NSG 212 - Final Exam
1/437
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
438 Terms
Continuity of Care
Continuation of care smoothly from one provider to another, so that the patient receives the most benefit and no interruption in care.
Stages of Nursing Process
ADPIE
-Assessment
-Diagnosis
-Planning
-Implementation
-Evaluation
Nurses Role in admission
-room assignment (fall risk, infection control)-ID of patient and any risks on wristband (fall, allergies, etc)-Thorough assessment-Review advanced directives-Diagnostic testing-obtain necessary consents-Implementation of providers orders-PATIENT TEACHING IS ONE OF YOUR TOP PRIORITIES
nurses role in discharge
-type of discharge (ordered by physician, AMA)-actual date and time of discharge, who accompanied client, and how client transported-where was the client discharged (home, facility)-a summary of clients condition at discharge-any unresolved difficulties and plans for follow up-dispositions of valuables, meds from home-copy of clients discharge instructions
Nurses role in transfer process
-continuity of care
-info sharing
-SBAR report
Concepts of AMA
-against medical advice
-legally free to leave
-choice carries a risk for increased illness and complications
-Pt must sign release form
-pt is informed of risks prior to signing
-pt signature must be witnessed
-form become part of medical record
Factors that affect Urination
age, environmental factors, medication hx, psychological factors, muscle tone, fluid balance, current surgical or diagnostic procedures, presence of disease conditions
-caffein and alcohol = increase
-high sodium = decreases
Med affects on urination
-diuretics prevent reabsorption of water
-antihistamines and anticholinergics = urinary retention
-chemo= toxic for kidneys
-phenazopyridine = orange, red
-amitriptyline = green-blue
-levodopa = dark
- riboflavin =bright yellow
-roughly 30 mL/hr = 720 mL/day
Alterations in Urinary Function
-polyuria (diuresis) = abnorm large amount 2500 mL/day
-oliguria - less than 500 mL/day
-anuria - less than 100 mL/day
-nocturia = freq at night
-urgency = immediate
-dysuria = painful/difficult
-maturational enuresis = involuntary urinations after 4-5 yrs old.
-urinary retention = inability to fully empty
Assessment of fluid balance
I&O
-output cannot equal input because of absoprtion
-roughly 2400 mL/day
-measureable
DW
-most accurate assessment of fluid balance
-same time
-gain or loss greater than 1lb = mostly fluid
indwelling cath
- double lumen (foley)
-indwelling cath cannot = urinary retention
indwelling foley
-catheter remains in place (within client) for period of time
coude cath
-has a bend
Used for males with prostate complications BPH- benign prostatic hypertrophy(enlarged prostate)
nursing interventions for GI functioning/elim
-promote reg pattern
-meds
cathartics, suppositories
se of conservative methods 1st like mobility food, fluids
anti diarrheals
enemas
-digital removal of impact
-bowel training program
-food and fiber
fiber = 25+30g/day
surgical asepsis
techniques used to destroy all pathogenic organisms, also called sterile technique
-above waist
-dont turn back
-no cough sneeze
- 1 in border
-6 inches above
-dont reach across
what may indicate infection?
-increased WBC
normal is 5,000=10,000
-increased ESR
presence of pathogen in urine, blood, sputum, or draining cultures
Stages of infection
Incubation period
Prodromal stage
Full stage of illness
Convalescent period
incubation period
interval between initial infection and first signs and symptoms
prodromal stage
person is most infectious, vague and nonspecific signs of disease
full stage of illness
specific signs and symptoms
convalescent
recovering from illness
potential treatments for infection
antipyretics
-fever + discomfort
antimicrobial therapy
-kills/stops growth of micro org
anthelminthics
-worm infestations
how to prevent HAIs
freq and proper hand hygiene practice
-avoid electronic equipment
disinfect all equip
-barrier contact precautions
-private rooms
native immunity
Restricts entry or immediately responds to a foreign organism through the activation of phagocytic cells, complement, and inflammation
passive immunity
the short-term immunity that results from the introduction of antibodies from another person or animal.
