Microbio: Bacteriology pt.2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Average size of prok. bacteria
0.2—>2.00 μm
3 basic shapes of bacteria
Spherical (round), Rod-Like, Spiral
Coccus (Spherical Bacterium)

Bacillus (Rod-Like)

Coccobacilli (shirt rod)

Comma shape/Vibrio

Spirillum pl.spirilla (rigid wavy)
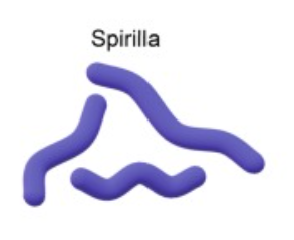
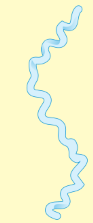
Spirochete (Corkscrew shape)
Monomorphic (Most bacteria are monomorphic)
Bacteria that keep one consistent shape (don’t change form).
Pleomorphic
Bacteria that can change shape or size depending on conditions (environment, age, or stress).
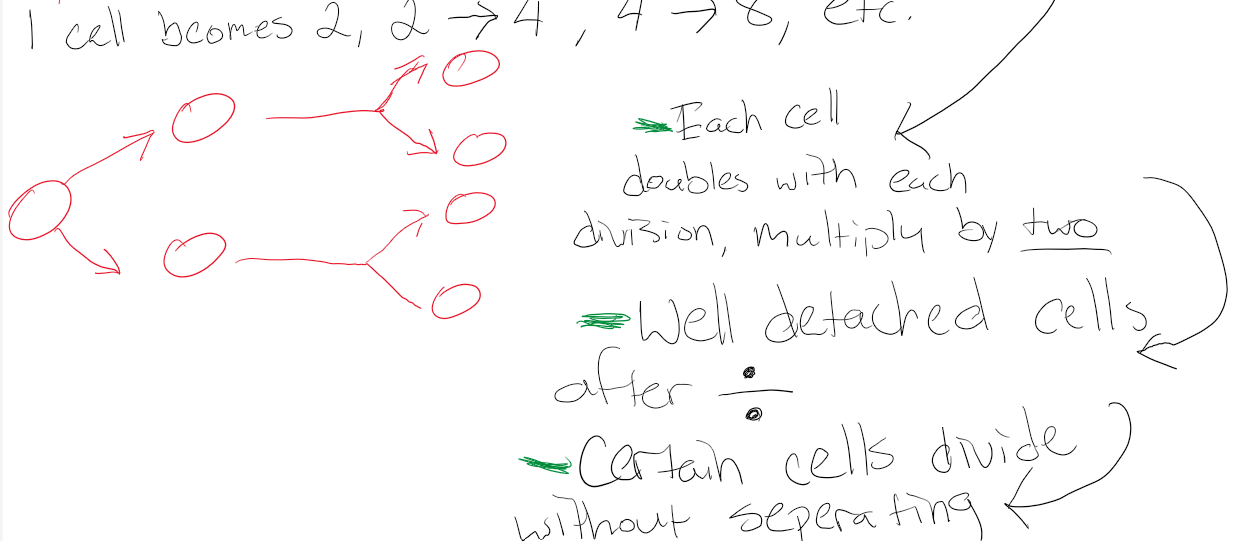
Binary Fission
Division and Multiplication amongst Prokaryotes
Diplococcus
Groups of 2

