What type of body symmetry do flatworms in Phylum Platyhelminthes exhibit?
Flatworms exhibit bilateral symmetry.
What are the three main types of flatworms?
The three main types are planarians (free-living), flukes (parasitic), and tapeworms (parasitic).
How do planarians feed?
Planarians are free-living flatworms that feed on dead organic matter or tiny aquatic animals through a single opening.
What is the reproductive strategy of flatworms?
Flatworms can reproduce sexually as hermaphrodites or asexually through fragmentation or binary fission.
What is the function of the scolex in tapeworms?
The scolex is the head of a tapeworm that contains hooks and suckers for attachment to the intestinal wall of the host.
What are proglottids in tapeworms?
Proglottids are segments of the tapeworm that contain male and female anatomy, where fertilization occurs.
What is the body plan of hydra in Phylum Cnidaria?
Hydra has a polyp shape with a mouth on the dorsal surface and tentacles pointing upward.
How do cnidarians capture their prey?
Cnidarians use tentacles with cnidocytes that contain nematocysts to kill or paralyze prey.
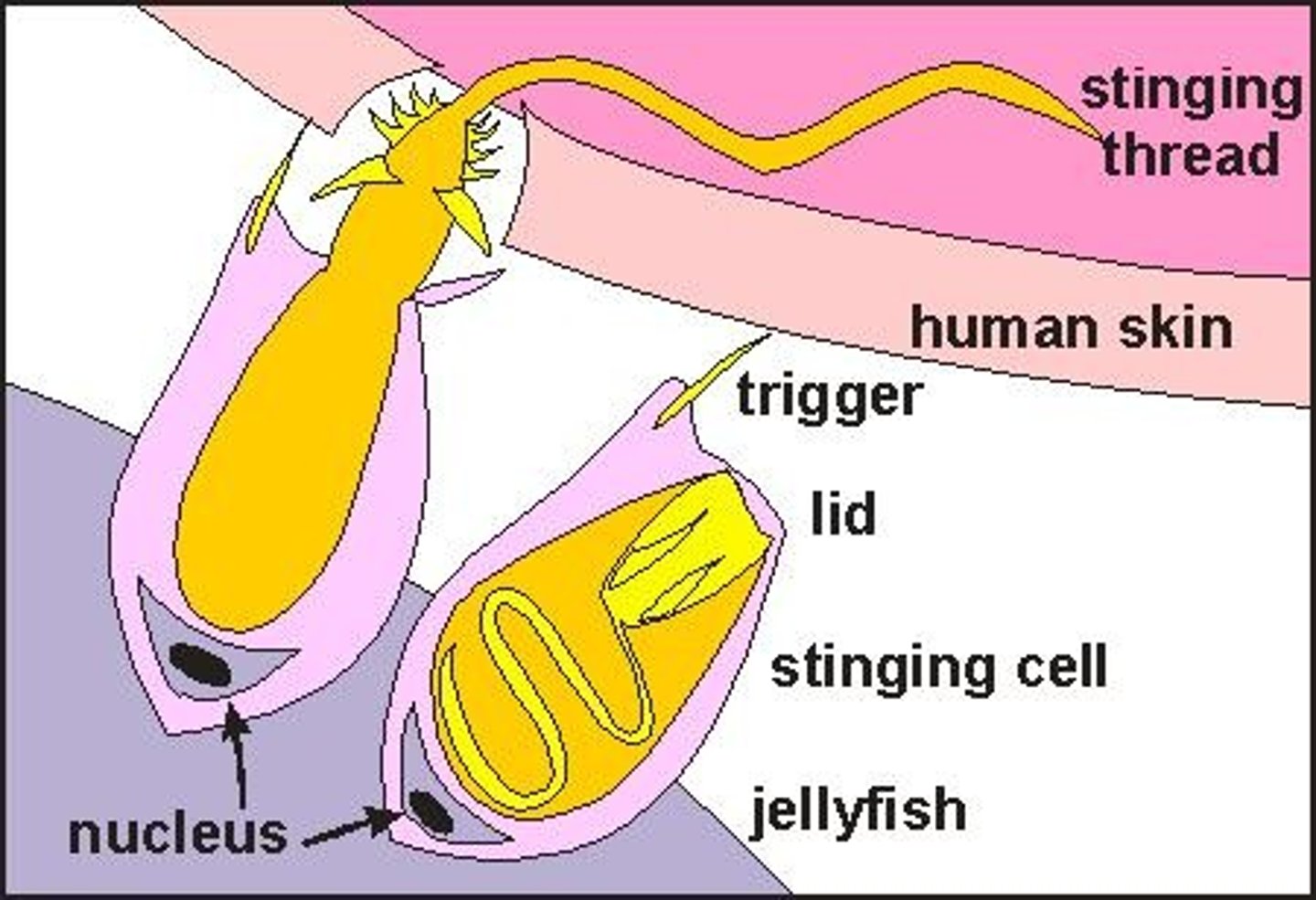
What is a hydrostatic skeleton?
