Period 3 Pt. II: Articles of Confederation through John Adams' Presidency
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Federalist Number 10
Madison states that one of the strongest arguments in favor of the Constitution is the fact that it establishes a government capable of controlling the violence and damage caused by factions

Constitution
A document which spells out the principles by which the government runs and the fundamental laws that govern a society

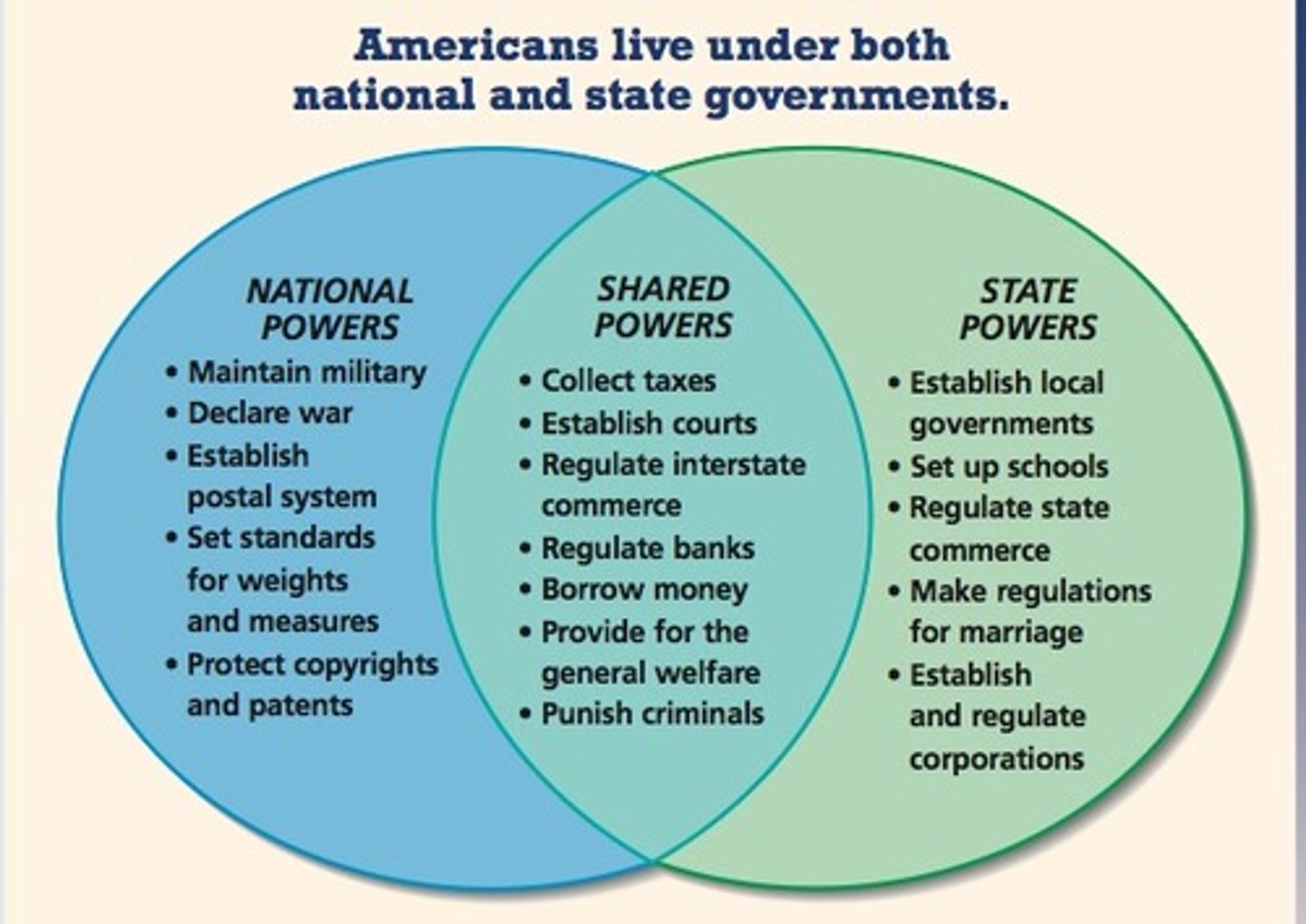
Federalism
The sharing of power between the nation and the states; as upheld by Amendment #10 (powers reserved to the states)
French Revolution
The revolution that began in 1789, overthrew the French absolute monarch; eventually would be a challenge to Pres. Washington's Proclamation of Neutrality; most Americans supported the French Rev, because the French were following in America's footsteps

