Comprehensive Cardiac & Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Key Concepts and Protocols
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
What populations does cardiac rehabilitation serve?
Patients who underwent heart surgery, heart attack, coronary angioplasty, ICD fitted, and stable heart failure.
What is Phase 1 of cardiac rehabilitation?
Acute monitoring phase, typically inpatient immediately following heart attack, cardiac arrest, or surgery.
What is Phase 2 of cardiac rehabilitation?
Sub-acute conditioning phase, outpatient sessions with a nutritionist, typically 36 sessions, 3x/week for 12 weeks.
What is Phase 3 of cardiac rehabilitation?
Training and maintenance phase, reduces monitoring, no time limit, not usually reimbursed by insurance.
What is Phase 4 of cardiac rehabilitation?
Disease prevention program, similar to Phase 3, focuses on long-term maintenance and risk factor management.
What is pulmonary rehabilitation?
An evidence-based, multi-disciplinary intervention for symptomatic chronic respiratory diseases designed to reduce symptoms and optimize functional status.
What are common barriers to pulmonary rehabilitation?
Non-attendance among females, current smokers, and those who live alone; non-adherence in extremes of age and current smoking.
What is a key difference between pulmonary and cardiac rehabilitation?
Pulmonary rehab focuses on breathing difficulties and disease management, while cardiac rehab focuses on heart health and recovery.
What are the goals of pulmonary rehabilitation?
To reduce symptoms, optimize functional status, increase participation, and reduce health care costs.
What does pulmonary rehabilitation educate patients about?
Oxygen therapy, breathing retraining, and symptom assessment.
What is the typical structure of Phase 2 cardiac rehabilitation?
Outpatient sessions with a focus on exercise, nutrition, and education over 12 weeks.
What is the main focus of Phase 3 cardiac rehabilitation?
Maintaining activity levels with reduced monitoring and emphasis on long-term exercise habits.
What is the purpose of the acute monitoring phase in cardiac rehab?
To monitor patients immediately after a cardiac event or surgery for safety and recovery.
How many sessions are typically included in Phase 2 cardiac rehabilitation?
36 sessions.
What is the frequency of sessions in Phase 2 cardiac rehabilitation?
3 times per week.
What is the focus of the disease prevention program in Phase 4 cardiac rehabilitation?
To identify significant impairments and prevent the negative effects of inactivity.
What role does education play in pulmonary rehabilitation?
It teaches patients about disease management and self-care strategies.
What are some common reasons for non-adherence in pulmonary rehabilitation?
Extremes of age, current smoking, and long-term oxygen therapy use.
What is the aim of the training and maintenance phase in cardiac rehabilitation?
To maintain physical activity and reinforce healthy lifestyle changes.
What is the significance of medical surveillance in cardiac rehabilitation?
To monitor patients' responses to physical activity and ensure safe discharge home.
What does the term 'ADL' refer to in the context of cardiac rehabilitation?
Activities of Daily Living.
What is the primary purpose of the Framingham Study?
To understand the impact of cardiovascular disease (CVD) including hereditary and lifestyle influences.
What are the core components of the Framingham Study?
Baseline patient assessment, nutrition counseling, risk factor management, psychosocial management, activity counseling, prescribed exercise therapy, and outcome analysis.
What is one goal of the Framingham Study?
To develop and implement a safe and effective exercise and lifestyle activity program.
What considerations are important in the Framingham Study?
Safety & risk stratification, patients' vocational requirements, orthopedic limitations, premorbid & current activities, and personal health and fitness goals.
What is the focus of Phase 1 in inpatient rehab programs?
Early mobilization and identification and education of CVD risk factors.
What should a patient demonstrate in Phase 1 of inpatient rehab?
Understanding of physical activities that may be inappropriate or excessive.
What is the recommended intensity for exercise programming post-MI?
Heart rate should be less than 120 bpm or resting heart rate plus 20 bpm.
What is the recommended duration for exercise in early mobilization?
Begin with intermittent bouts for 3-5 minutes as tolerated.
What is the definition of tidal volume?
The volume of air inhaled or exhaled in a normal breath.
What is the purpose of the conducting zone in the respiratory system?
Air transport, warming, humidification, and filtration.
What is myocardial ischemia?
A lack of blood flow to the myocardium that causes pain in heart muscles.
What are the symptoms of stable angina?
Episodic pain or a crushing/squeezing sensation in the chest during exertion.
What is the prognosis for patients with 1-vessel disease?
Mortality of 2-4%.
What characterizes unstable angina?
Crescendo angina or angina with minimal exertion or at rest.
What is congestive heart failure?
A condition where the heart fails to pump adequately, leading to fluid retention.
What is the difference between compensated and uncompensated heart failure?
Compensated heart failure maintains adequate cardiac output, while uncompensated cannot.
