PCR & DNA Polymerase
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
How is DNA concentration measured?
By using a spectrophotometer with a tube containing
Water + DNA
What wavelength is used to measure DNA concentration when using a spectrophotometer
260 nm
What is PCR?
Polymerase Chain Reaction — it is a technique that amplifies a specific region of DNA around 100 bp to 6kb to create many copies for analysis
What types of analysis can be done with PCR?
RFLP
VNTR
DNA Sequencing
qPCR
Why is PCR useful?
It allows for the amplification of a specific DNA region for a detailed analysis
What are primers in PCR?
Short (15-30 bp) single-stranded DNA molecules that bind to the template DNA to start replication
What is the role of primers in DNA replication
They provide a starting point for DNA polymerase to begin DNA replication
What happens in each PCR cycle?
The DNA amount doubles
1 cycle = 2 DNA copies
2 cycles = 4 DNA copies
3 cycles = 8 DNA copies
7 cycles = 128 DNA copies
What is Taq DNA polymerase and why is it used in PCR?
Taq: Thermophilus Aquaticus
It is an enzyme that withstands HIGH temperatures around 95 degrees Celsius and it can copy DNA strands during replication.
What role does the template DNA play in PCR?
It guides the synthesis of a new complementary strand by matching the correct dNTPs.
What is the purpose of primers in PCR?
They provide a starting point for Taq DNA polymerase to begin DNA synthesis
What are dNTPs?
Deoxy Nucleotide Triphosphates that DNA polymerase added to the growing DNA strand, pairing with complementary bases on the template.
What role does MgCl2 play in PCR?
It stabilizes the DNA structure and acts as a cofactor for Taq Polymerase, helping with binding and elongation
Why is molecular-grade water (mH2O) used in PCR?
It dilutes components and is free from contaminates that could breakdown DNA, RNA, or enzymes. It is a more pure type of water to use
what is the purpose of using a thermocycler in PCR?
It changes temperature to control the melting, annealing, and extension phase in DNA amplification
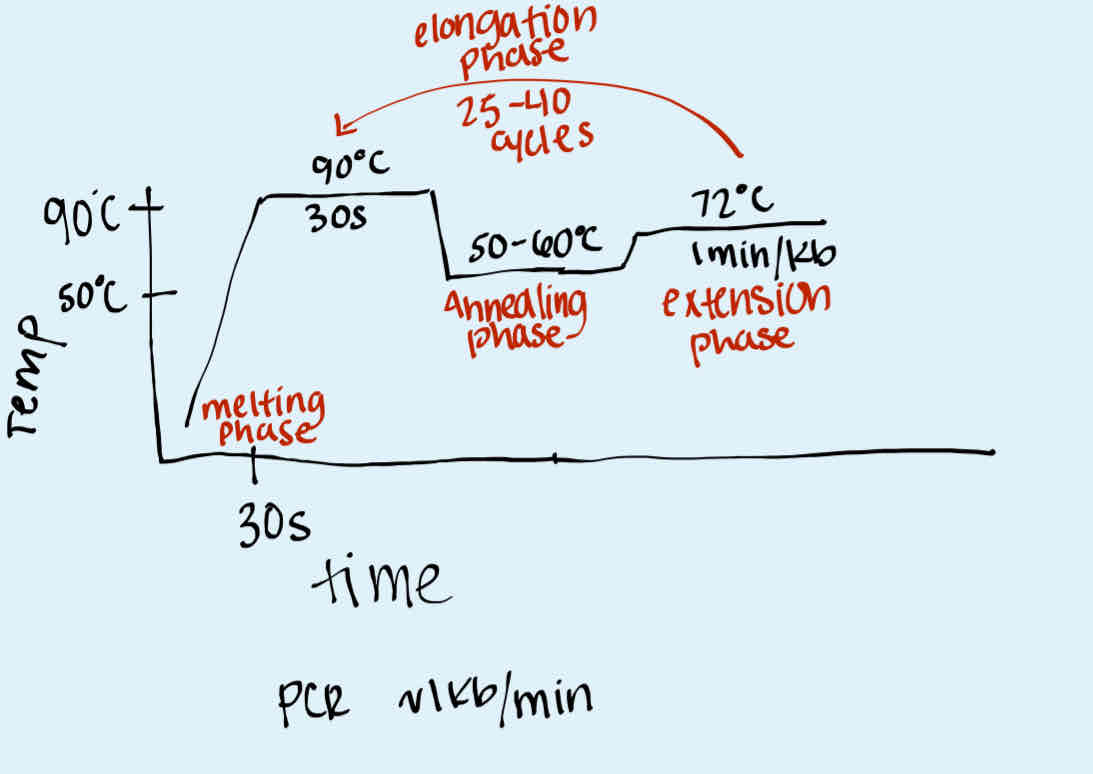
What are the 3 main phases in a thermocycler during PCR along with their temperatures?