Republicanism
System of government in which power is held by the people and is exercised by elected representatives responsible for promoting the common welfare
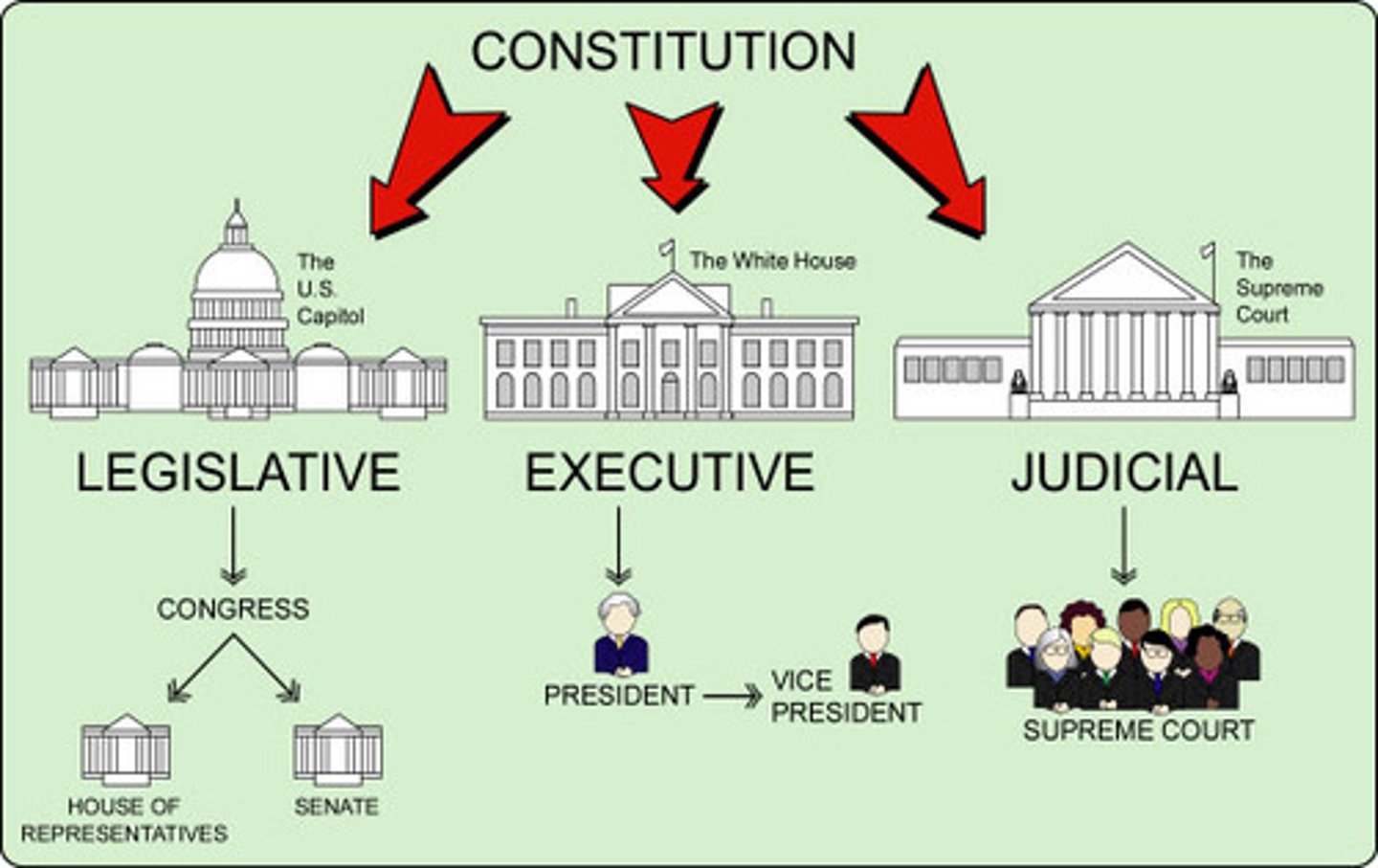
Legislative Branch
Branch of government that makes the laws; bicameral legislature = House of Reps and Senate

