Diffusion, Osmosis and active transport
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Diffusion
Is a net movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a lower concentration down the concentration gradient
Factors Effect Diffusion
1.The higher the the temperature the higher the rate of diffusion because heat energy is converted to kinetic energy so molecule will move faster
2.Concentration gradient: the higher the difference between the two regions the higher the rate of diffusion.
3.The thicker the wall the slower the rate of diffusion
4.The larger the surface area the higher the rate of diffusion
5.The smaller the molecules the faster they move.
Osmosis
It is the net diffusion of water molecules from area of higher water potential to area of lower water potential through partially permeable membrane down the concentration gradient
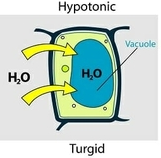
Hypotonic solution
Turgid Putting plant cells in a solution of higher water potential than the inside of the cell
Hypertonic solution
Plasmolysed Putting plant cell in a solution with lower water potential than the inside of the cells
Isotonic solution
Flaccid plant is put in a solution with same water potential as the inside of the cell
Hypotonic solution in animal cell
Lysed burst
Hypertonic in animal cell
Shrink
Isotonic in animal cell
Normal
Percentage change in mass
End mass - start mass / start mass×100
Active Transport
Is the movement of ions from a region of low concentration toa higher concentration across a membrane using energy released during respiration against the concentration gradient via a protein pump
What Active transport needs for transporting substances across the membrane
Protein carriers
An example of active transport
The absorption of mineral ions from the soil
Root hair cell
Its main function is to absorb water from the soil by osmosis and mineral and ions by active transport
Root hair cell Structure
Increase the surface area for absorption.
The cell sap is concentrated to create water potential gradient for more water absorption
It has many mitochondria for more aerobic respiration and release of energy for active uptake
Preparing a slide and use a microscope
Cut a thin section using a scalpel.
Apply the section on a glass slide.
Add stain for contrast
Wash off excess stain
Apply coverslip, carefully avoiding trapped
air bubbles
Start with lowest power objective lens for focusing. Then observe under high power
Focus by moving the objective lens away from the specimen to avoid damage of the objective lens when touching the specimen
Magnification
Measured length \ Actual length