1.3 marketing
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Marketing strategy -
A medium to long-term plan to achieve marketing objectives through the use of its marketing mix.
Marketing mix –
How a business uses the four key components of its marketing strategy: Product, Price, Place & Promotion (the 4Ps)
Marketing tactics -
short term activities to boost sales, e.g. sales promotions.
Mass versus niche
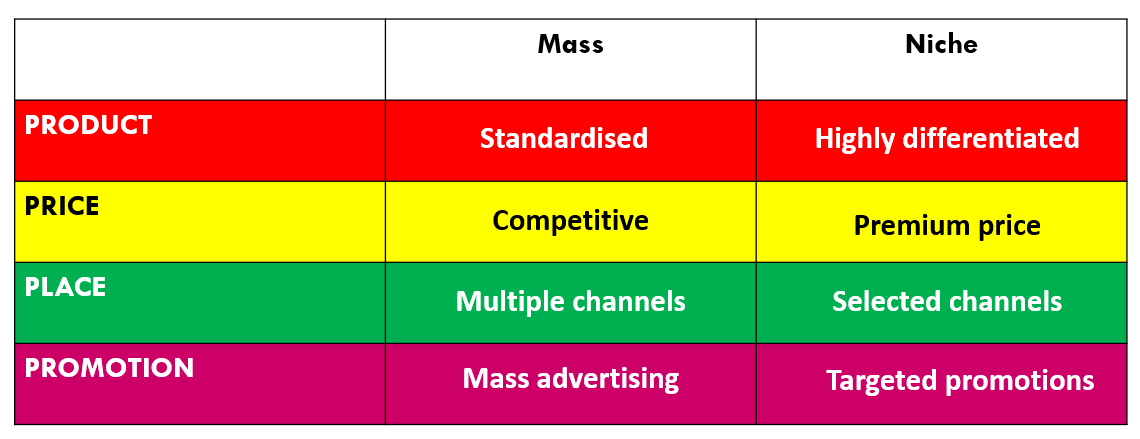
important differences with B2B marketing that you should note are:
Number of customers
Power of buyers
Supplier/Customer Relations
Complexity of buying process
The design mix -
The features of a product that allow it to both meet the needs of the market and make effective use of a business’ resources. Elements include: aesthetics, function and economic manufacture.
Sustainability –
Designing products and producing them in a way that avoids resource depletion, i.e. does not affect the long-term supply of inputs used.
Waste minimisation –
Designing products that can be produced and used with minimum waste, e.g. they are durable, can be easily repaired or can be reused or recycled.
Ethical sourcing -
involves selecting suppliers who behave responsibly towards the environment and treat their workforce fairly.
areas of the design mix
Cost, aesthetic and function
The Design Mix & Social Trends, may include-
1. Sustainability
2. Ethical Sourcing
Responding to Social Trends
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Source of competitive advantage: Differentiation By emphasising ethical sourcing or sustainability in branding, businesses can differentiate their product from rivals. This can help both to retain existing customers and to attract new ones. Customers that prioritise these issues are likely to remain loyal to the brand, helping to maintain or even increase market share.
| This may only matter to a small segment of the market, limiting sales. This is especially true where sustainability / ethical sourcing requires a significant trade off in terms if function, aesthetic and cost of manufacture (and therefore likely selling price). |
Ability to charge a premium price Some consumers will care a great deal about these issues. Knowing that a product has been produced ethically/sustainably adds value to the product in their eyes. This reduces their price sensitivity/makes demand less price elastic. This allows the business to charge a premium. | Costs are likely to be higher, which may offset this benefit.
Is there a trade-off between profit and ethics??
|
Stakeholder satisfaction As well as customers, other stakeholders may care a lot about these (e.g. employees and shareholders). This can help with recruitment, retention and raising finance. | Greenwashing? Risk of damage to the brand if the business fails to live up to claims of sustainability/ethical sourcing. |
The Product Life Cycle –
A theoretical model which describes the stages a product goes through over its life
Extension strategy –
A medium to long term plan to extend the life of a product and delay/prevent decline.