Separation of Powers
Constitutional division of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with the legislative branch making law, the executive enforcing the law, and the judiciary interpreting the law
Ratification Process of the Constitution
the ratification of the Constitution required only nine of the thirteen states (not unanimity, like the Articles of Confederation); 2/3 Congress votes to approve, 3/4 states must ratify

George Washington
1st President of the United States (established precedents of the Executive Branch); commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution; set precedent of serving only two terms in office; gave Farewell Address in 1796 - 3 warnings - no political parties, do not form foreign alliances, do not accumulate large public debt

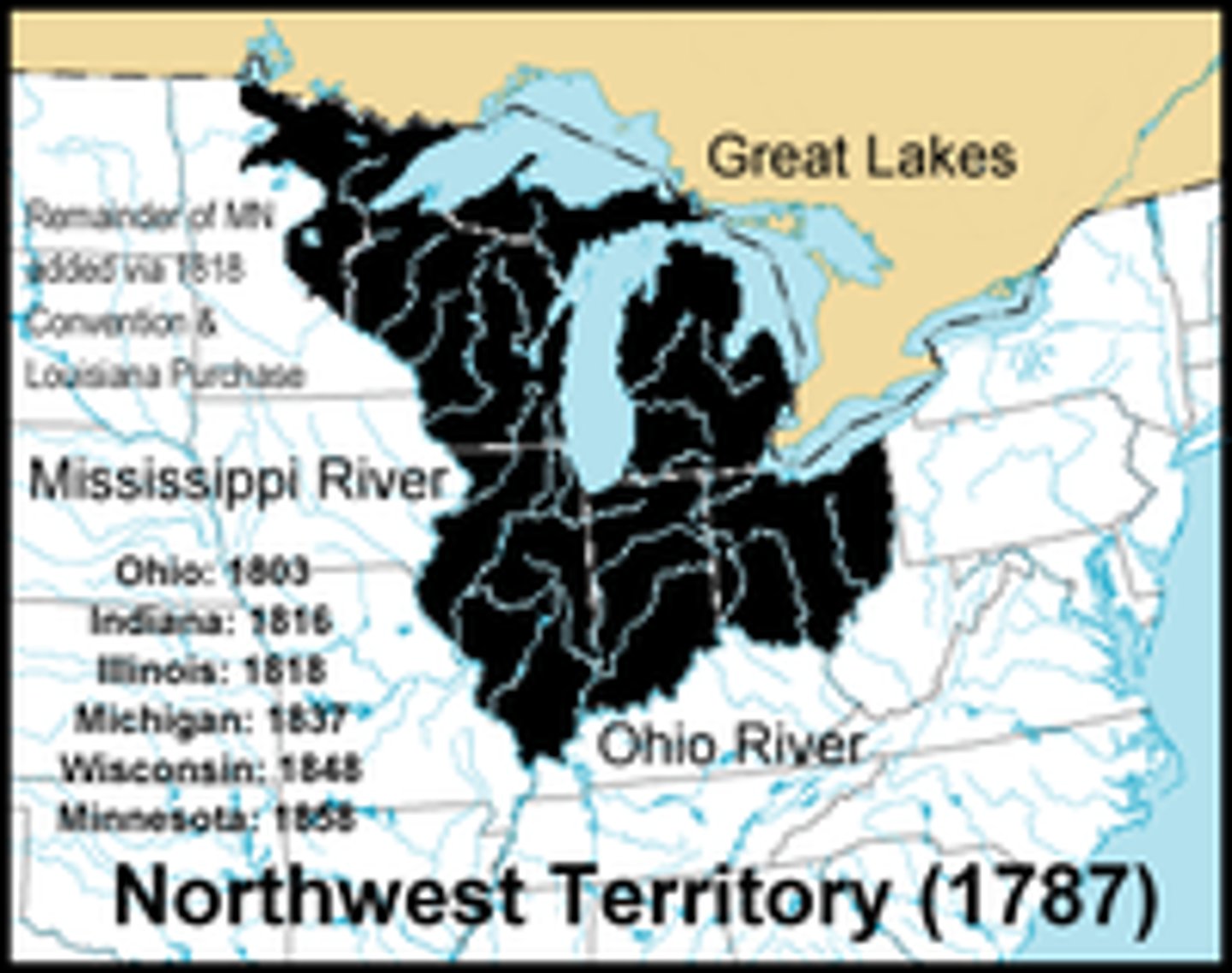
Northwest Ordinance of 1787
Considered the one strength of the Articles of Confederation (in regards to the organization of western lands); it established a system for setting up governments in the western territories; provided that the territory would be divided into 3 to 5 states, slavery was banned in the territory, 5,000 free men = territorial status, 60,000 free citizens = population required for statehood
Articles of Confederation
1st Constitution/form of govt after independence; created to be very weak-no executive, no judicial, no power to tax, no power to regulate trade, one-house congress), one vote per state