A hydrostatic skeleton is a fluid-filled cavity that provides internal support for cnidarians.
What is the function of eyespots in flatworms?
Eyespots in flatworms can sense light but do not distinguish shapes or images.
What is the digestive system structure of cnidarians?
Cnidarians have a gastric cavity with one opening for both food intake and waste expulsion.
What is the habitat of flatworms?
Flatworms can be found in both aquatic and terrestrial environments.
What is the significance of cephalization in flatworms?
Cephalization refers to the concentration of sensory organs at the anterior end, indicating a more complex nervous system.
What are nematocysts?
Nematocysts are poison-filled, stinging structures within cnidocytes that are used to capture prey.
What is the role of ganglia in flatworms?
Ganglia are simple groups of nerve cells that control the nervous system in flatworms.
What type of symmetry do cnidarians exhibit?
Cnidarians exhibit radial symmetry.
What is the primary feeding structure of hydra?
The primary feeding structure of hydra is its mouth, located on the dorsal surface.
What is the body shape and mouth orientation of a jellyfish?
Jellyfish have a medusa shape with the mouth on the ventral surface and tentacles pointing downward.
What type of habitat do jellyfish inhabit?
Jellyfish are found in marine habitats.
How do cnidarians reproduce?
Cnidarians can reproduce sexually or asexually; polyps reproduce asexually through budding, while others reproduce sexually through external fertilization.
What is the body plan of roundworms in Phylum Nematoda?
Roundworms are unsegmented with a digestive system that has two openings (mouth and anus) and are pseudocoelomates with bilateral symmetry.
What is the feeding behavior of roundworms?
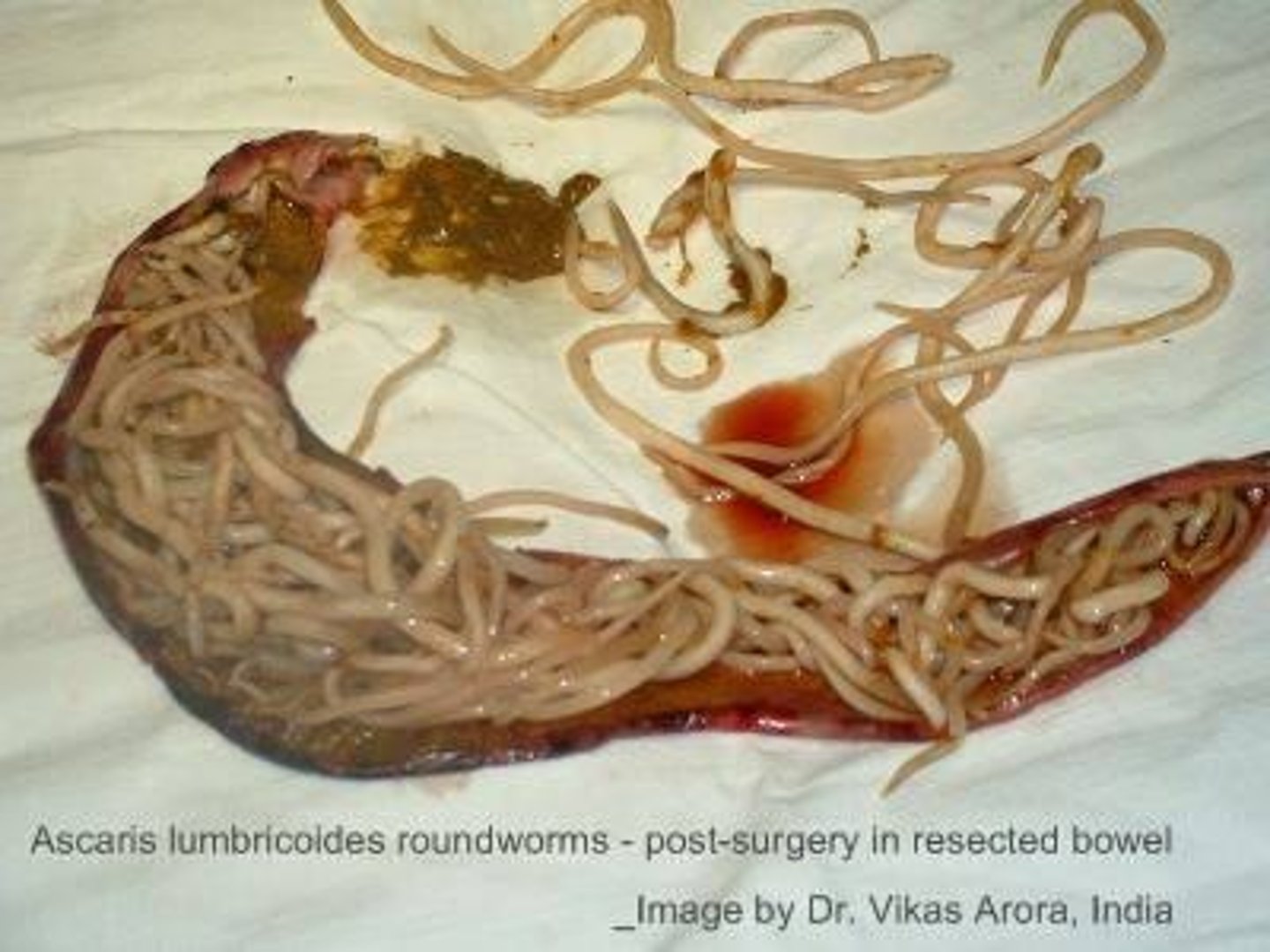
Roundworms can be free-living or parasitic; many are human parasites like Ascaris, pinworms, hookworms, and Trichinella.
What is the life cycle of Ascaris?
Ascaris lives in the intestines of its host, where the female lays eggs that exit the host through feces.
What symptoms do pinworms cause in humans?