Streptococcus
Chainlike formation

Tetrod
Group of 4; undetached cells

Sancinal
Group of 8; undetached cells

Staphylocacci
Group like function; Numerous groups
Appendage of Prok. cells
Outermost/external part
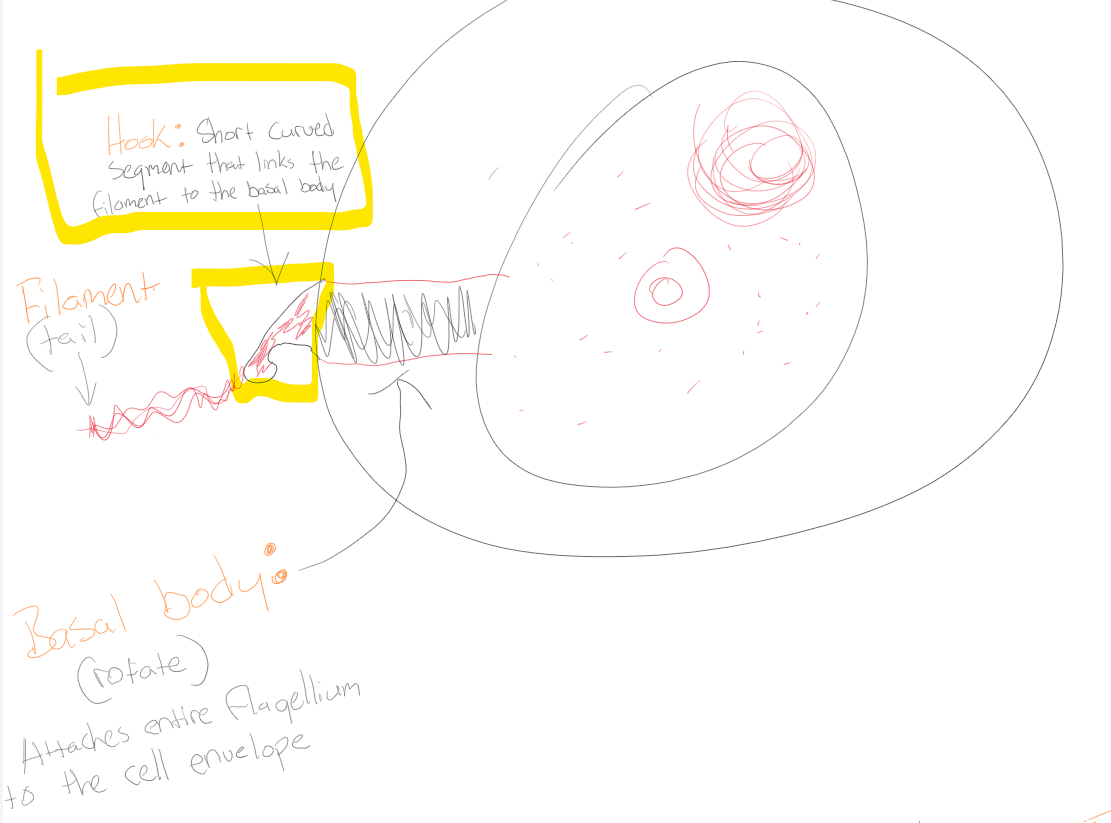
Hook