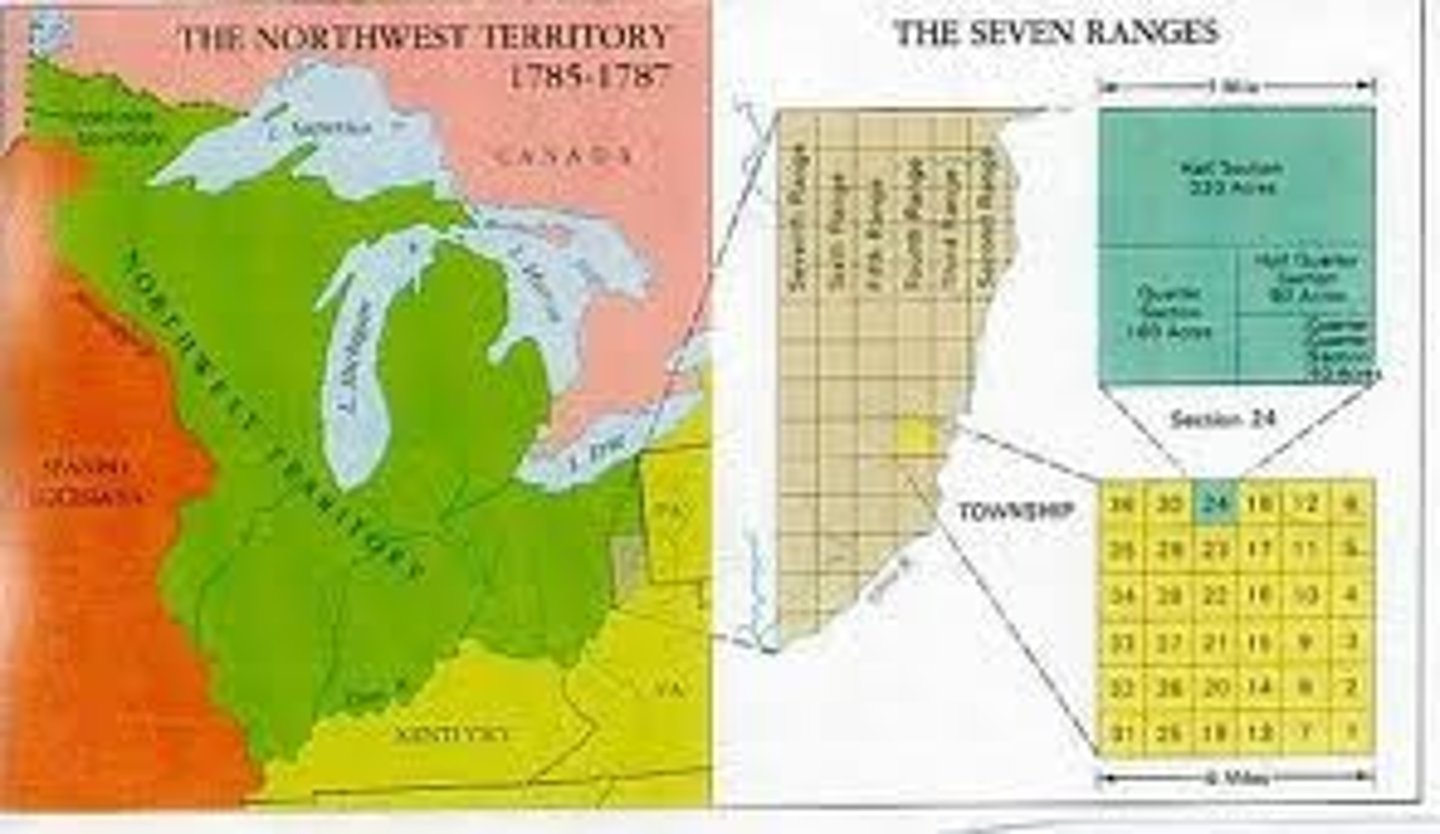
Ordinance of 1785
Considered the one strength of the Articles of Confederation (in regards to the organization of western lands); a law that divided the Northwest Territory into a system of townships to facilitate the sale of land to settlers; 640 acre sections could be sold to the highest bidder for not less than $1/acre
Shays' Rebellion
Massachusetts farmer rebellion led by Daniel Shays in 1786-1787, protesting farm foreclosures; rebellion highlighted the need for a stronger national government as the Articles were too weak and the federal govt could not stop rebellions

