unit 4: chromosome discovery & structure
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
1
New cards
Mendelian “factors”
**Discovery of the Chromosome:**
* carried traits from one generation to the next
* carried traits from one generation to the next
2
New cards
Walther Flemming
**Discovery of the Chromosome:**
* recognized and explored the fibrous network within the nucleus: **chromatin** or "__stainable__ material"
* recognized and explored the fibrous network within the nucleus: **chromatin** or "__stainable__ material"
3
New cards
the precise distribution of nuclear material
**Discovery of the Chromosome:** *Walther Flemming*
* observed cells in various stages of division and recognized that **chromosomal movement** during __mitosis__ offered a **mechanism** for **___** during cell division
* observed cells in various stages of division and recognized that **chromosomal movement** during __mitosis__ offered a **mechanism** for **___** during cell division
4
New cards
Theodor Boveri
**Discovery of the Chromosome:**
* provided the first evidence that **germ cell chromosomes imparted continuity** between generations
* one of the pioneers of embryology
* looked at not only the nuclei but other changes
* provided the first evidence that **germ cell chromosomes imparted continuity** between generations
* one of the pioneers of embryology
* looked at not only the nuclei but other changes
5
New cards
Ascaris embryos
**Discovery of the Chromosome:** *Theodor Boveri*
* provided one of the first descriptions of __meiosis__
* provided one of the first descriptions of __meiosis__
6
New cards
