Multi-store Model (MSM)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is the multi-store model? (2)
Simplistic model inspired by computer science
Suggested by Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968)
What were the 3 suggestions of the model?
Model Suggests…
Memory consists of a number of separate locations in which information is stored
Memory processes are sequential
Each memory store operates in a single uniform way
Describe or draw the MSM model
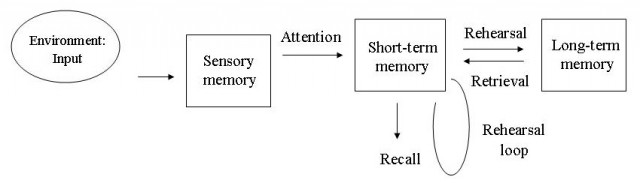
What are the 3 memory stores?
sensory memory, short-term memory (STM), and long-term memory (LTM)
What is the sensory memory store? (5)
where stimuli enters
modality specific (stores information separately based on the sensory modality, therefore each sense has its own separate store)
visual store (iconic memory) and the auditory store (echoic memory) are the most important
duration: a few seconds
selective attention is the ability to focus on important stimuli while filtering out irrelevant ones. It is a key factor in determining whether information moves from sensory memory to STM.
What is the STM store? (4)
gateway to long-term memory
capacity: (assumed to be limited to) 7+/-2
duration: approx. 6-18 seconds
So information is quickly lost or displaced by new information if not rehearsed. This makes rehearsal vital to keeping material active in STM by repeating it until it can be stored in LTM
Who proposed the “Magic Number 7” (plus or minus 2)?
Miller (1956) proposed the “Magic Number 7” (plus or minus 2) and the average memory span is between 5 and 9 items. In this experiment, participants were asked to memorize a list of numbers, each time increasing by one digit.
Who argued against “Magic Number 7” (plus or minus 2)?
Cowan (2010) argued this task allows for the practice effect. So, Cowan had participants recall a “running span procedure” where they listened to a list of numbers but were unaware of how long the list would be. He found participants recalled a range of 3 to 5 digits.
Biological research supports Cowan’s findings:
Brain scans indicate that the activity in the parietal cortex correlates with STM capacity. Activity increases with every additional number that needs to be recalled, until 4 digits. Then activity levels out in this area. (Vogel and Machizawa, 2004)
What is the LTM store? (4)
storehouse of information
unlimited in capacity and duration (currently psychologist do not know how much information can be stored there)
stored material is not an exact replica of information (e.g. events or facts) but is stored as some outline form
memories can be distorted when they are retrieved because we fill in the gaps to create a meaningful memory
What are 2 studies that support the MSM?
HM/ Milner (1966) and Glanzer and Cunitz (1966)
What are 2 strengths of the MSM?
Significant supporting research
both from experimental [Glanzer and Cunitz (1966)] and biological [HM: Milner (1966)] research
Historical Importance
Influenced our understanding of memory and was the basis for many other models
What are 2 limitations of the MSM?
oversimplified
assumes that each of the stores works as an independent unit
fails to explain… (4)
memory distortion, role of emotion in memory (flash bulb memories), why some things may be learned with a minimal amount of rehearsal, or why even when we rehearse a lot to remember information, it is not transferred to LTM
What study challenged the simplicity of the STM in this model??
Logie (1999) challenged the assumption that the STM is simply a gateway to LTM through rehearsal. He argues that there must be an interaction between STM and LTM in which the information is interpreted with previously stored knowledge and experiences. Therefore, STM is a “workstation” that handles and computes information coming from the sensory store with knowledge already stored in the LTM.
What is the primacy effect?
the cognitive tendency to remember information presented first because it had time to be rehearsed and transferred to long-term memory
What is the recency effect?
the cognitive tendency to remember information presented recently because they are still in short-term memory
What is chunking?
the technique of remembering information by grouping it into smaller groups