Exam 2 study guide
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology
norris
kennedy norris
JSU
cells
cell theory
prokaryote
prokaryotic
eukaryote
eukaryotic
ribosomes
bacteria
endomembrane system
cell junctions
metabolism
energy
types of energy
energy types
autotrophs
heterotrophs
consumers
producers
thermodynamics
proteins
photosynthesis
sunlight
light dependent reactions
light independent reactions
cell respiration
cellular respiration
aerobic cellular respiration
anaerobic cellular respiration
University/Undergrad
Last updated 4:18 PM on 11/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
3 basic parts of the cell
cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm
2
New cards
principles of cell theory
all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, cells arise from pre-existing cells, hereditary info is passed from cell, all cells have basic chemical composition, energy flow occurs within cells
3
New cards
cell membrane
Separates insides of cell from the outside environment. Dictates what passes through the cell
4
New cards
defining characteristic for difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotes don’t have a nucleus, eukaryotes do have a nucleus
5
New cards
this type of cell HAS a nucleus
eukaryotic
6
New cards
this type of cell does NOT have a nucleus
prokaryotic
7
New cards
ribosome function
synthesize proteins
8
New cards
structure used during bacterial conjugation
pili
9
New cards
know these structures:
cell membrane, nucleoid, flagella
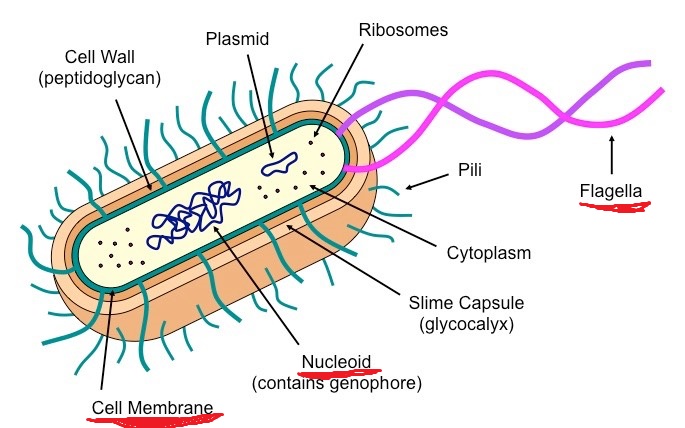
10
New cards
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
Father of Microbiology. discovered cells with microscope
11
New cards
function of the endomembrane system
modifies, transports, and packages proteins and lipids in the cell
12
New cards
cell junctions found in animal cells
tight junctions, adhering junctions, gap junctions
13
New cards
cell junctions found in plant cells
plasmodesmata
14
New cards
tight junctions
fasten cell membranes of adjacent cells together, keep bodily fluid contained
15
New cards
adhering junctions
make up cardiac muscles and skin
16
New cards
gap junctions
closable channels between cells; let substances flow quickly between cells
17
New cards
plasmodesmata
open channels between cytoplasm of two cells, similar to gap junction in animal cells.
18
New cards
what are the different structures cells use to move
motor proteins, cilia, pseudopods
19
New cards
exocytosis
moving something inside the cell to the outside. movement of vesicles and their content outside of the cell
20
New cards
ATP
cell currency, produces energy
21
New cards
chemical energy
energy stored in chemical bonds
22
New cards
kinetic energy
the energy of motion; type of energy associated with movement
23
New cards
potential energy
stored energy related to something's position
24
New cards
autotrophs
make own food using the sun's energy; producers
25
New cards
heterotrophs
doesn't make own food, eats others for energy; consumers
26
New cards
first 2 laws of thermodynamics
1: energy can't be created or destroyed
2: energy tends to disperse
2: energy tends to disperse
27
New cards
exergonic reactions
energy releasing, spontaneous
28
New cards
endergonic reactions
energy consuming; need energy
29
New cards
catabolism
destroys; uses and produces energy
30
New cards
anabolism
builds; uses energy
31
New cards
metabolism
chemical reaction in body's cells that change food into energy
32
New cards
energy
ability to do work; ability to cause some kind of change
33
New cards
activation energy
minimum amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
34
New cards
enzymes are..
reusable
35
New cards
coenzymes are..