Short curved segment that links the filament to the basal body
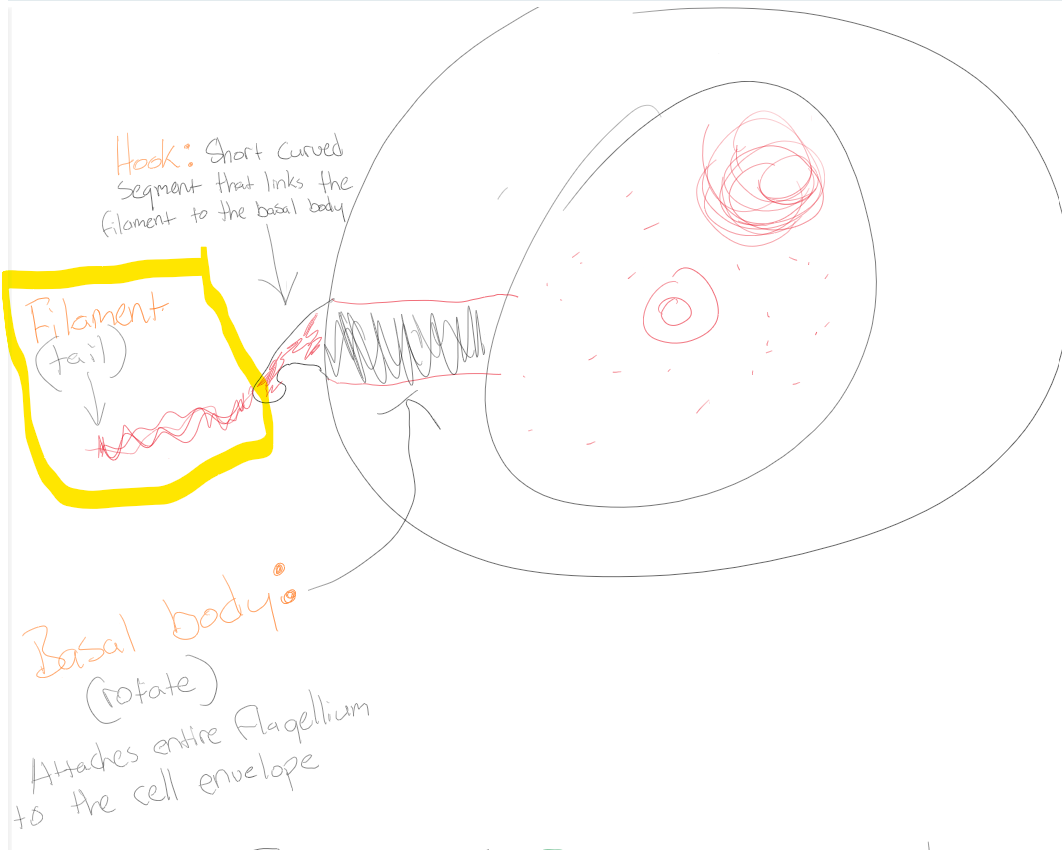
Filament
Tail
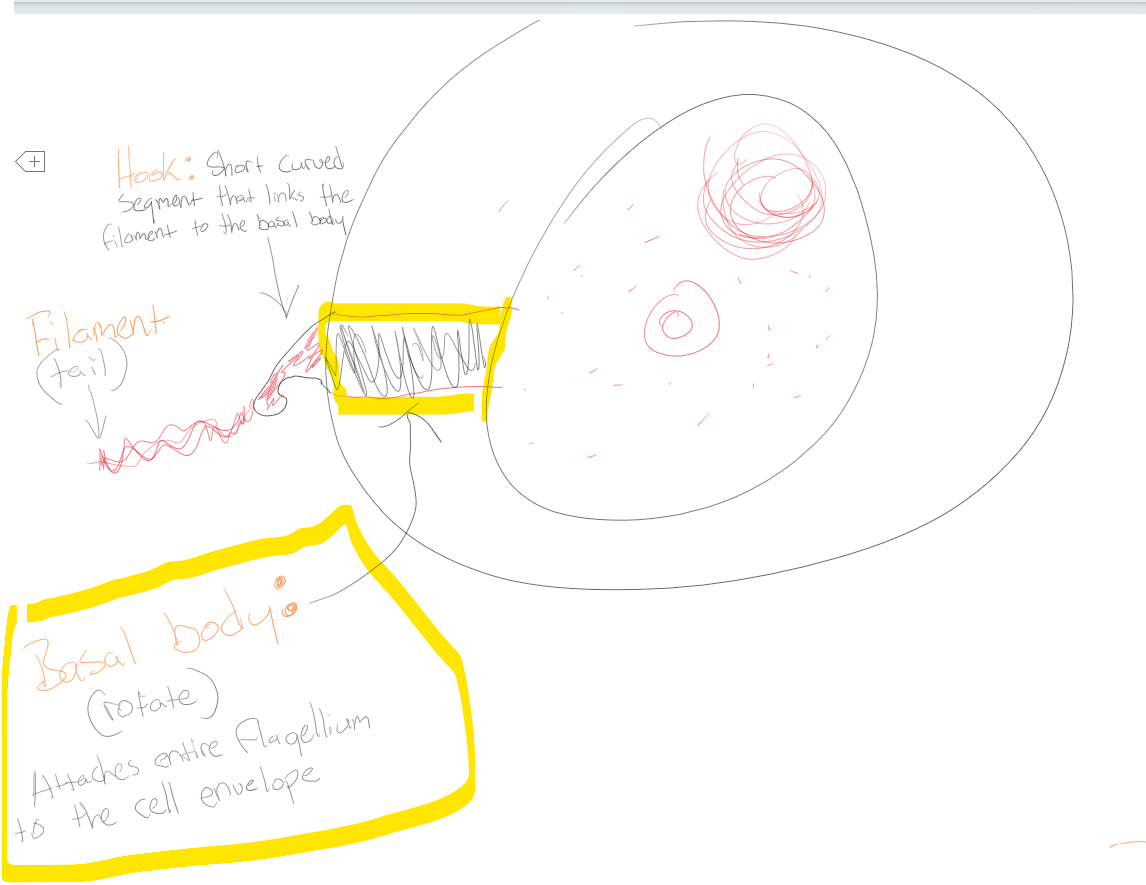
Basal body
Attaches entire flagellum to the cell envelope
Atrichous Bacteria
Bacterial devoid without flagellum