Virginia Plan
"Large state" proposal for the new constitution, calling for state populations to be used to determine representation in Congress (the larger the state's population, the more representatives); illustrates struggle between states for representation in Congress
New Jersey Plan
"Small state" proposal for the new constitution, calling for equal representation in Congress; illustrates struggle between states for representation in Congress

Great Compromise (aka Connecticut Compromise)
Compromise between the large and small states; created a bicameral legislature; House of Reps (lower house) is where representation would be based off state populations and "the people" would elect their reps; the upper house or the Senate would have equal representation or 2 Senators per state (states would choose the Senators). The compromise combined the needs of both large and small states and formed a fair and sensible compromise over the issue of representation in Congress

Three-Fifths Compromise
Agreement that three out of five slaves would could into the population for the purpose of representation in Congress and for taxation ; slaves had no voting rights

Electoral College
Developed because the founding fathers did not trust "the people" to directly elect the President; electors selected by a state cast votes for presidential candidates based off the popular vote of their state

Executive Cabinet
Advisers for the President consisting of the heads of the executive departments (originally Treasury, State, War), the Vice President, and a other officials selected by the President.

Bill of Rights
First ten amendments of the Constitution that protect individual/civil rights; was not originally a
part of the Constitution (Feds said it was unnecessary b/c they are implied rights); Antifederalists refused to ratify the Constitution w/out a Bill of Rights - said Constitution insufficiently protected the rights of citizens ; James Madison drafted the Bill of Rights; ratified in 1791
1st Amendments
1st Amendment: Freedom of Religion, Speech, Press, Assembly, and Petition
Bank of the United States
Proposed by Alexander Hamilton as the basis of his economic plan, which also included paying off the nation's and the states debts; he proposed the bank as a means to collect taxes. It would also provide a strong and stable national currency. Thomas Jefferson opposed the bank; he thought it was unconstitutional. This issue brought about the issue of implied powers (or the elastic clause of the Const).