Pinworms cause anal itching when they lay eggs around the anus.
How can humans contract Trichinella?
Humans can contract Trichinella by eating undercooked pork infected with the worm.
What is C. elegans and its significance?
C. elegans is a non-parasitic roundworm that feeds on rotten vegetation and is used in genetic research.
What is the body plan of segmented worms in Phylum Annelida?
Segmented worms have a one-way digestive tract with a mouth and anus, and their segments are separated by septa.
What type of digestive cavity do annelids have?
Annelids are coelomates with a tissue-lined, fluid-filled body cavity (coelom).
What is the feeding behavior of earthworms?
Earthworms feed on decaying vegetation and often ingest clay and sand, producing beneficial castings for soil.
How do leeches feed?
Leeches are external parasites that use razor-sharp jaws or a proboscis to make incisions in hosts and feed on their blood.
What is the habitat of annelids?
Annelids are found in both terrestrial and aquatic environments.
How do annelids reproduce?
Annelids reproduce sexually, and some are hermaphrodites that must swap gametes with another annelid.
What is the function of nephridia in annelids?
Nephridia are tubes used by annelids to excrete liquid waste.
What is the body plan of mollusks in Phylum Mollusca?
Mollusks have a soft body, and most have a shell, either external or internal.
What is the defining characteristic of gastropods?
Gastropods are shell-less or single-shelled mollusks that move using a muscular foot located on the ventral side.
What is the role of the clitellum in annelids?
The clitellum secretes a mucous covering for gamete release and fertilization.
What type of symmetry do roundworms exhibit?
Roundworms exhibit bilateral symmetry.
What is a hydrostatic skeleton?
A hydrostatic skeleton is a fluid-filled cavity that provides internal support.
What is the function of the muscular foot in gastropods?
The muscular foot produces slime that enables gastropods to glide more easily across their terrain.
What type of symmetry do gastropods exhibit?
Gastropods have bilateral symmetry.
What is the mantle in mollusks?