Product life cycle
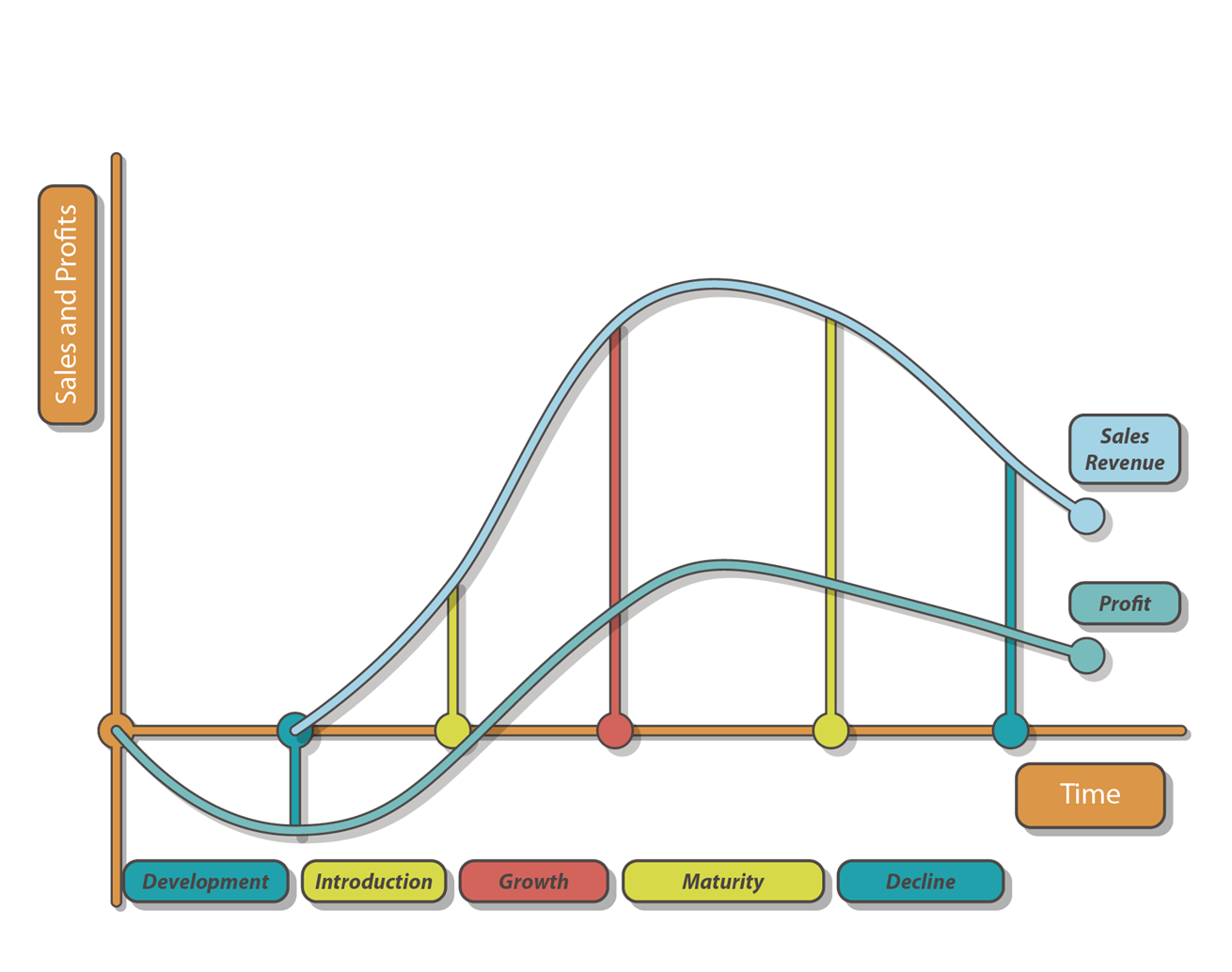
extension strategies

Cannibalisation:
Introducing new versions or adaptations may cannibalise sales of other products. This can result in increased competition within the company's own product portfolio.