What is ventricular tachycardia?
A fast heart rhythm originating from the bottom chambers of the heart.
What are the contributors to a myocardial infarction?
Ischemia, atherosclerosis, thrombus, arterial spasm, and hypovolemic shock.
What is the treatment for myocardial infarction?
Rapid management to limit the size of the infarct and scope of damage, including anti-thrombolytics and PTCA.
What is the typical survival rate for sudden cardiac death outside of a hospital?
12%.
What is the role of surfactant in the respiratory system?
To reduce surface tension in the alveoli and facilitate gas exchange.
What is the definition of residual lung volume?
The volume of air remaining in the lungs after a forced expiration.
What is the significance of the forced vital capacity?
It measures the total amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after taking the deepest breath possible.
What are foam cells in the context of atherosclerosis?
Macrophages that have engulfed lipids, contributing to the formation of fatty streaks in arteries.
What is the purpose of pharmacological intervention in heart failure?
To help maintain cardiac output and manage fluid volume.
What is the typical heart rate response for post-surgery patients during exercise?
Resting heart rate plus 30 bpm.
What condition can occur if more than 40% of the myocardium is necrotic?
Fib or cardiogenic shock
What is a potential complication of papillary muscle rupture after a myocardial infarction?
Mitral valve insufficiency
What is an intraventricular septal rupture?
A tunnel-like lesion through the septum
What is a ventricular aneurysm formation?
Caused by tenuous repair of a rupture
When does pericarditis typically occur post-myocardial infarction?
2-3 days post-MI
What are common symptoms of pericarditis?
Pain over the precordium, aggravated by breathing and relieved by upright sitting
What is thrombosis?
A blood clot, primarily due to venous stasis, with potential for embolism
Where do deep vein thromboses usually form?
In the calf, commonly in sedentary individuals, smokers, hypertensives, and diabetics
What is a mural thrombus?
A clot that forms in the ventricular wall after a myocardial infarction
What are the symptoms of a mural thrombus?
Sudden pain, numbness, or coldness of an extremity
What is the treatment for a mural thrombus?
Surgical embolectomy
What is a resting electrocardiogram used for?
To assess heart rhythm/rate baseline and show ischemia
What does Holter monitoring assess?
Captures every heartbeat for 24 hours to assess rhythmic changes and palpitations
What is the purpose of a stress exercise tolerance test?
To monitor heart function during exercise in a medically supervised environment
What is echocardiography used to evaluate?
How well heart valves function and blood flow in chambers
What is the purpose of enhanced external counter-pulsation?
To treat patients with chest pain who are not candidates for open heart surgery
What is a percutaneous transluminal coronary angiogram?
A procedure to open blocked coronary arteries using a catheter
What is an automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator?
A device that controls arrhythmias and delivers shocks during abnormal rhythms
What is the purpose of the Watchman device?
To prevent strokes in patients with atrial fibrillation
What characterizes restrictive lung disease?
Difficulty fully expanding the lungs, leading to reduced lung volume
What is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
A progressive disease characterized by fatigue, cough, chest tightness, and shortness of breath
What is pulmonary fibrosis?
Scarring and thickening of lung tissue
What is the purpose of a chest x-ray?
To diagnose causes of shortness of breath, chest pain, and chronic cough
What does a chest CT scan show?
The size, shape, and position of structures in the lungs
What are common causes of shortness of breath (SOB) or chest pain (CP)?
Tumor, excess fluid, or pulmonary embolism.
What does an echocardiogram evaluate?
The amount of pressure occurring in the right side of the heart (pulmonary hypertension).
What is the normal range for oxygen saturation measured by oximetry?
95-99%.
What indicates hypoxia in terms of blood-oxygen saturation?
Less than 94%.
What does spirometry measure?
How much air the lungs can hold and how quickly air moves out of the lungs.
What is the normal airflow capacity percentage?
85%.
What are the non-modifiable ACSM risk factors?
Age/gender, family history, and ethnicity.
What age and gender are considered higher risk for cardiovascular disease?
Men over 45 years and women over 55 years.
How does estrogen affect cardiovascular risk in women?
Pre-menopausal estrogen acts as a buffer against atherosclerosis.
What is the significance of family history in cardiovascular risk?
MI, revascularization, or sudden cardiac death in 1st degree relatives before age 55 for men and 65 for women indicates higher risk.
Which ethnic group has a 30% higher likelihood of dying from heart disease?
African Americans.
What are the blood pressure categories for hypertension?
Normal: <120/<80, Elevated: 120-129/<80, Stage 1: 130-139/80-89, Stage 2: ≥140/≥90, Crisis: >180/>120.
What lifestyle modifications can reduce hypertension?
Attain recommended body fat levels, limit alcohol, exercise regularly, reduce sodium intake, stop smoking, and lower saturated fat & cholesterol.