Monotrichous
One flagellum (mono=1)

Amphitrichous
1 flagellum at both poles (Amphi= both poles)

Lophotrichous
Cluster of flagella at one end or both side (Lopho=cluster)

Peritrichous
Flagella are spread evenly around the cell (Peri=around)

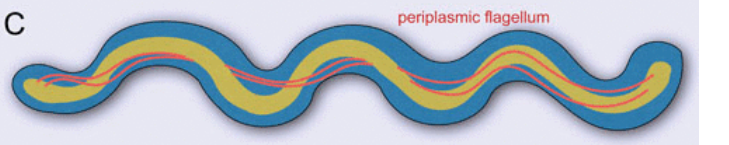
Periplasmic/Endo-flagella
Flagella wraps around cell (associated with spirochete)

Pilus/pl. Pili
Short, fine, hair-like appendages. Not associated with locomotion (movement). (aprx.1000 pili per cell)
2 types of Pili
Attachment (Fimbriae) & Sex/Conjugation
Attachment (Fimbriae) Pili
Adhesion to surfaces
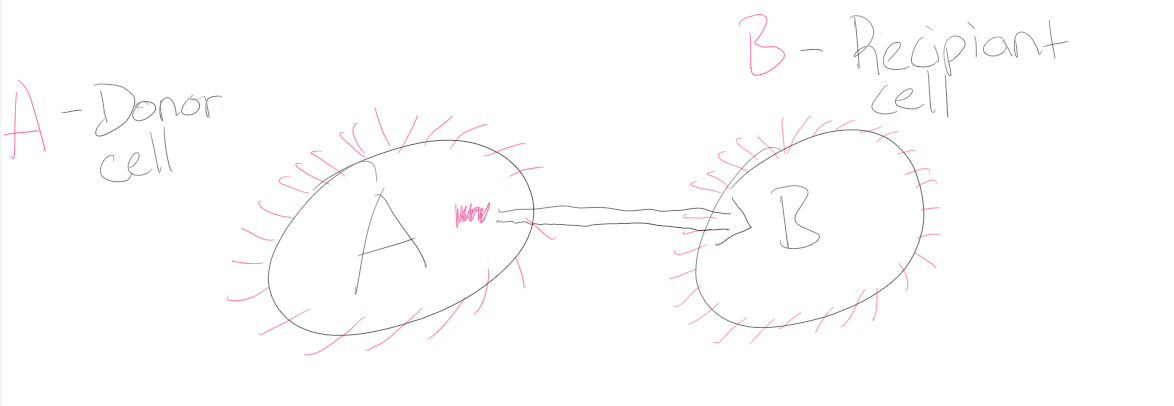
Sex/Conjugation Pili
Helps bacteria exchange genetic material (DNA) from cell A (Donor cell)—>B (Recipiant)
Cell envelope
All the layers that surround the cytoplasm of a bacterial cell (membrane(s) + cell wall).
Glycocalyx
Polysaccharide sugar coat lying outside of cell wall (2 types: Capsule & Slime layers)
Capsule
(Thick armor) Organized, not washed off easily and Protects bacteria from phagocytosis
Slime layer
(Sticky glue) Loose unorganized, easily washed off. Helps with attachment to surfaces
Phagocytosis
A process where a cell (phagocytes) engulfs and digests particles, such as bacteria.
Cell wall
A rigid layer that lies outside the plasma (cytoplasmic) membrane. Provides shape and protection for the cell. Site for antibiotics. peptidoglycan
Osmotic Lysis
Cell bursting from too much water (hypotonic)
Gram stain
To classify bacteria as Gram-positive or Gram-negative based on cell wall structure (peptidoglycan thickness).
Gram positive (q+)
Bacteria stained purple or blue; Thicker peptidoglycan layer; Teichoic acid & Lipoteichoic acid
Gram negative (q-)
Bacteria stained red or pink; Thinner peptidoglycan layer; Outer membrane
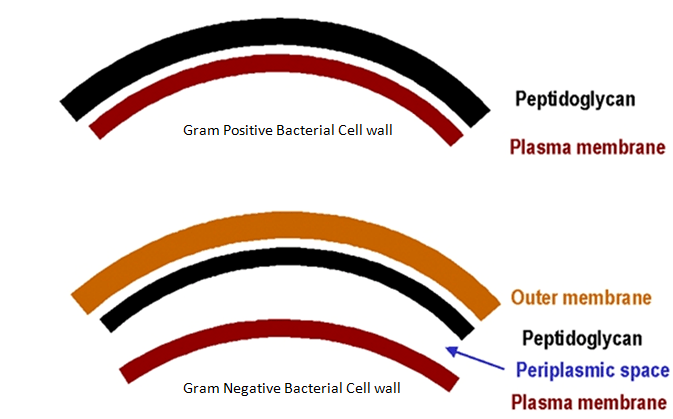
Periplasmic Space
Location between plasma membrane and the outer membrane fluid in the periplasmic space called periplasm.
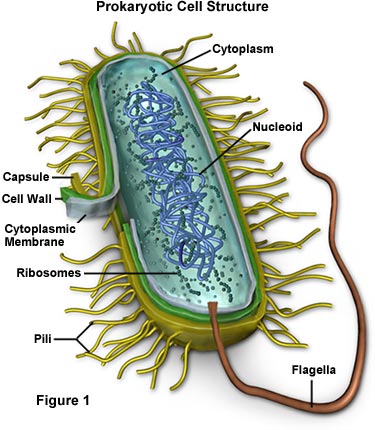
Cytoplasm