Walter Sutton
**Discovery of the Chromosome:**
* confirmed and expanded upon Boveri's observations
* described the **configurations of individual chromosomes** in cells at various stages of __meiosis__ (testes of *Brachystola magna*)
* confirmed and expanded upon Boveri's observations
* described the **configurations of individual chromosomes** in cells at various stages of __meiosis__ (testes of *Brachystola magna*)
7
New cards
Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
**Discovery of the Chromosome:** *Sutton & Boveri*
* provided the physical basis of the Mendelian law of heredity
* provided the physical basis of the Mendelian law of heredity
8
New cards
1910, Thomas Hunt Morgan
**Discovery of the Chromosome:** *Sex Chromosomes & Specific Genes*
* Experimentally demonstrated Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance using *Drosophila melanogaster*
* pioneered “**Fly Room**” experiments
* Experimentally demonstrated Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance using *Drosophila melanogaster*
* pioneered “**Fly Room**” experiments
9
New cards
1916, Calvin Bridge
**Discovery of the Chromosome:** *Sex Chromosomes & Specific Genes*
* helped establish the **chromosomal basis of heredity and sex**
* **non-disjunction/separation** of chromosomes during meiosis
* helped establish the **chromosomal basis of heredity and sex**
* **non-disjunction/separation** of chromosomes during meiosis
10
New cards
Aneuploidy
**Discovery of the Chromosome:** *Sex Chromosomes & Specific Genes -* __*Bridge*__
improper/abnormal number of a chromosome set
improper/abnormal number of a chromosome set