Strict v. Loose Interpretation of the Constitution
Strict interpretation: literal interpretation of the Const; whatever is not mentioned specifically in the Constitution cannot be done
Loose interpretation: broad interpretation of the Constitution; bend the rules, implied powers; this was favored by Alexander Hamilton as a means to of create the Bank of the US
Implied Powers (Elastic Clause)
Powers not specifically mentioned in the constitution

Whiskey Rebellion (1794)
W. Pennsylvania farmers rebelled against Hamilton's excise (luxury) tax on whiskey; October, 1794, the army, led by Washington, put down the rebellion (one time a president led troops into a conflict). The incident showed that the new government under the Constitution could react swiftly and effectively against challenges to the federal government, in contrast to the inability of the government under the Articles of Confederation to deal with Shay's Rebellion

Jay's Treaty (1794)
Treaty signed between the U.S. and Britain in which Britain sought to improve trade relations, stop impressment of American sailors, and agreed to withdraw from forts in the Northwest Territory in order to finally have peace along the frontier lands

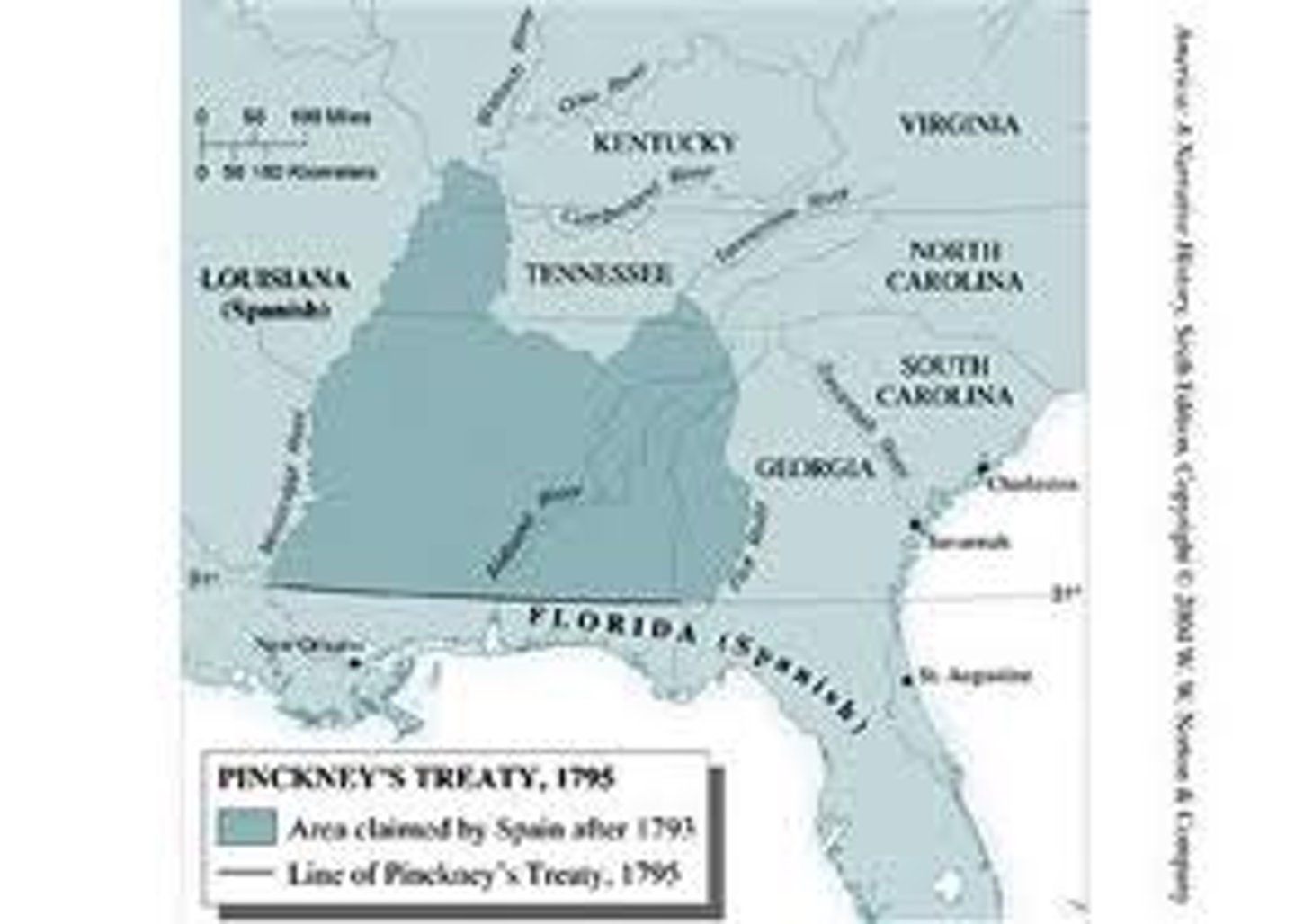
Pinckney's Treaty (1795)
Treaty with Spain that allowed Americans to use the Mississippi River and have the right of deposit in the city of New Orleans and minimized tensions created with western expansion
Washington's Farewell Address, 1796
Washington issued three warnings to the American people:
1. do not form political parties
2. do not accumulate a large public debt
3. do not form foreign alliances (remain neutral) with European nations