What is considered a high HDL level?
Greater than 60 mg/dL.
What is the BMI classification for obesity?
BMI > 30 kg/m².
What waist girth measurements indicate obesity risk?
>102 cm (40 in) for men and >88 cm (38 in) for women.
What is the significance of psychosocial factors in cardiovascular risk?
Depression, anxiety, and stress can elevate risk.
What does a complete blood count (CBC) assess?
RBC for anemia, WBC for inflammation/infection, and platelets for blood clotting.
What does BNP stand for and what does it indicate?
Brain natriuretic peptide; higher levels indicate heart failure.
What are the symptoms suggestive of cardiovascular disease?
SOB, dizziness, orthopnea, ankle edema, palpitations, and unusual fatigue.
What is the AACVPR classification for low risk?
Absence of complex dysrhythmias, angina, and normal hemodynamics with functional capacity ≥ 7 METs.
What characterizes moderate risk in AACVPR classification?
Presence of angina or significant symptoms, functional capacity < 5 METs.
What defines high risk in AACVPR classification?
Complex dysrhythmias, significant symptoms, and low resting EF (< 40%).
What is the action potential in cardiac cells?
The rapid rise and fall of electrical membrane potential leading to muscle contraction.
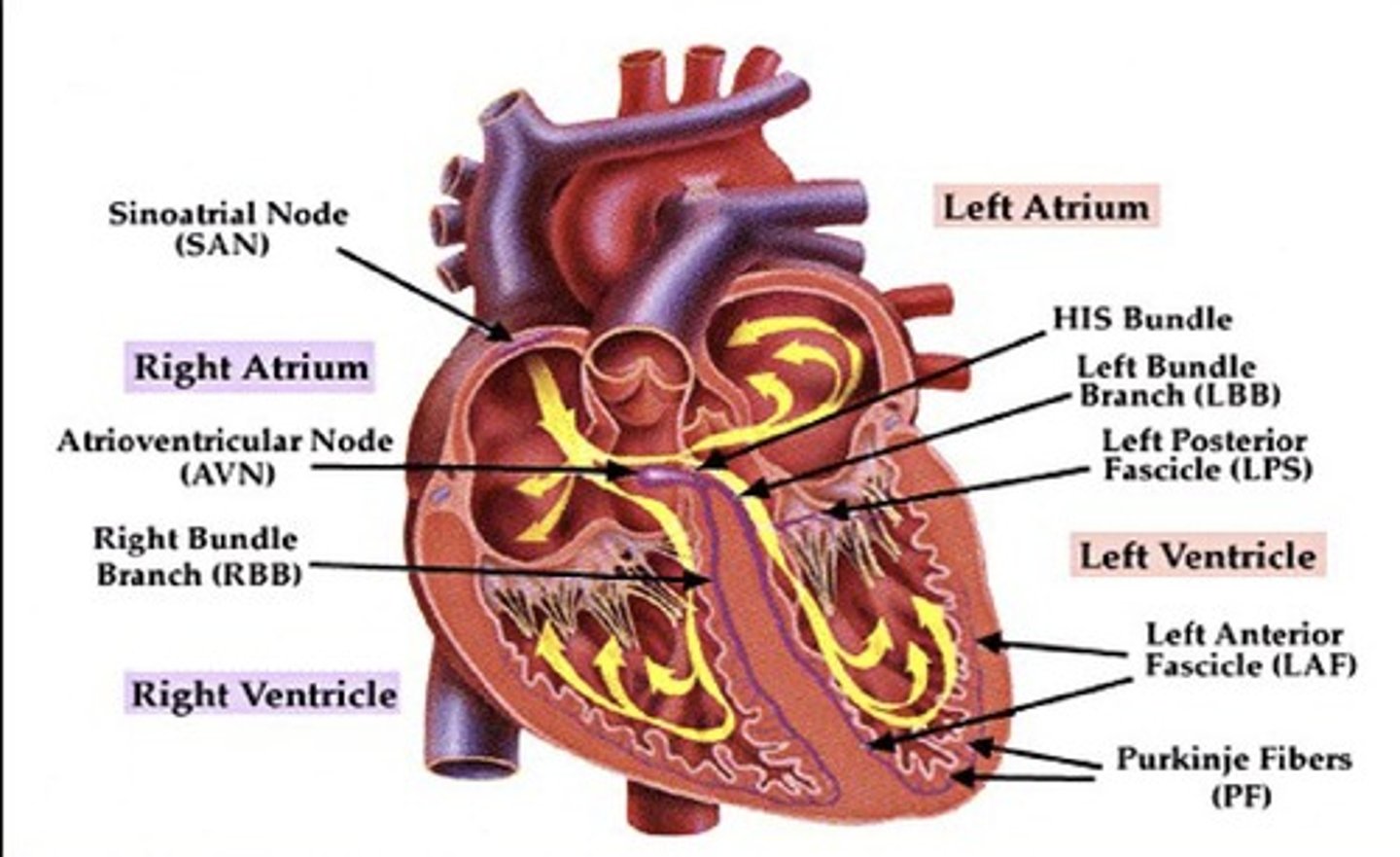
What is depolarization in cardiac physiology?