11
New cards
Chromosome
* Threadlike structures or “**colored bodies**”
* Factors that distinguish one species from another
* Factors that distinguish one species from another
12
New cards
Made of protein and a single molecule of DNA
Chromosome composition
13
New cards
histones
**Chromosome**:
protein component involved in the wrapping of the DNA molecule until it becomes a hyper-looped structure
protein component involved in the wrapping of the DNA molecule until it becomes a hyper-looped structure
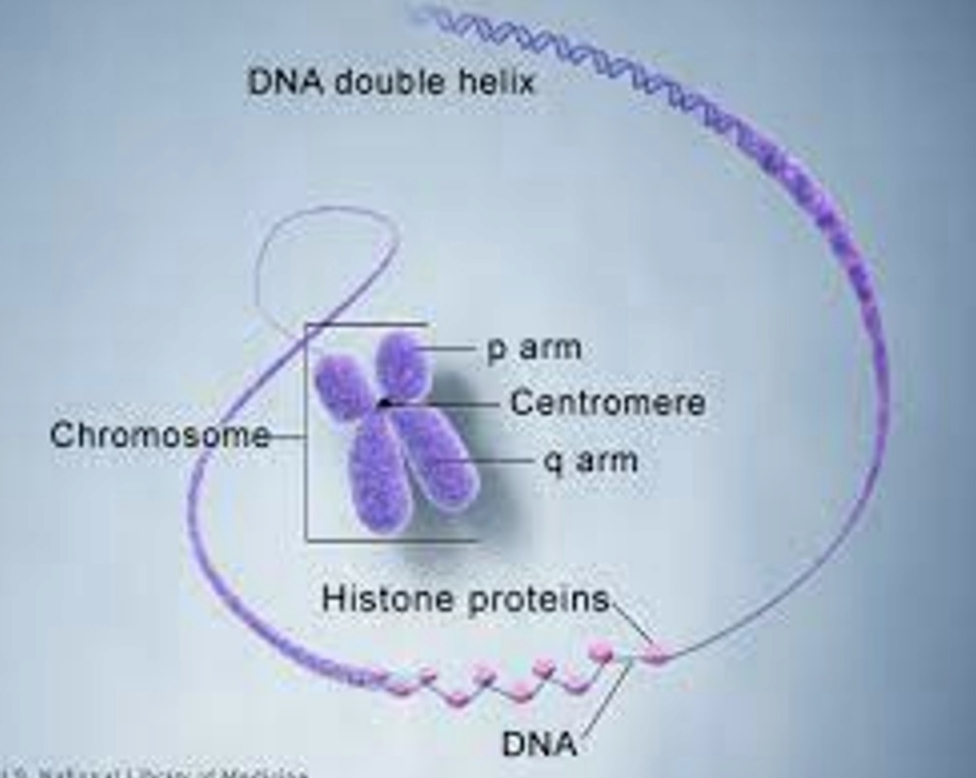
14
New cards
Enable **transmission of genetic information** from one generation to the next
What do chromosomes do?
15
New cards
mitosis
**What do chromosomes do?**
Ensure daughter cell **retains** its own complete genetic complement
Ensure daughter cell **retains** its own complete genetic complement
16
New cards
meiosis
**What do chromosomes do?**
Enable each mature ovum and sperm to contain a **unique** single set of parental genes
Enable each mature ovum and sperm to contain a **unique** single set of parental genes
17
New cards
44
**Human Chromosome:**
autosomes
autosomes
18
New cards
2
**Human Chromosome:**
sex chromosomes/gametes
sex chromosomes/gametes
19
New cards
Autosomal inheritance
**Human Chromosome:**
inheritance through the cell’s bodies
inheritance through the cell’s bodies
20
New cards
Modern way of staining chromosomes
**Human Chromosome:**
chromosomes are given different colors
chromosomes are given different colors
21
New cards
euchromatin and heterochromatin
**Human Chromosome:**
banding patterns
banding patterns
22
New cards