Melting phase (~90 degrees Celsius)
Annealing phase (50-60 degrees Celsius)
Extension (Elongation) phase (~72 degrees Celsius)
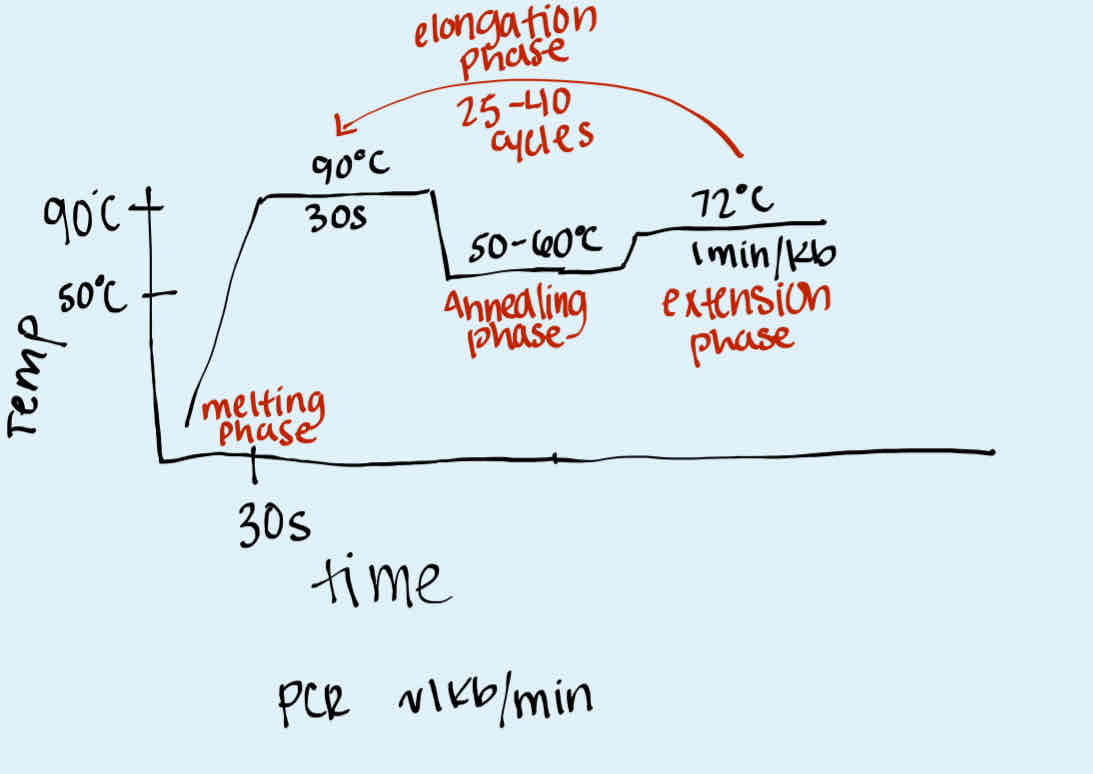
How many times is the PCR cycle repeated in a thermocycler?
Elongation phase: 25-40 times
What does VNTR?
Variable Nucleotide Tandem Repeats is a DNA sequence repeated back-to-back at a specific location in the genome. VNTR differs in length between different individuals.
Why are VNTRs useful in forensics?
They vary between individuals, making them valuable for genetic fingerprints and population genetics
How long are VNTR sequences?
Between 100-1000 bp
How is PCR used with VNTRs?
PCR amplifies VNTRs to create multiple copies for analysis
What is done with VNTRs after PCR amplification?
They are run on a gel to measure the length and count the number of copies to be used for building instruction sets.
What is RFLP
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism - technique that fragments DNA with restriction enzymes and analyzes the pattern on a gel to identify the DNA source.
What information does RFLP analysis provide?
It reveals the location of restriction sites and identifies the DNA source.
Give an example of RFLP analysis
Circular DNA cut with the restriction enzyme EcoRI. It yields a pattern on the gel that indicates the DNA source.
What is a restriction enzyme’s role in RFLP?
It binds a unique DNA pattern and cuts the DNA at a specific site.