XYZ Affair
US envoy sent to France in 1797 to discuss the disputes that had arisen out of the U.S.'s refusal to honor the Franco-American Treaty of 1778 and the impressment of American sailors; Pres. Adams sent three delegates to meet with French foreign minister Talleyrand; France sent three agents/delegates (X,Y,Z) and told the American delegates that they could meet with Talleyrand only in exchange for a very large bribe; the Americans were insulted, returned to America, Federalists were outraged and called for war against France

Alien and Sedition Acts (1798)
Used by the Federalists to stop the growth of the Dem-Rep party as immigrants joined it; contains four parts:
1) Extended the residency requirement for American citizenship from 5 to 14 years
2) Alien Act - Gave the President the power to imprison or deport foreigners considered dangerous
3) Alien Enemies Act - Allowed US govt power to arrest and deport all aliens who were citizens of foreign nations at war with the US
4) The Sedition Act - made it a crime to speak or write critically about the Pres, Congress, federal govt or federal laws - violates the 1st amendment (freedom of speech/press)

Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions
Democratic-Republican documents that argued that the Alien and Sedition Acts were unconstitutional (violated the 1st Amendment); also states that states could ignore federal laws they saw as unconstitutional

Native American Policy under Washington
By 1795, the US government set out to dispossess (take land from) the Native Americans and continue to drive them west beyond the Mississippi River

Alexander Hamilton (Federalist)
Founded the Federalists; believed in loose construction of Const, industrialized/commercial economy, strong military, wealthy & educated running the nation, Pro-British, created the Bank of the US (to house fed govt money)

Thomas Jefferson (Democratic-Republican)
Founded the Democratic-Republicans; believed in strict construction of Const, agricultural/agrarian economy, farmers & laborers running the nation, Pro-French, opposed Bank of US; sought to get new national capital relocated to the South as a compromise to Hamilton's Economic Plan

Popular Sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power in the government system resides in the people; the people are the authority/voice in the govt system; "We, the people"