The mantle is the soft outer layer of their bodies that secretes the shell.
What is the visceral mass in mollusks?
The visceral mass contains the internal organs of the mollusk.
What feeding strategies do gastropods employ?
Gastropods can be herbivores, carnivores, filter feeders, scavengers, or parasites.
What is the radula and its function in gastropods?
The radula is a tongue-like organ covered with tiny teeth used for scraping algae or tearing apart prey.
What specialized structure do gastropods use to sense light and movement?
Eye stalks.
What are some examples of gastropods?
Snails, conchs, and slugs.
What is the body plan of bivalves?
Bivalves have two shells held together by powerful muscles and lack bilateral or radial symmetry.
How do bivalves feed?
Bivalves are filter feeders that use their gills to obtain oxygen and trap food particles from the water.
What unique ability do certain bivalves have?
Certain bivalves, such as oysters, can make pearls.
What initiates pearl formation in bivalves?
Pearl formation begins when a foreign object lodges between the mantle and the shell.
What is the body plan of cephalopods?
Cephalopods have soft bodies with a head attached to a single foot that is divided into tentacles or arms.
What are some examples of cephalopods?
Squid, octopus, and nautilus.
What specialized structures do cephalopods have for camouflage?
Chromatophores enable cephalopods to change skin color to blend into their environment.
What is the function of ink sacs in cephalopods?
Ink sacs release ink to create a smoke screen when threatened by predators.
What is the body plan of arthropods?
Arthropods are segmented invertebrates with joined appendages and an exoskeleton.
What is the composition of the exoskeleton in arthropods?
The exoskeleton is a hard outer covering made of chitin.
What is molting in arthropods?
Molting is the process by which arthropods shed their exoskeleton to grow.
What are the two main body sections of crustaceans?
Crustaceans typically have a cephalothorax (fused head and thorax) and an abdomen.
What are chelipeds in crustaceans?
Chelipeds are the front legs attached to the cephalothorax, typically functioning as claws.
What is the function of swimmerets in aquatic crustaceans?
Swimmerets aid in swimming.
What types of feeding habits do crustaceans exhibit?
Crustaceans can be scavengers, herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores.
Where do crustaceans primarily live?
Crustaceans are primarily aquatic, but some, like the pill bug, live on land in damp areas.
Name three examples of crustaceans.
Examples include shrimp, crayfish, and lobster.