Euchromatin
**Human Chromosome:**
genetically “**transcriptionable**” areas of the chromosome
genetically “**transcriptionable**” areas of the chromosome
23
New cards
chromosomes as **hereditary vehicles**
**What do Chromosomes do?**
facilitates reproduction and maintenance of species
facilitates reproduction and maintenance of species
24
New cards
Extra-chromosomal DNA
**Human Chromosome:**
Other DNA materials found in mitochondria
Other DNA materials found in mitochondria
25
New cards
Metaphase Chromosome
Replicated condensed chromosome with sister chromatids
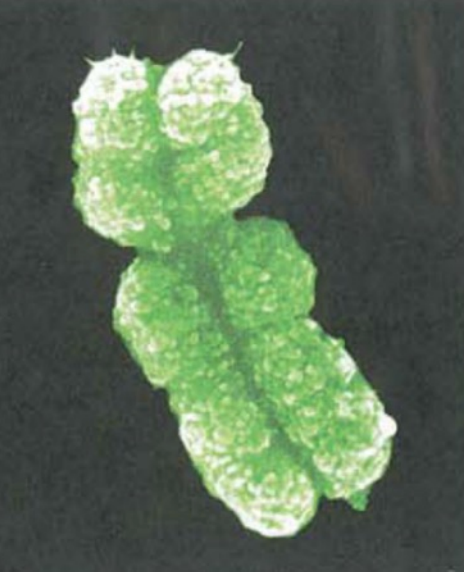
26
New cards
Telomere
**Metaphase Chromosome:**
* regions at the end of **linear** chromosomes
* look like **aglets**
* **protect** the chromosomes from **being destroyed at the tips**
* without this, there will be less information at the end regions
* regions at the end of **linear** chromosomes
* look like **aglets**
* **protect** the chromosomes from **being destroyed at the tips**
* without this, there will be less information at the end regions
27
New cards
pairing of homologous chromosomes
**Metaphase Chromosome:** *Telomere*
* attach the cells at the side of nuclei that allows for ___
* attach the cells at the side of nuclei that allows for ___
28
New cards
telomerase
**Metaphase Chromosome:** Telomere
* enzyme that makes sure information at the end of the chromosome is kept
* enzyme that makes sure information at the end of the chromosome is kept
29
New cards
Male karyotype at metaphase
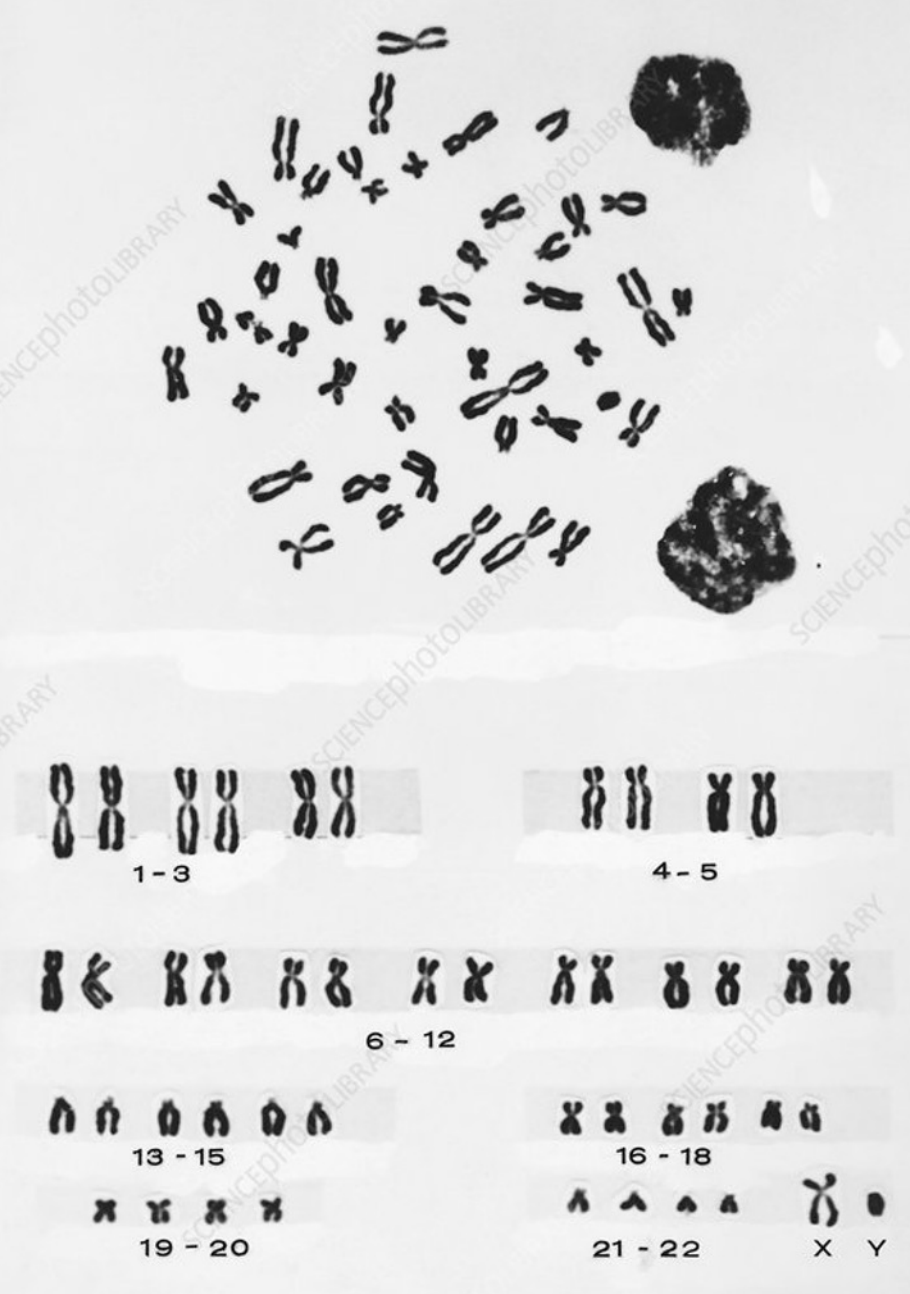
30
New cards
**147** nucleotide pairs of DNA
**Metaphase Chromosome:**
wrapped around the histone