-breast milk, placenta
active immunity
A form of acquired immunity in which the body produces its own antibodies against disease-causing antigens.
Primary prevention
directed towards promoting health and preventing the development of disease processes or injury
-ex immunization clinics
Secondary prevention
focus on screening for earl detection of disease with prompt diagnosis and treatment of anything found
Tertiary prevention
begins after an illness is diagnosed and treated, with the goal of reducing disability and helping rehabilitate pts to a maximum level of function
mental impairment in older adults
-Dementia
-Alzheimer's Disease
-Sundowning Syndrome
-Cascade Iatrogenesis
-delirium
-depression
-UTI
principles of pt education
influencing pt behavior to effect change in knowledge, attitude, and skills with the goal of improved health-ongoing and interactive-compliance and adherence
principles of learning domains
• Cognitive: storing and recalling of new knowledge in the brain (KNOWLEDGE)• Psychomotor: learning a physical skill (SKILL)• Affective: changing attitudes, values, and feelings (ATTITUDE)
factors influencing diffusion of gases (O2-CO2)
Factors Influencing Diffusion(Diffusion is gas exchange)
Change in surface area
-Removal of the lung
-Atelectasis
-Collapse of the alveoli... Prevents the exchange of gas by diffusion in the lungs...
Thickening of the membrane
-Pneumonia (lung infection)
-Pulmonary edema
Partial pressure change
-Decrease in environmental oxygen...high altitudes, lack of 02
Solubility and molecular weight of the gas
physiological factors that may increase or decrease respiration
Rate and depth of respirations
-Increase rate/depth in the presence of low 02 or high C02
-Respiratory center; in the medulla of the brain; stimulated by an increase of CO2 and by decreased 02 ( lesser degrees)
Chemoreceptors in the aortic arch and the carotid arteries are sensitive to change in blood gas levels and blood pressure and can activate the medulla to increase the rate/ depth of respirations.
chemoreceptors
sensitive to oxygen saturation
-aortic arch
-carotid arteries
-in response to low oxygen they will increae respirations
medulla (CNS)
triggered to control respirations
rate and depth of respirations
increase rate/depth in the presence of low O2 or high CO2
contributing factors for alterations in the Cardiovascular system
Dysrhythmia or arrhythmia
-Something other than “lub-dub”…Problem with electrical signals; SA node
Myocardial ischemia
-Decreased oxygen supply to the heart…MAIN cause of a heart attack (MI)
Angina
-Coronary Artery Vasoconstriction; decreased oxygen= muscle pain=chest pain
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
-Heart Attack…Caused by lack of oxygen to a part of the heart (blockage)
Heart Failure (Congestive Heart Failure [CHF])
-Failure of the Left Ventricle to pump…Back up of blood into the lungs…Heart AND Lung problem
Dysrhythmia or arrhythmia
disturbance of heart rhythm
-something other than "lub-dub"
-problem with electrical signals;SA node
myocardial ischemia
Lack of oxygen to the heart muscle
-decreased oxygen supply to the heart
=Main cause of a heart attack (MI)
angina
muscle pain=chest pain
-coronary artery vasoconstriction; decreased oxygen
myocardial infarction (MI)
heart attack
-caused by lack of oxygen to part of the heart(blockage)
heart failure
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
-failure of the left ventricle to pump
-back up of blood into the lungs
-heart and lung problem
factors affecting cardiopulmonary function and oxygenation
Level of health
-Other chronic illnesses
Developmental considerations
-Lifespan
Medication considerations
-Opioids decrease respiratory drive
Lifestyle considerations
-Occupation, smoking
Environmental considerations
-Pollution
Psychological health considerations
-Stress, hyperventilation
how is oxygen carried?