Costs of Implementation:
Implementing extension strategies incurs costs, such as marketing expenses for promotional campaigns or the costs of adapting the product. If the strategy is not successful (which is a serious risk as extension strategies do not always succeed in revitalising a product) these costs may not be recouped.
how useful is the Boston matrix?
Advantages | Disadvantages |
•Helps managers to identify suitable strategies for their products based on their position in the matrix.
•Helps managers to achieve a balanced portfolio.
| •Strategies suggested will not suit all situations, e.g. sometimes Dogs can earn significant cash flows or profit and should not be divested in the short-term.
•It only looks at current data – does not look at trends or predictions for the future.
•Looks at only two factors when analysing the product portfolio: market share and growth. Other factors may be more important e.g. profit/profitability. |
Public relations –
activities planned to get favourable publicity in the media, e.g. issuing press releases, giving interviews or holding special events.
Personal selling –
direct communication between a sales person and customers, e.g. in-store, by telephone or (especially in B2B) in sales meetings.
Factors influencing choice of promotional strategy
Target market/ position
nature of the product
stage in the plc
competition
marketing objectives
external factors
Advertising pros and cons
Advertising | Mass Reach: Advertising allows businesses to reach a large and diverse audience. Through various channels such as television, radio, print, and online platforms, companies can expose their message to a broad demographic. Control Over Message: Advertisers have control over the content and presentation of their message. They can carefully craft the message to convey specific brand values, product features etc. | High Costs: Creating and placing advertisements, especially on popular platforms, can be expensive. For small businesses with limited budgets, it might be unaffordable. Limited Interaction: Advertising is generally a one-way communication method. There is limited opportunity for immediate interaction with customers, making it hard to gauge reactions/close a sale. |
Direct marketing pros and cons
Direct marketing | Targeted Communication: marketers can tailor messages to specific individuals or groups. This can increase the relevance of the message, making it more likely to resonate with the intended audience. Measurable Results: Businesses can track response rates, conversion rates, and other key metrics, enabling them to assess the effectiveness of their campaigns and make data-driven decisions. | Potential for Intrusiveness: Telemarketing or unsolicited emails, can be perceived as intrusive. This can lead to negative reactions from consumers and damage the brand's reputation. Cost of database management: Specialists will be needed to manage data (although costs could be reduced by outsourcing). |
Sales promotion pros and cons
Sales promotions | Stimulates Immediate Sales: Discounts, coupons, or limited-time offers, can create a sense of urgency, encouraging consumers to make immediate purchasing decisions. Customer Loyalty: Well-executed sales promotions can enhance customer loyalty. Offering exclusive deals or rewards for repeat purchases can help retain existing customers and attract new ones. | Potential for Brand Erosion: Overreliance on sales promotions may lead consumers to associate the brand only with discounts. This can erode the perceived value of the product or service at its regular price. Reduced profit margin: Sales promotions often boost sales, but lower profitability. |
Public relations pros and cons
Public relations | Enhances Credibility: Public relations efforts, such as press releases or media coverage can be seen as credible, especially if the third-party endorsements are from reputable sources that consumers trust. Cost-Effective: Compared to some advertising , PR can be a cheaper way of getting the brand seen on mass media. | Limited Control Over Message: marketers have less control over how their message is portrayed by the media. Negative stories or misinterpretations can damage the brand. Time-Consuming: Building and maintaining positive relationships with the media and other stakeholders takes time. Opportunity cost? |
Sponsorship pros and cons
Sponsorship | Enhanced Brand Visibility: Sponsorship provides opportunities for brand exposure at events or through partnerships. This increased visibility can increase brand awareness. Targeted Audience Engagement: Sponsoring events or activities related to the brand's target audience allows for more focused and relevant engagement. This can lead to stronger connections with potential customers. | High Costs: Securing sponsorship deals, especially for popular events or with high-profile partners, can be expensive. May not be possible on a limited budget. Potential for Negative Association: If the sponsored event or entity faces controversy or negative publicity, the sponsoring brand may also be negatively affected by association. |
Personal selling pros and cons
Personal selling | Personalised Interaction: Personal selling allows for direct, one-on-one interaction with potential customers. Sales representatives can tailor their pitch to the individual needs and preferences of each customer. Immediate Feedback: Salespeople can receive immediate feedback from customers, addressing concerns or objections on the spot. | High Costs: Labour-intensive, requiring the employment of a sales force. Inconsistent quality: The effectiveness of personal selling can vary depending on the skills and knowledge of individual sales representatives; can impact overall brand coherence. |
Brand -
a business or product that is easily distinguished from competitors.