wrapped around the histone
31
New cards
H1
**Metaphase Chromosome:**
* serves as the **closer of the DNA loop** around histones
* octamer
* allows for the **zigzag** structure which creates a tighter structure
* serves as the **closer of the DNA loop** around histones
* octamer
* allows for the **zigzag** structure which creates a tighter structure
32
New cards
basic amino acids
**Metaphase Chromosome:**
Histone is rich in ___ which allows for **positive charges** to be present & **attract phosphate**
Histone is rich in ___ which allows for **positive charges** to be present & **attract phosphate**
33
New cards
Nucleosomes
**Metaphase Chromosome:**
* **“beads on a string”**
* 3D zigzag structure
* **“beads on a string”**
* 3D zigzag structure
34
New cards
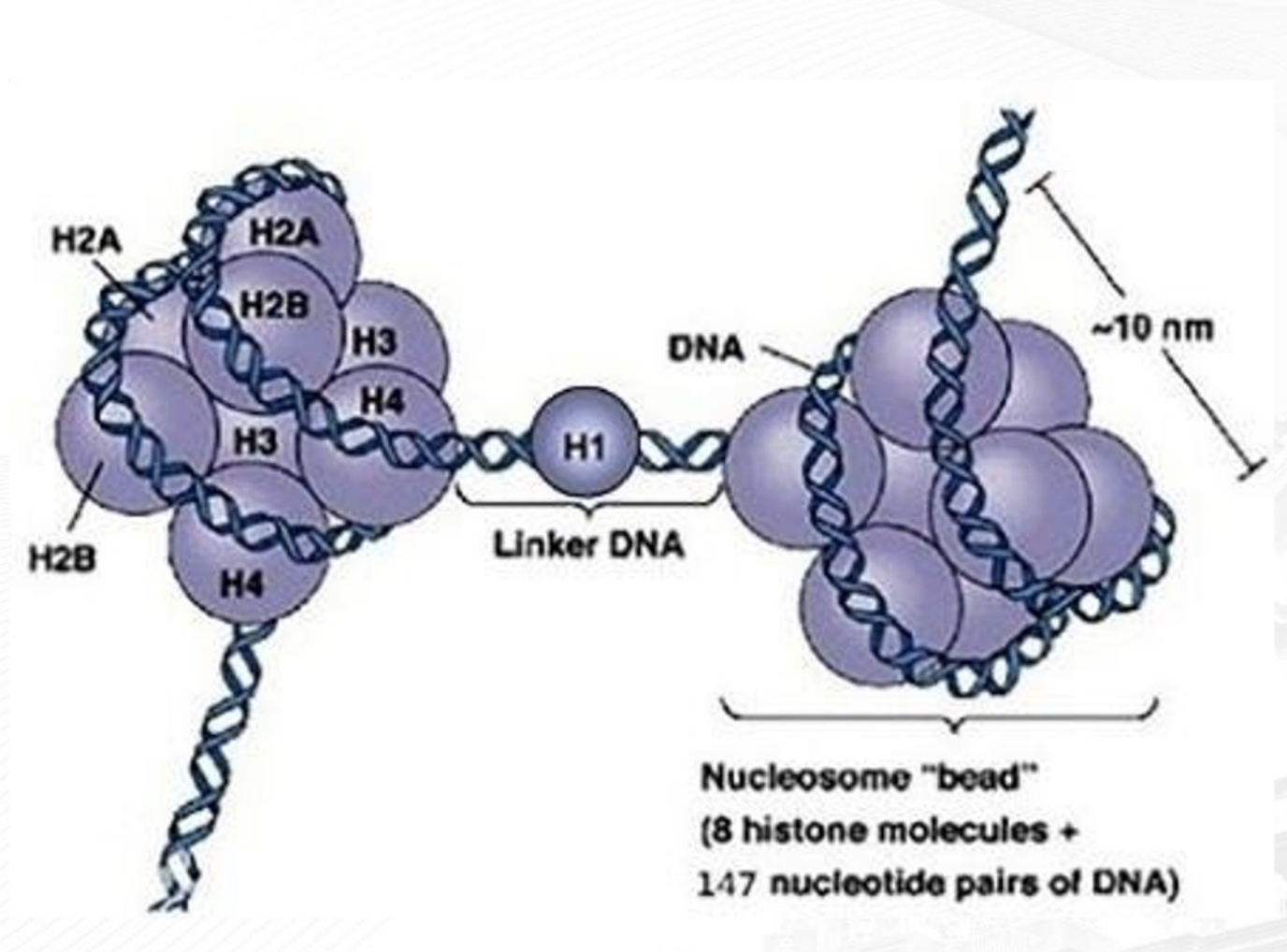
8 subunits of globus(?)/globular proteins
**Nucleosomes:**
a bead is composed of ___
a bead is composed of ___
35
New cards
anchoring proteins/scaffold
**Metaphase Chromosome:**
helper proteins
helper proteins
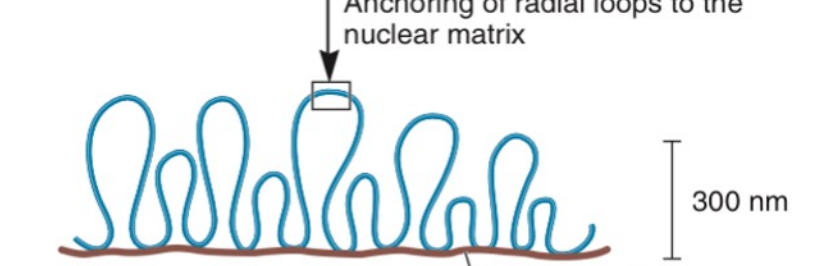
36
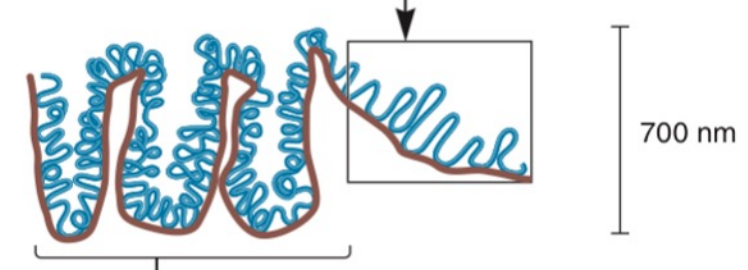
New cards
Radial loop domains
**Metaphase Chromosome:**
compaction of radial loops
compaction of radial loops
37
New cards
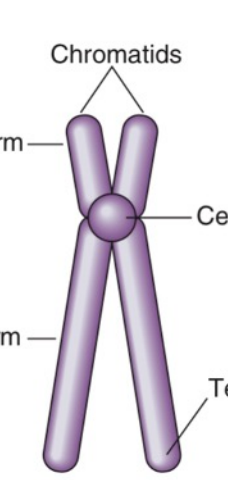
Chromatids
**Morphology of Chromosomes:**
Two identical strands which are the result of DNA replication
Two identical strands which are the result of DNA replication
38
New cards
Centromere
**Morphology of Chromosomes:**
* **Central** region
* Primary constriction where sister chromatids are linked