via plasma and red blood cells
hypoxia
-Low oxygen saturation of the body, not enough oxygen in the blood
-can be caused by hypovolemia, hypoventilation, and interruption of arterial flow
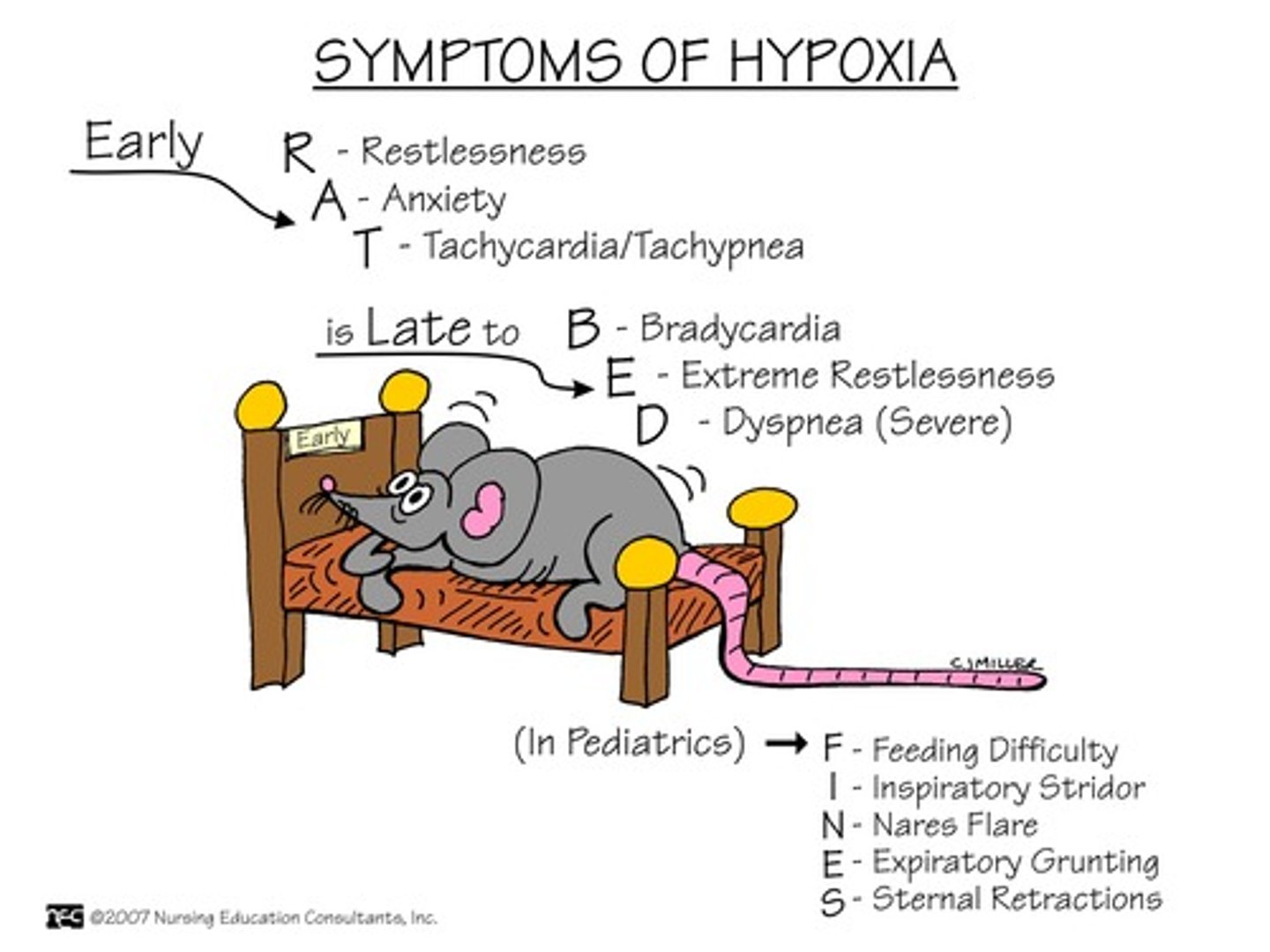
early hypoxia s/s
S/S of Early:
-Tachypnea
-Tachycardia
-Restlessness (ENGAGE)
-Pallor
-Increased BP
-Use of accessory muscles
-Nasal flaring
-Tracheal tugging
-Adventitious lung sounds
-Dyspnea
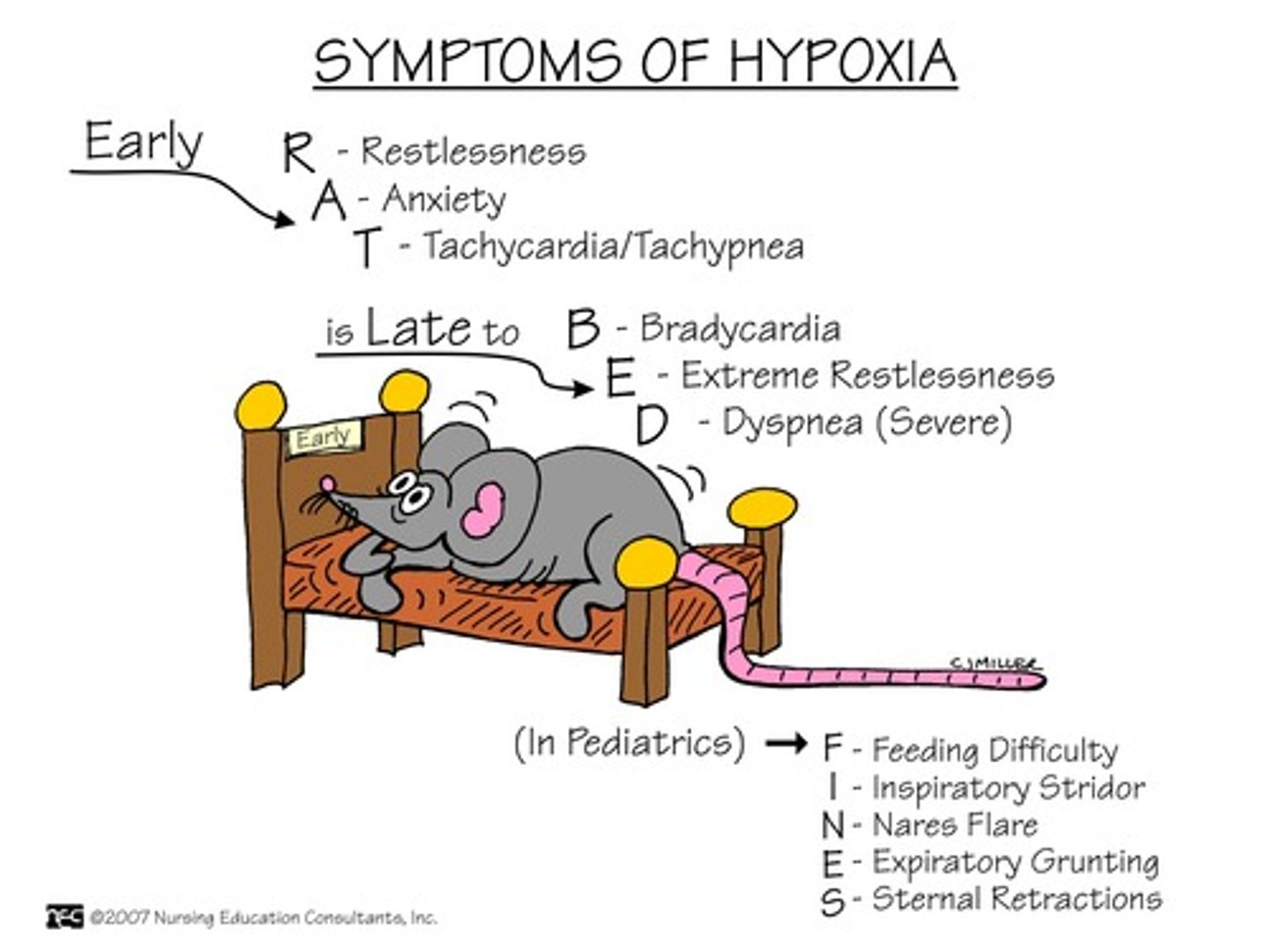
late hypoxia s/s
S/S of LATE:
-Bradypnea
-Bradycardia
-Confusion and stupor,
-Cyanosis
-Hypotension
-Cardiac arrhythmias
-Metabolic acidosis
decreased rate or depth of air movement into the lungs
-acute disease
-can cause hypercarbia(high CO2)
s/s
-restlessness
-HT
-headache
chronic hypoxia
-live in a state of low oxygen due to disease process
s/s
-Headaches
-Chest pain
-Enlarged heart
-Clubbing the of fingers/toes
-Anorexia
-Constipation
-Decreased urine output
-Weakness
-Muscle pain
-Right sided heart failure
-Respiratory acidosis
safe oxygen administration
Delivered via nasal cannula:
-1 liter 24 %
-2 liters 25 %
-3 liters 32 %
-4 liters 36 %
-5 liters 40 %
-6 liters 44 %
-Humidification 3-4 Liters
Oximizer
high flow nasal cannula
simple mask
40-60% of oxy, 5-8 liters/min-never less than 5 L or CO2 build up can occur
partial rebreather
60-75% at a flow of 6-11 liters/min
-1/3 of expired air from exhaled breath