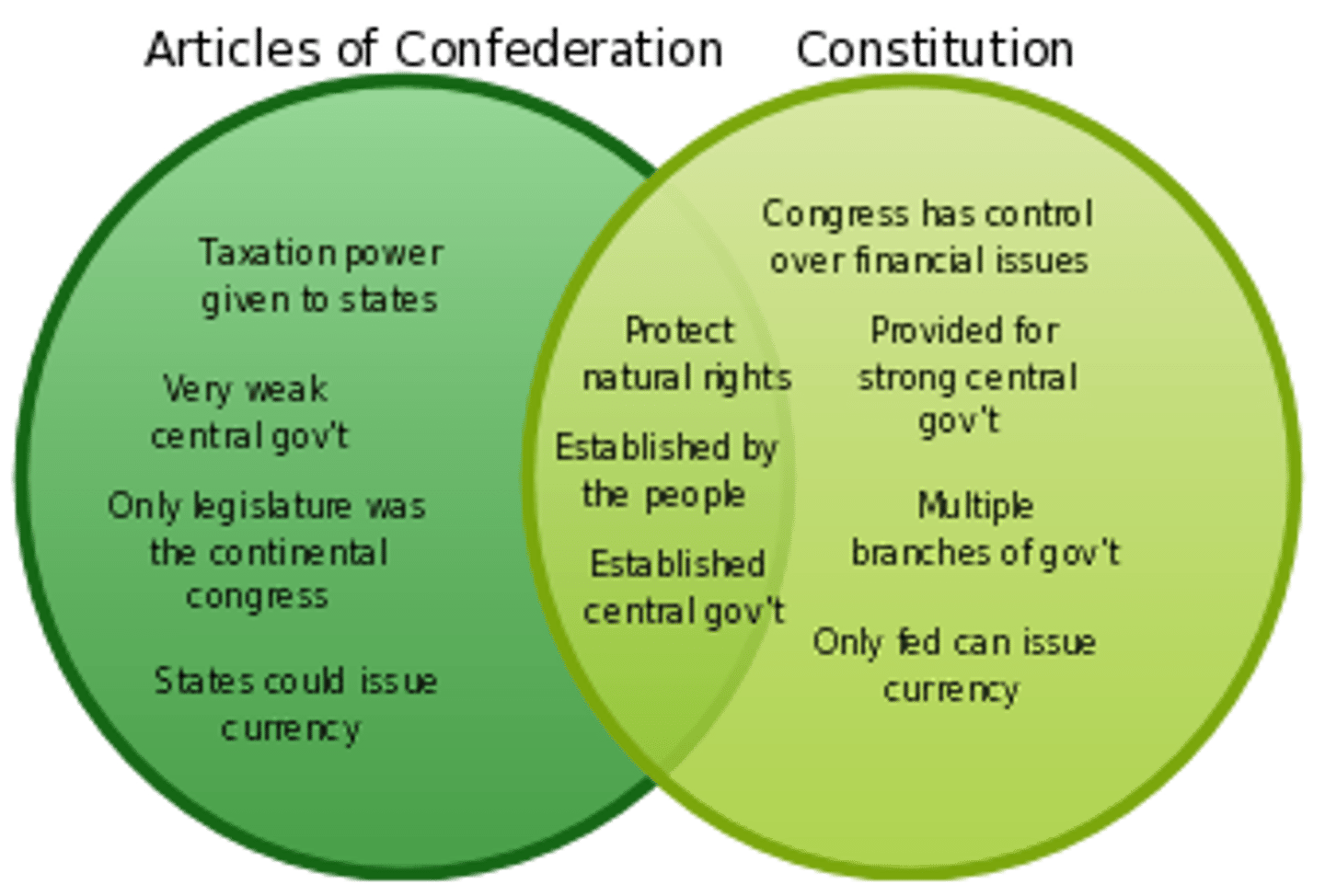
Articles of Confederation vs. the Constitution
Articles of Confederation = authority/power mostly held within the states; difficult to pass laws (9/13 states); difficult to amend laws (13/13 states); established the orderly expansion west in the NW Territory and how to admit new states to the union.
Constitution = strong federal govt; shared powers with states (like taxation) - both may tax the people; print coin money for the entire nation (each state would no longer print own money); could elect reps to a bicameral legislature giving people a voice in govt; federalism - Const grants specific powers to fed govt and reserved other powers to the states
Federalists
A term used to describe supporters of the Constitution during ratification debates in state legislatures; led by Hamilton, Madison, Jay
Antifederalists
Opponents of ratification of the Constitution and of a strong central government; desired strong state governments; led by Jefferson, Henry, Mason
Political Parties in the 1790s
Democratic-Republican and Federalists; many of the Founding Fathers felt that political parties were selfish and threatened the existence of the republican system of government