A positive change in cell membrane potential due to calcium and sodium influx.
What is repolarization in cardiac physiology?
The return of membrane potential to a negative value as ions return to resting state.
What is the role of cardiac pacemakers?
They generate and discharge electrical impulses for heart rhythm.
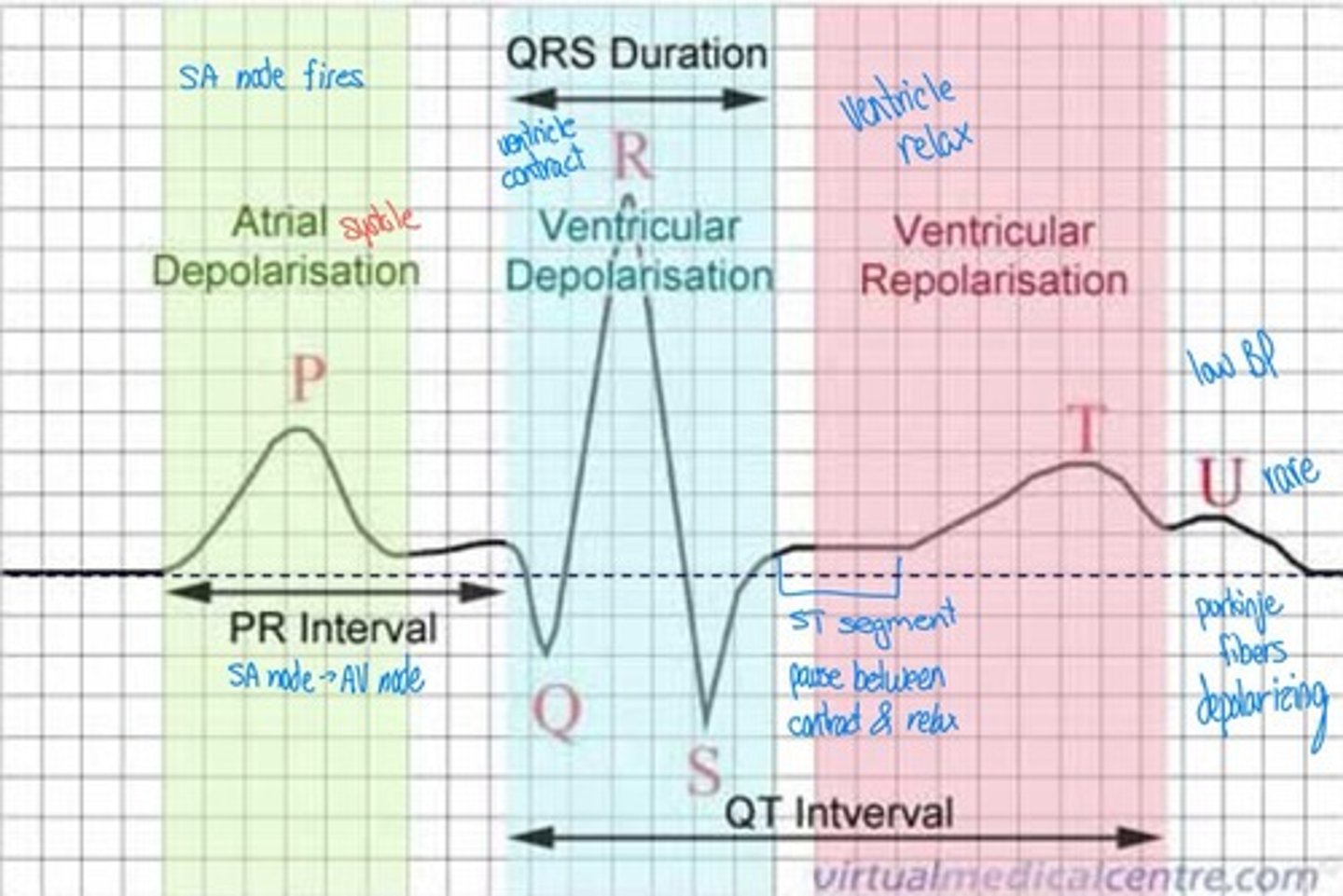
What is the significance of the triplicate method in ECG interpretation?
It measures heart rate by counting thick lines between QRS complexes.
What is the normal sinus rhythm range?
60-100 bpm with identical P waves and PR intervals.