-bag should stay 2/3 full, complete deflation of the bag during inspiration can cause CO2 build up
non rebreather
80-95% except for intubation; flow of 10-15 liters/min
-Non-rebreather means they are NOT REBREATHING any of their CO2.
-That means that what they ARE breathing in is almost 100% oxygen.
venturi mask
delivers precise amount of O2
-used to prevent oxygen toxicity in pts with COPD
aerosol mask/face tents
fits loosely around the face and neck
oxygen is
combustible
no high levels for
COPD pts
-drive to breath is LOW oxy
diagnostic testing for cardiopulmonary and respiratory diseases
-cardiac coronary cath
-cardiac exercise stress testing
-echocardiogram
-holter monitor
-arterial blood gases
-cardia biomarkers
-CBC
-cytologic sputum
-thoracentesis
cardiac coronary cath
can view and open up blocked coronary arteries
cardiac exercise stress testing
can detect blocks in the arteries (STRESS the heart)
echocardiogram
measures heart conduction
holter monitor
continuous monitor, can pick up changes in conduction
arterial blood gases
-drawn directly from a artery
-direct measurement of O2 and CO2
cardiac biomarkers
--creatinine kinase (CK-BM)
-troponin
-both elevate in the blood due to cardiac damage
complete blood count (CBC)
the body's response to illness
cytologic sputum
may detect cancerous cells
thoracentesis
-Procedure of puncturing the chest wall and aspirating pleural fluid or air from the chest