not reusable
36
New cards
where does catalysis occur on enzymes
the active site
37
New cards
difference between linear and cyclic pathways
linear reactions happen in order and stop. cyclic reactions happen in order and the last one restarts the reaction chain
38
New cards
receptor proteins
Trigger change in cellular activity in response to stimuli
39
New cards
adhesion proteins
Fasten cell’s membranes together
40
New cards
transport proteins
Transports substances across lipid bilayer
41
New cards
enzymes
Catalyzes reactions at membrane
42
New cards
active use of transport proteins
requires energy to move across cell membrane, goes against gradient differences
43
New cards
passive use of transport proteins
doesn't require input to happen
44
New cards
phosphorylation
donates phosphate group to enzyme which donates to reaction
45
New cards
diffusion
spontaneous spreading of molecules or atoms through a fluid or gas
46
New cards
catalysis
speeds up reactions
47
New cards
osmosis
the movement of fluid across membranes
48
New cards
where does photosynthesis occur in eukaryotic cells?
chloroplasts, thylakoid, stroma
49
New cards
visible light
light with a wavelength of 380-750nm
50
New cards
different colors come from..
different wavelengths of light
51
New cards
photon energy is () to wavelength
inverse
52
New cards
what pigment gives plants their green color
chlorophyll a
53
New cards
photon
a particle of light
54
New cards
Theodor Engelmann
Discovered sunlight is driver for photosynthesis, hypothesized color of light affects photosynthesis; blue and red are best for driving photosynthesis
55
New cards
where do light dependent reactions take place?
the thylakoid membrane
56
New cards
cyclic light dependent reactions use..
PSI
57
New cards
noncyclic light dependent reactions use..
PSI and PSII
58
New cards
what flows through the ATP synthase to trigger phosphorylation
H+ ; hydrogen ions
59
New cards
products of cyclic light dependent reactions
ATP
60
New cards
products of noncyclic light dependent reactions
ATP, NADPH, Oxygen
61
New cards
carbon fixation
taking carbon atoms from inorganic molecules (CO₂) to attach them to organic molecules (sugar)
62
New cards
products of light independent reactions
sugars (glucose)
63
New cards
where do light independent reactions occur
stroma
64
New cards
this enzyme starts the Calvin Cycle (light independent reactions)
rubisco
65
New cards
most molecules of PGAL are () back into the Calvin Cycle
recycled
66
New cards
C3 Plants
fix carbon by the calvin cycle. 85% of modern plants. produces CO2 and ammonia during photorespiration
67
New cards
C4 Plants
fix carbon twice. 3% of modern plants. minimizes photorespiration
68
New cards
CAM Plants
fix carbon twice. stomata open at night, conserve water, desert plants. 12% of modern plants
69
New cards
carbon dioxide is a ( ) of photosynthesis [product or reactant]
reactant
70
New cards
DNA is stored here in eukaryotic cells
nucleus
71
New cards
what structure do photosynthetic eukaryotes NOT use during photosynthesis
cytoplasm
72
New cards
T/F photons with high energy will have longer wavelengths
False
73
New cards
the transport protein ATP synthase using what to activate and attach a phosphate group to make ATP?
hydrogen ions
74
New cards
this type of plant only uses the basic steps of the calvin cycle (only fixes carbon once)
C3 Plants
75
New cards
how did oxygen negatively affect the Earth
it was toxic, it polluted the air
76
New cards
Great Oxidation Event
killed off most anaerobic life, triggered an ice age, gave rise to multicellularity.
77
New cards
oxidative stress
Free radicals accumulating and stopping the mitochondria from functioning, damages tissues.
78
New cards
aerobic
can live in the presence of oxygen
79
New cards
anaerobic
without oxygen
80
New cards
antioxidants
minimizes damages caused by oxygen
81
New cards
glycolysis
this process happens in the cytoplasm
82
New cards
glycolysis produces..
ATP by converting glucose to pyruvate
83
New cards
what does oxygen do during electron transfer phosphorylation?
O₂ accepts electrons from transfer chain and other H+. creates H₂O
84
New cards
why is fermentation less efficient than aerobic respiration
It doesn’t fully break down glucose and only produces 2 molecules of ATP vs aerobic respiration producing 36 molecules of ATP