What is DNA polymerase in PCR?
The enzyme that replicates DNA by making one copy into two copies in PCR.
Where is the PCR mixture prepared, and what does it contain?
In a test tube with the DNA template + Primers (reactants)
What is a thermocycler’s role in PCR?
It cycles the PCR mixture through specific temperatures to enable DNA amplification
How many times does a PCR cycle repeat in a thermocycler?
20-40 times
What happens in the melting phase of PCR?
Around 30 seconds, DNA separates into single strands
What happens in the annealing phase of PCR?
About 30 seconds, primers bind to their specific sites on the DNA template.
What happens in the extension phase of PCR?
For every 1 minute per 1 kb, DNA polymerase replicates the DNA template
Why are the 2 primers needed in PCR?
To amplify a specific DNA region in both directions.
How do primers help in PCR?
They bind to the edges of a DNA portion, allowing targeted amplification
Why is PCR useful in forensics?
It amplifies LOW quantity DNA samples for analysis. When there is low quantities of DNA collected, it cannot be analyzed because of the low copy amounts so PCR is used to make more copies.
How are PCR products analyzed for size?
By using electrophoresis to view the size of the DNA fragments.
What is the purpose of using restriction enzymes on PCR products?
To cut DNA copies for additional information before electrophoresis
How does VNTR analysis work in electrophoresis?
It creates DNA fragments of different sizes based on the DNA source.
What does qPCR measure?
The number of accumulated DNA copies for more detailed information
What does DNA sequencing reveal in PCR products?
The nucleotide letter sequence of the DNA of interest.
What role do primers and DNA polymerase play in PCR?
Primers bind to the DNA template and DNA polymerase amplifies the sequence between them
How are new DNA templates created in each PCR cycle?
Each cycle uses the DNA copies made in the previous round as templates.
What does PCR reveal about human chromosomes?
It reveals differences between individuals, especially in polymorphic intergenic regions
What does polymorphic mean in DNA analysis
It refers to DNA patterns that are repeated a number of times in a specific region
How does PCR identify polymorphic regions?
By using primers that can amplify tandem repeats in specific regions
How do repeat numbers affect PCR products?
MORE repeats result in LONGER PCR products
What does VNTR analysis show on a gel?
The differences in DNA fragment lengths based on the number of repeats
How many VNTR variations exist globally and within a population
Around 70 globally and about 5 within a population
Why analyze multiple VNTRs to identify individuals?
To create a DNA fingerprint that distinguishes one individual from others.
Why do two bands appear in electrophoresis
One band comes from each parent, showing allele variations
What does a single big band indicate in electrophoresis?
Homozygous alleles (same allele from both parents)
What does two separate bands indicate in electrophoresis?
Heterozygous alleles (different alleles from each parent)
What is the PCR master max solution?
20-50 microliter reaction mixture containing all the components needed for PCR
What components are included in the PCR master mix?
DNA template
dNTPs
MgCl2 buffer,
Primers
Taq DN polymerase
What role do dNTPs play in PCR?
They serve as the building blocks of nucleotides for making DNA copies
Why are primers needed in PCR?
To amplify the DNA by binding to specific regions on the top and bottom strands
What is Taq polymerase’s function in PCR?
It copies DNA by adding nucleotides to the growing DNA strand
Why are VNTR regions used in PCR analysis
To determine the length and allow amplification to occur around the targeted area
What are the 5 rules on designing primers?
Primer binds to template by BASE PAIRING
Primer binds to template ANTIPARALLEL
Primer becomes part of the product
DNA polymerase begins replicating from the 3’ end of a primer
Primers need to be specific or unique to stick
What’s wrong with designing primers within the VNTR region?
It results in an inconsistent size of the product if it’s built IN the VNTR region. Primers need to be designed OUTSIDE of the VNTR region but within close proximity to the portion we need to amplify.
What are the 2 factors the temperature influences in the annealing phase?
Primer length
longer primer = hotter
GC% Content
more GC% = hotter
What is the normal range of nucleotides?
18 to 25 in length
How would you order primers?
By reading the DNA sequencing information in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
If a high GC content correlates with high temperature and low GC content correlates with low temperature, what temperature would give you a better product to use during the extension phase of the PCR cycle?
The LOWER TEMPERATURE is better to give you a better product. High temperature would result in the primer failing to bind. If the temperature is too cool, it will still allow the primer to stick but would result in a PORTION of the primer sticking and sometimes it can stick in places it shouldn’t resulting in unnecessary products being created in the reaction mixture or incorrect products.