-At the bedside or under fluoroscopy if they want to really visualize
-Sterile procedure
-Patient sits on side of bed or in a chair
-Monitor VS, ABC's
-Max amount removed is 1000 ml
complications to thoracentesis
-Pneumothorax...Collapsed lung
-Pulling off too much volume
-Tracheal deviation
-Dyspnea/ Very labored breathing
-Assess for respiratory distress, blood tinged sputum, severe coughing
-Notify MD immediately.
good Samaritan laws
-laws to protect individuals providing aid
-need to provide aid within training and scope of practice
-do not leave until assistance arrives or becomes dangerous or going to get assistance
safety is the
first priority
ABCs
airway, breathing, circulation
CABs
chest compressions, airway, breathing
-apply AED as soon as its available
external bleeding
find source and apply direct pressure and elevate area above heart
nosebleed
-pinch soft part of nose
-tip head forward
-after 10 mins go to ED
internal bleeding
harder to tell-monitor ABCs, and LOC
shock
-insufficient O2/nutrients to meet the body's needs=lack of circulation
-SX: First rapid pulse and cold clammy skin; then cyanosis, weakness, N/V, thready pulse; finally lost peripheral pulses, restlessness, yawning/gasping, unconsciousness
shock treatment
-Try to maintain blood flow: Lay down and raise legs (TRENDELENBURG POSITION)
-cover with blanket.
