C
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Coriolis Effect
the deflection of moving objects (air or water) via the rotation of the earth
this influences wind patterns, oceanic surface currents, etc.
Eutrophication
when a body of water becomes over-riched with nutrients
Mainly Nitrogen (N) and Phosphorus (P)
This leads to excessive plant and algae growth
C4 Pathways
Special pathways plants use to avoid photorespiration and fix caron more efficiently
Is used during hot and dry environments
In change minimizing water retention
Methods of water retention
Having Internal Respiratory Organs
CAM Photosynthesis (stomata opens at night)
Ectothermy vs Endothermy Advantages
Endothermy - Warm blooded animals regulating body temperature using metabolic heat. Causing them to be active at all temperatures and active in broader geographic ranges
Ectotherm - Cold blooded animals have a need for low energy and can survive long times without consuming food. More energy goes to reproduction and growth
Defining factors of a land-scape study
Patchiness
Grain & extent
Larger Islands support more resources and promote higher diversity
Getting fewer immigrant species the small island vs the large island they have no reason to inhabit the small one
NPP vs GPP
GPP Gross Primary Productivity - Total amount of energy fixed by photosynthesis in an ecosystem
NPP Net Primary Productivity - Energy available to growth and to consumers (herbivores).
NPP = GPP - R
R (plant respiration for self-maintenance and metabolism)
Temperate Grassland
biome dominated by drought tolerant individuals with hot summers and harsh winters.
Tropical Savanna
Dry seasons all around wet and dry
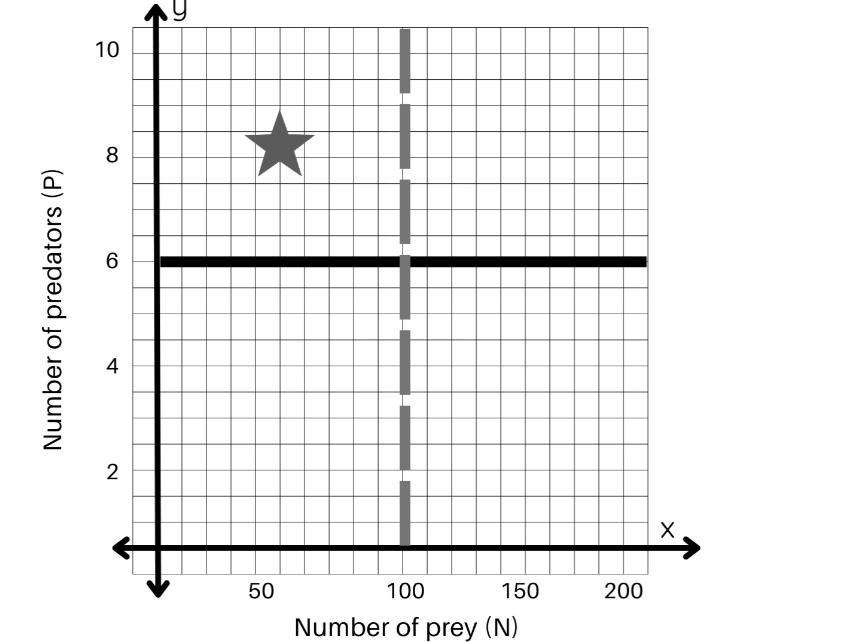
What is happening at the star ?
Both are decreasing
Primary sexual characteristics refer to phenotypic traits that help attract mates
False
Primary sexual characteristic refer to functions that make reproduction possible
Secondary sexual characteristics refer to phenotypes.
Polygyny
One male - multiple females
Polyandry
One female - multiple males
Monogamy
One male - One female
Promiscuity
Multiple males - multiple females
A major cost to sexual reproduction
Lower genetic fitness
this is because you only can pass half of your gene
Difference between GPP and NPP
NPP is GPP minus energy plants use for respiration
Characteristics of Eusocial species
Cooperative care of young
Overlapping generations
Distinct worker and reproductive castes
Ruderals
Pioneer species - rapid growth and high seed production
Competitor
thrive in stable environments, resource rich, tall fast growth
Stress-tolerant
thrive in harsh environments. slow growth and long-lived
A life table is used to
calculate population growth using age-specific values
What is the primary reason natural selection favors eusociality?
Maximizes gene copies passed to the next generation
Natural selection doesn’t care about harmony or cooperation. Just genes passed down to the next generation
Types of interactions (+,-) etc.
Parasitism (+,-)
Mutualism (+,+)
Commensalism (+,0)
Directional Selection
One extreme phenotype is favored
Stabilizing Selection
Intermediate phenotypes are favored; stable environmental conditions
Disruptive Selection
Mediocrity is not favored and both extremes are favored
Sexual Selection
Traits that increase mating success are favored
Type I Functional Response
Predator consumption linearly increase with prey density
Type II Functional Response
Curved line that slows or plateaus due to handling time
Type III Functional Response
S shaped line that is generalist and switches based on what is available
Patch Definition
discrete portion of one habitat type
Most accessible medium of nutrients in terrestrial systems
decomposition
T/F Communities have distinct and easily definable boundaries
False
When ecosystems undergo significant changes after crossing a tipping point
An alternative stable state
Corliolis Effect directs moving air …
sideways
Northern Hemisphere : to the right
Southern Hemisphere : to the left
Most carbon is found in
Earth’s crust
Lotka-Volterra predator prey models define
The growth rates of predator and prey populations
dN/dt
Instantaneous rate of change
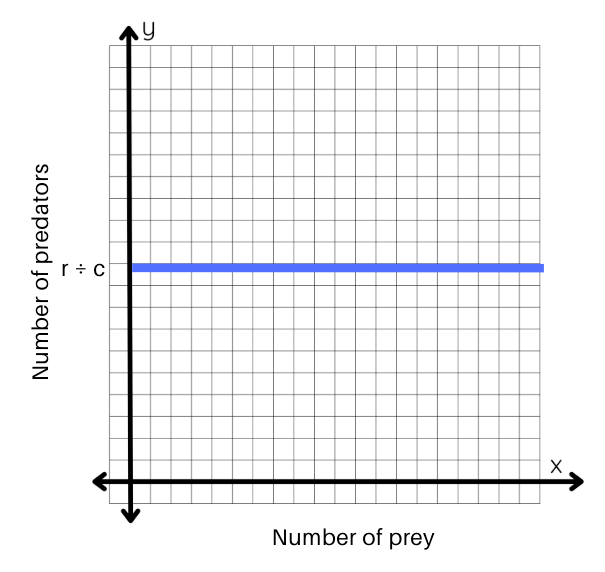
What does the below line represent
Prey zero growth isocline
If competition coefficient α = 0.5, what does this mean?
Resource consumption of 1 of Species 2 is equivalent to 0.5 of Species 1
In Lotka Volterra, when do the two competing species coexist
When intraspecific competition (K) limits size more than interspecific competition (a,B)