Evaluation Feedstuff for Farm Livestock
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANSC 405 - Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
procedures to evaluate feedstuff
nutrient composition
palatability
digestibility
productive value
physical or handling characteristic
provide economic comparisons
what are the types of analytical methods?
chemical procedures
biological procedures
microbiological procedures
what does the chemical procedure include?
gravimetric, titration and colorimetry
gravimetric is…
weight
titration
technique where a solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution
colorimetry
measurement of the wavelength and the intensity of electromagnetic radiation in the visible region of the spectrum
biological procedures include…
lab animals
microbiological procedures
employ isolated bacteria
obtaining a good sample of feedstuff is key to…
reliable feed nutrient evaluation
list the steps to evaluate feedstuffs
identification
sampling
general
what are the methods used to estimate the nutritional value of a feedstuff?
laboratory-based analyses
animal-based analyses
additional or miscellaneous considerations
nutritional value
describes the estimated nutritional quantity and quality of a feedstuff
nutritional value is dependent on ______ and __________ _____
species; physiological state
the 3 components of estimating nutritional value:
estimating nutrient content
efficiency of nutrient use
identifying the presence of antinutritional factors
what’s an antinutritional factor?
components that decrease the nutritional value of the feed
lab-based analyses
measure the amount of each individual component (nutrient) in the feedstuff
what was the initial procedure used to estimate quantity of individual components of feedstuff?
Proximate Analysis System
proximate analysis is a combination of analytical procedures that provides the different fractions of feedstuff. what are these fractions?
dry matter
dry inorganic material
crude protein
ether extract (EE)
CHO
what method breaks down the forage into fractions of readily digestible and indigestible portions, and is a better method than proximate analyses?
Van Soest (Detergent) Method
why is there no routine analysis for vitamins?
because of the diversity of compounds
what are the 3 ways energy content is expressed?
dry matter basis
as-fed basis
air-dry basis
what is the dry matter basis when expressing energy content?
amount contained in only the dry matter fraction without water
what is the as-fed basis when expressing energy content?
amount contained in feed as it would be fed to animal, includes water
what is the air-dry basis when expressing energy content?
assumed to be ~90% DM; air-dry and as-fed may be the same for many common feeds
what basis is the most accurate measurement of both feed composition and nutrient requirement
dry matter basis
feeding trial
gives an indication as to whether the animal will accept the feedstuff and the performance obtained from the feedstuff compared to others.
in digestion or metabolism trials, what does chemical analysis measure?
you start with chemical analysis to determine the nutritive value of feed
digestibility is measured as…
difference between what went in and what came out
what are factors that affect digestibility within species?
age
particle size and/or extent of feed processing
feed source and composition
level of feed intake
rate of passage through intestinal tract
nutrient excess or deficiency
feedstuff energy
used to denote value of feed for its primary function
what is the primary function of feed that’s just ingested?
to furnish energy for body processes and to form the non-nitrogenous organic matter of tissues and secretions, functions in which all organic nutrients can take part
what are all different measures of feed energy value?
total digestible nutrient (TDN)
gross energy
digestible energy
metabolizable energy
net energy
roughage/concentrate ratio
total digestible nutrient (TDN)
a general measure of nutritive value of feed, digestion coefficients are used to compute its content of TDN
list the different energy units
calorie (cal)
kilocalorie (kcal) - 1000 small calories
megacalorie (Mcal) - 1000 kcal or 1,000,000 cal
what are some common effects of energy deficiencies?
decreased production level such as weight gain or milk production
decreased performance level such as speed or endurance
decreases reproduction efficiency such as conception and/or pregnancy rates
increased incidence of metabolic disorders like ketosis
what is the most accurate method to compare interspecies energy expenditures and energy requirements?
comparing metabolic body weight
what are other factors that affect energy requirements between interspecies?
activity level
production level
environmental conditions
nutritional deficiencies
general health
what are the stages of development in an animal?
maintenance
growth
production
reproduction
maintenance
support of an animal when doing no work and yielding no product
how much feed consumed by animals is used for maintenance?
1/2
growth
the general development of an animal from the time it’s born until its reached maturity
production
animals being fed for production of market animals such as those for meat, milk, wool and work
reproduction
from conception until birth; it’s important to neither overfeed or underfeed the mother during this time
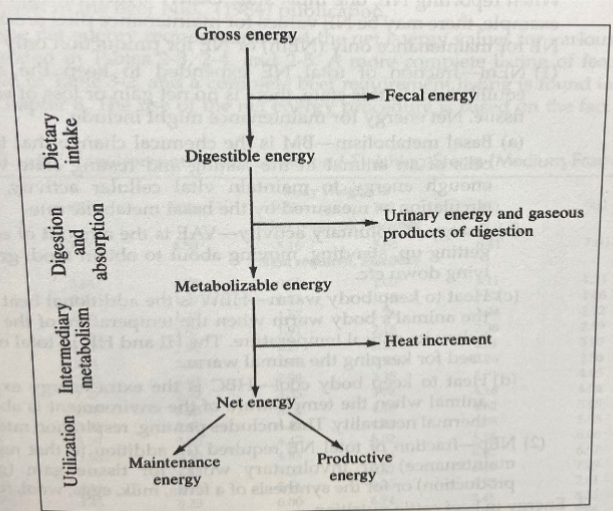
gross energy (GE)
total potential energy of a feedstuff consumed
fecal energy (FE)
waste product during digestion and absorption
digestible energy (DE)
measurement takes account of digestible losses and is subject to same variables that affect digestion and same additional losses in metabolism as in TDN
GE-FE
gaseous products of digestion (GPD)
combustible gases that escape body during digestion and absorption process
urinary energy (UE)
energy excreted via urine
metabolizable energy (ME)
usable portion of ingested energy
Me = DE-UE-GPD
heat increment (HI)
increase in heat production following eating feed when animal is in thermally neutral environment
net energy (NE)
energy used for either maintenance only or for maintenance and production
NE = ME-HI
list the types of feedstuff energy in digestion and metabolism
gross energy
fecal energy
digestible energy
gaseous products of digestion
urinary energy
metabolizable energy
heat increment
net energy
ways to physically evaluate feedstuffs
eye appraisal of feed
palatability
accounting for factors that might influence the value of a feedstuff
list factors that might influence the value of a feedstuff
soil fertility
growing conditions
harvesting
processing and storage
feedstuff energy in digestion and metabolism table.
what is used to determine gross energy?
bomb calorimeter
**make sure to study equations**