-Check ABC’s—maintain patent airway.
-Stop bleeding; treat underlying cause.
-Call EMS immediately if unconscious.
-If anaphylaxis, use epinephrine-pen—inject through clothes; need to hold in place for 10 sec prior to withdrawing.
wounds/injury
-do not removed embedded objects, stabilize and get help
-direct pressure
thermal burn
burn caused by heat-cool with lots of cold water for 15-30min-cover with non-adhesive dressing-if large area call for EMS
dont use --- directly on burns
Ice or use ointment or break blisters
-blisters are protective
electrical burns
-be sure no lice electricity
-cover entry and exit wounds
-monitor ABCs
musculoskeletal inujries
rest, ice, compression, elevation=RICE
concussion
Very short period of unconsciousness, confusion, vomiting, anxiety, amnesia, visual disturbances
compression injury
Above symptoms to a higher degree, with symptoms worsening over time
objects or chemicals in the eye
-Do not remove embedded objects; rinse with copious sterile water/saline; pull down upper or lower lid.
-Go to ED for chemical spill in eye.
heat exhaustion
mild
-sweating, pale, muscle cramps, weakness, H/A, N/V, faintness
-treatment= loosen clothing, cool moist cloths, move to cool location, cold drinks
heat stroke
emergency
-altered LOC, flushed, hot, dry skin, hyperventilation, 105>
-call EMS, douse in cold water, cover in cold towels, ice packs to groin, neck, and armpits
Stroke
-SX: Facial, arm, or unilateral weakness; speech problems; blurred or dec. vision (especially in 1 eye); sudden severe H/A
-Call EMS.
-Help to comfortable position, observe ABC's.
-If unconscious, place in recovery position on unaffected side.
MI or angina
-SX: Chest pain/tightness, possibly radiating to shoulders, jaw or L arm; nausea/indigestion (especially in women); pale, clammy or gray skin; anxiety; denial
-Call EMS.
-Loosen tight clothing and put in "W position (lying back a bit with knees bent).
-If alert and not on anticoagulants, give 1 adult aspirin.
-If have angina, give nitro; if unrelieved after 2 nitro, call EMS.
-Monitor ABC's and VS.
seizures
-Protect from injury.
-Do not put anything in mouth during seizure.
-After seizure, place in recovery position; monitor respirations.
-Try to monitor time in seizure.
-More to come on this!
Skin cancer S/S
-developed new moles or lesions?
-moles or lesions changed in any way(color, borders, size)?
pressure ulcers
-NOT "bed sores"
-Caused by pressure
-Tissue injury/ischemia caused by external forces
-Results in unrelieved pressure resulting in ischemia and damage to the underlying tissues
-Time + pressure = ulceration
-Braden Risk Assessment
Factors:
-Age
-IMMOBILITY
-Incontinence/ moisture
-Skin friction and shearing
-Vascular disorders
-Obesity
-Mental Status
-Impaired skin integrity
-Poor nutrition/ hydration
-Fever
-Edema
-Chronic disease ( DM, CKD, CHF, COPD)
-Sedation
wounds
injuries in which the skin is broken
-intentional
-unintentional
-open
-closed
-acute
-chronic
-contusion
-abrasion
-laceration
-penetrating
-puncture
intentional wound
a wound that is the result of a planned surgical or medical intervention
unintentional wound
A wound resulting from trauma
open wound
the skin or mucous membrane is broken
closed wound
an internal injury with no open pathway from the outside
acute wound
usually heal within days to weeks