Fluid of cell minus chromosome and plasmid. Contains everything else (ribosomes, inclusion bodies, minerals, amino acids, sugars, nutrients, proteins/enzymes, various chemicals).
Cytosol
Liquid (solution) of the cell/cytoplasm
Prok. Ribosomes
Associated with protein synthesis and are 70’s (Svedberg-unit of sedimentation)
Single coiled chromosome
Attached to inner lining of plasma membrane; Contains 4,000 genes avg.
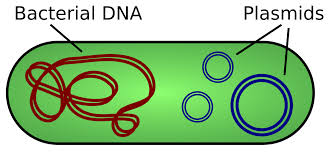
Plasmid
Circular autonomously replicating DNA contain 5-100 genes, some which code for antibiotics, conjugation, and toxic production.
Inclusion bodies (Granules)
Reserve deposits in the cytoplasm of Prok. Bacteria. Non-living chemical compounds and byproducts of cellular metabolism.
Metachromatic Granules
Large inclusions, collectively known as Volutin, representing a reserve of Inorganic Phosphate used in Membrane Phospholipids, ATP and DNA/RNA synthesis.
Polysaccharide Granules
Starch and glycogen, both are polymer (chain) or glucose molecule
Lipid Inclusions
Indispensable (important) in the foundation of cell membrane (phospholipids)
Sulfur Granule
Important in synthesis of certain amino acids to form proteins.
Carboxysomes
Associated with bacteria that “fix carbon” such as photosynthetic bacteria and nitrogen fixing bacteria.
Magnetosomes
Inclusions of Iron Oxide (Fe₃O₄). Bacteria use magnetosome to move downward until they find an attachment site at the bottom of shallow lakes. (Acts as magnets)
Gas Vacuole
Provides buoyancy to bacteria to head to surface for photosynthesizing (autotrophs)
Lysozymes
An enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls by cutting the bonds in peptidoglycan (glycosidic). Found in tears, saliva, mucus, and sweat
Glycosidic Bonds
Connect glucose derivatives NAM and NAG
Transpeptide bridge
A short chain of amino acids that links one peptidoglycan chain (NAM-tetrapeptide) to another, giving the cell wall strength and rigidity.
Transpeptidase
Bacterial enzyme manufactures or synthesizes transpeptide.
What interferes with making of Transpeptidase?
Penicillin
What enzyme breaks apart penicillin?
Penicillinase