Corporate branding
The process of creating and promoting a brand image for an entire corporation, encompassing its values, identity, and reputation.
Product branding
- Creating and promoting a unique brand identity for a specific product, distinguishing it from competitors in the market.
Own-brand -
Products that are branded with the retailer's name rather than the name of the manufacturer.
Umbrella brand –
Brands that are assigned to more than one product, e.g. Dairy Milk.
Brandnomers -
Words that have become synonymous with a particular brand, often used generically. For example, using "Hoover" to refer to any vacuum cleaner
Rebranding -
The process of changing the identity of a brand to revitalise its image and/or appeal to a different target market.
Product differentiation -
where a business distinguishes its products/services from rivals. E.g. via a USP or really effective branding.
Emotional branding –
Building a brand by creating an emotional connection with consumers, often using storytelling and values to evoke specific feelings or associations with the brand.
Building a brand needs
Usp/ differentiations
advertising
sponsorship
social media
Benefits of strong branding
added value, reduced competitive threat, reduces risk of product development
why does customer loyalty matter?
Repeat business, reduced PED, Cost efficiency, brand advocacy
How does a business create customer loyalty?
consistent quality, Consistent branding, customer service, loyalty program, customer engagement and personalisation
What intermediaries are in a distribution channel?
Wholesaler, retailer, producer, consumer, online retail, own websites
Whole salers pros and cons
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Wide Market Coverage: Wholesalers typically have established relationships with retailers across different regions > easier to get products onto shelves. Reduced costs: Sell large quantities to a small number of wholesalers > lower costs of distribution Better service for small retailers > Wholesalers take on cost/risk of storing stock > can supply just-in-time to small retailers who cannot buy/store large amount.
| Loss of profit as the wholesaler requires a cut (as well as the retailer) OR Higher price paid by the consumer reducing demand (effect depends on PED) Loss of contact with the consumer>harder to identify/respond to change Lack of control over how the product is sold/presented etc as there is no direct contact with the consumer
|
retailers pros and cons
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Enables producers to meet the needs of customers better:
•Retailer often handles advice/after-sales service. •Provide credit terms to customers. Allows manufacturers to concentrate on their area of strength without the need to be distracted by retail.
|
|
direct channel pros and cons
Advantages | Disadvantages |
•Keep all of the profit margin •Retain control over how the product is priced/promoted. •Communicate directly with consumer – allows control over how the product is presented to customers/allows direct feedback.
|
|
Multi-Channel Distribution
This involves a business using more than one type of distribution channel and is very common today.
pros and cons
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Wider market reach: Can target different market segments more easily – e.g. offering physical stores may appeal to an older demographic, whereas retailing via social media may target younger customers more successfully. Improved competitiveness: Potential to gain a competitive edge by offering an integrated customer experience compared to competitors with a single-channel approach, e.g. order online, click and collect/return in store.
| Channel conflict: Conflict may arise between different channels, especially if they compete for the same customers (risk of cannibalising sales). Higher Costs: Setting up and managing different channels will increase expenses related to technology, logistics, marketing, and workforce (although some work can be outsourced, increasing efficiency).
|
Digital distribution pros and cons
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Higher sales: Allows for global reach / is highly convenient for customers, as they can purchase from their device and download/stream instantly > may retain customers more successfully long term due to better data analytics....
Data Analytics: Businesses can gather valuable data on consumer behaviour, preferences, and purchasing patterns through digital distribution platforms. This data can be used to make informed decisions and tailor offerings to customer needs, increasing loyalty/repeat purchase. Cost Efficiency: Compared to traditional distribution methods, digital distribution often involves lower costs. There are no expenses related to manufacturing physical products, shipping, or maintaining physical stores.
| Digital Divide: Not all consumers have equal access to digital platforms, leading to a potential digital divide. Some segments of the population may be excluded from digital distribution channels.