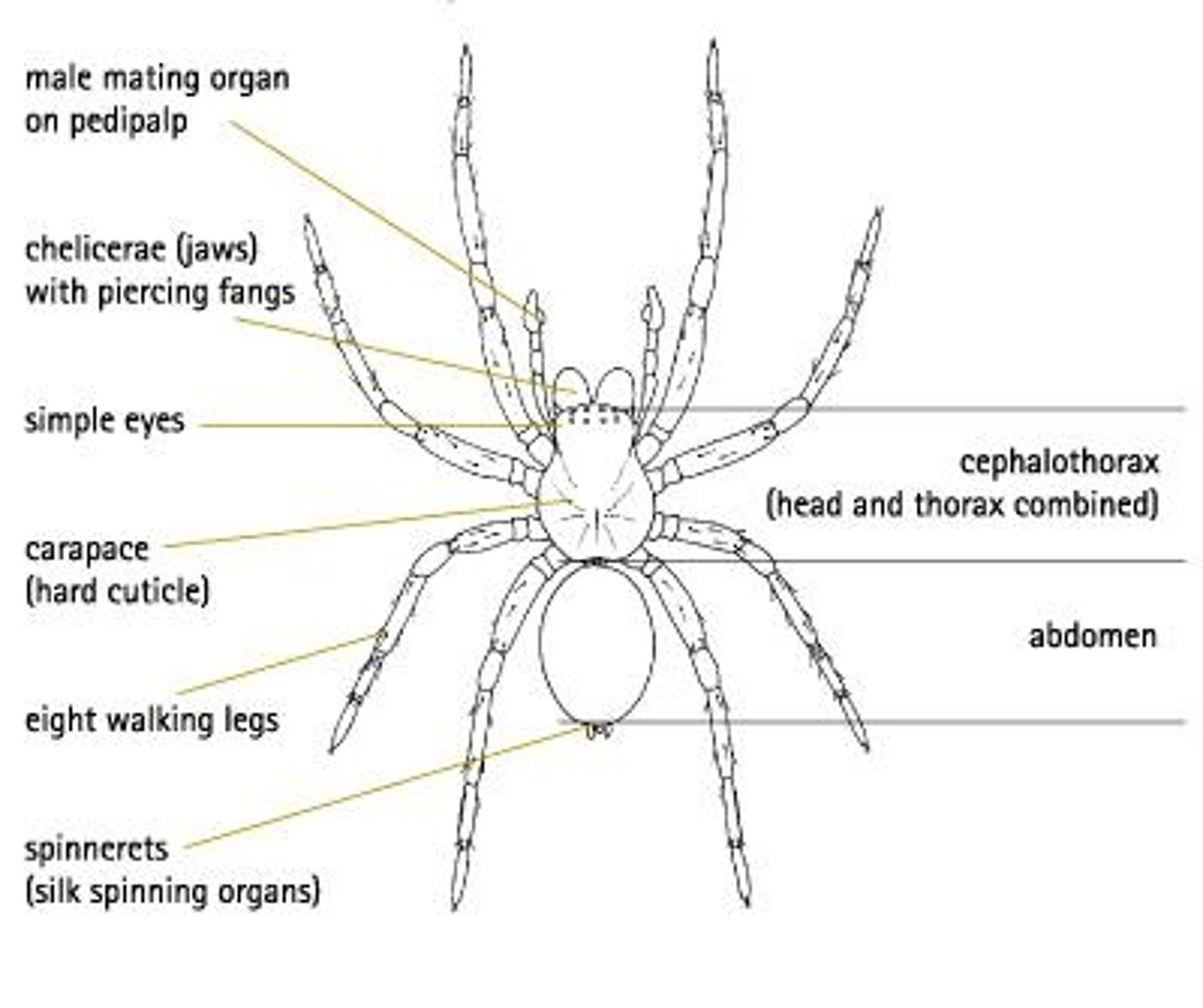
What are the two body sections of arachnids?
Arachnids have a cephalothorax and an abdomen.
What are chelicerae and their function in arachnids?
Chelicerae are mouth parts with fangs used to stab and paralyze prey.
How many legs do most arachnids have?
Most arachnids have 8 legs.
What is the feeding method of most arachnids?
Most arachnids are parasites or predators; spiders liquefy prey with digestive enzymes.
What specialized organ do spiders use to spin webs?
Spinnerets are organs that contain silk glands found at the end of the abdomen.
What is the body plan of insects?
Insects have 3 body segments: head, thorax, and abdomen, with compound eyes and six legs.
What types of feeding habits do insects exhibit?
Insects can be herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, or scavengers.
What is metamorphosis in insects?
Metamorphosis is a series of changes during which larvae become adults, with complete and incomplete types.
What distinguishes complete metamorphosis from incomplete metamorphosis?
In complete metamorphosis, larvae look completely different from adults and go through a pupal stage; in incomplete metamorphosis, larvae resemble smaller versions of adults.
What is the body plan of echinoderms?
Echinoderms are spiny-skinned coelomates with an internal skeleton and radial symmetry.
How do echinoderms move?
Echinoderms move using a water vascular system, which is a network of water-filled tubes.
What is the feeding method of predatory echinoderms?
Predatory echinoderms use tube feet to pull prey apart and digest it in its shell.
What special ability do sea cucumbers have when threatened?
Sea cucumbers can shoot out long, thin tubules or their entire digestive system to entangle or distract predators.
Name two examples of echinoderms.
Examples include starfish and sea urchins.
What is the habitat of echinoderms?
Echinoderms are primarily aquatic.
What are the specialized mouthparts of insects designed for?
Insects have specialized mouthparts for specific functions, such as mandibles for grinding food or proboscis for sucking nectar.
What is the role of the thorax in insects?
The thorax contains the legs and wings of insects.
What is the function of the abdomen in insects?
The abdomen contains the reproductive, respiratory, and excretory systems.
What are pedipalps in arachnids?
Pedipalps are the first pair of appendages used to grab prey.
What is the significance of bilateral symmetry in these animal groups?
Bilateral symmetry indicates that these animals have a symmetrical body plan, which is common among coelomates.