Digital Piracy: Digital products are susceptible to piracy and unauthorised distribution, which can result in revenue loss and challenges/costs in protecting intellectual property.
Initial Setup Costs: While digital distribution can be cost-effective in the long run, there may be significant upfront costs associated with developing and implementing digital platforms, especially for smaller businesses, affecting payback, ROI etc.
|
factors influencing price strategy
PLC, cost of business, level of competition, degree of price sensitivity, market position, extent of product uniqueness.
Penetration pricing -
Setting a low price at launch and increasing price later in the product lifecycle.
Price skimming -
Setting a high initial price at launch and lowering price later in the product life cycle.
Price skimming pros and cons
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Maximises revenue > high price contribute to an exclusive brand image > helps attract "early adopters" who have a low PED > maximum revenue can be squeezed out of this market segment before price is lowered to attract more price sensitive customers. | Limited sales > high initial prices will limit sales volume > likely to mean high limited economies of scale / low levels of capacity utilisation etc > high unit costs > reduced profit margins. |
Recovers development costs > high tech/complex products have high R&D costs > setting a high initial price can help to payback these costs quickly > this can be important as new competitors may soon enter the market making it hard to maintain sales/high prices long term. | May attract competition > high prices can act as a signal, attracting new entrants > unless the original product is well protected (e.g. a patent) new entrants may launch copycat alternatives > as new entrants are likely to have lower R&D costs they can price lower > could quickly steal market share. |
Price penetration pros and cons
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Grow market share > low price can encourage customers to switch/try the product > helps to build sales and establish the brand in the market > if product/brand is strong enough, loyalty may be established allowing price to be raised later, maximising revenue. | Risk to brand image > a low price may lead to a perception of relatively low quality > sales may not grow as planned /it may be difficult to raise price later without a substantial fall in sales volume. |
Economies of scale > if sales volume rises quickly can benefit from economies of scale > e.g. increased power over suppliers > bulk buying discounts > lower unit costs > help to make a good margin despite low initial price. | Low profit margins > low prices are likely to mean low profit margins until scale increases > harder to finance other costs that are high at this stage, e.g. promotion > may mean hard to grow sales. |
Cost-plus pricing -
Based on placing a percentage mark-up on the unit cost of producing a good or service
Pros and cons of cost plus pricing
Advantage | Disadvantage |
Ensures that the price chosen will generate the required profit margin>ROI for owners/for reinvestment into the business
| Market conditions are totally ignored (e.g. competitors prices, consumers' willingness to pay) > although margin may be adequate, sales may be too low to achieve adequate profit overall. |
Competitive pricing -
When a business sets a price for its products after considering the prices set by its competitors. This usually means setting price the at the same price as the market leader or below.
pros and cons of competitive pricing
Advantage | Disadvantage |
Avoids price wars > by charging a price similar or just below market leaders businesses can avoid price wars > these lead to lower prices and no increase in market share > this is very important for small businesses who would not win a price war due to lack of economies of scale. | Promotional cost > Avoiding competing on price will mean businesses need to compete in other ways > this is likely to mean spending heavily on promotion > margins will be reduced. High enough to cover costs? |
Dynamic pricing -
A flexible pricing strategy in which the price of a product or service is adjusted based on various factors in real-time, e.g. changes in demand, competitor actions etc.
pros and cons of dynamic pricing
Advantage | Disadvantage |
Allows businesses to maximise revenue by responding to market conditions.
| May be considered unethical / may lead to negative reactions from customers. |
Psychological pricing -
setting prices in a way that influences consumers' perceptions. E.g. £9.99 rather than £10 or bundling.
Pros and cons for psychological pricing
Advantage | Disadvantage |
Can maximise sales at virtually no cost to the business. | May be considered unethical / may lead to negative reactions from customers if they consider it to be manipulative. |
Predatory pricing –
Lowering price (sometimes to below unit costs) with the goal of forcing a competitor out of the market.
Reasons for changing from B2B to B2C
Growth, profitability, direct relationship with consumers, brand building- These will lead to changes in the marketing mix.