* Consists of several hundred **kilobases** **of repetitive DNA**
* Responsible for **chromosome movement** at cell division
* **Central** region
* Primary constriction where sister chromatids are linked
* Consists of several hundred **kilobases** **of repetitive DNA**
* Responsible for **chromosome movement** at cell division
39
New cards
p *(petite)*
**Morphology of Chromosomes:** *Centromere*
Short arm
Short arm
40
New cards
q (*queues or “g” = grande*)
**Morphology of Chromosomes:** *Centromere*
Long arm
Long arm
41
New cards
13 chromosomes
**Morphology of Chromosomes:** *Centromere*
we can actually see the long and short arm
we can actually see the long and short arm
42
New cards
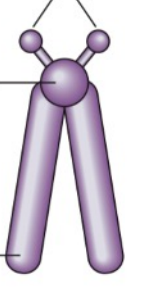
Kinetochore
**Morphology of Chromosomes:**
* attaching point of microtubules
* Microtubule organizing center (MTOCs)
* Facilitates **spindle formation**
* attaching point of microtubules
* Microtubule organizing center (MTOCs)
* Facilitates **spindle formation**
43
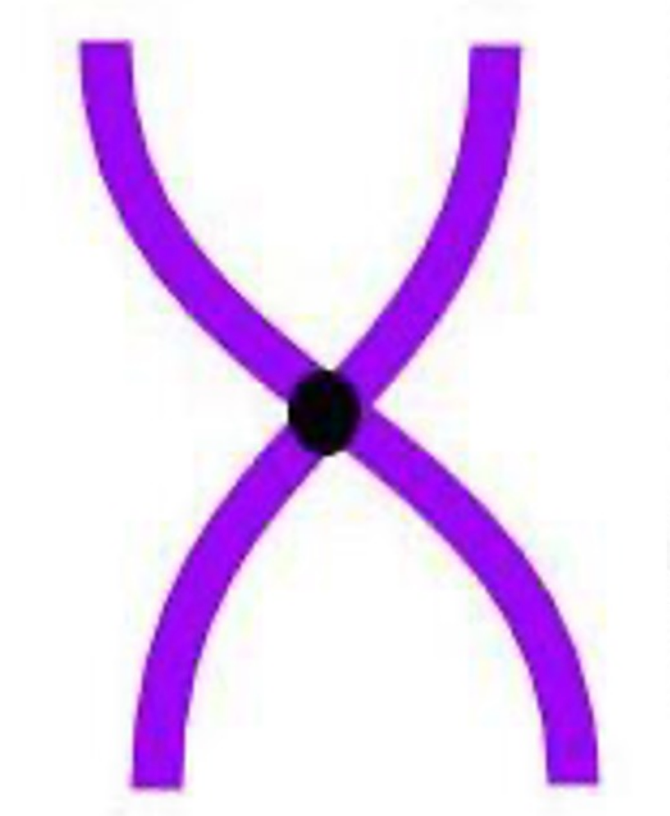
New cards
Monocentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Number*
* **Single** centromere
* Reliably transmitted from parental to daughter cells
* **Single** centromere
* Reliably transmitted from parental to daughter cells
44
New cards
Acentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Number*
* Lacks centromere
* **genetically unstable** because they __cannot be maneuvered properly__ during cell division and are usually lost
* Lacks centromere
* **genetically unstable** because they __cannot be maneuvered properly__ during cell division and are usually lost
45
New cards
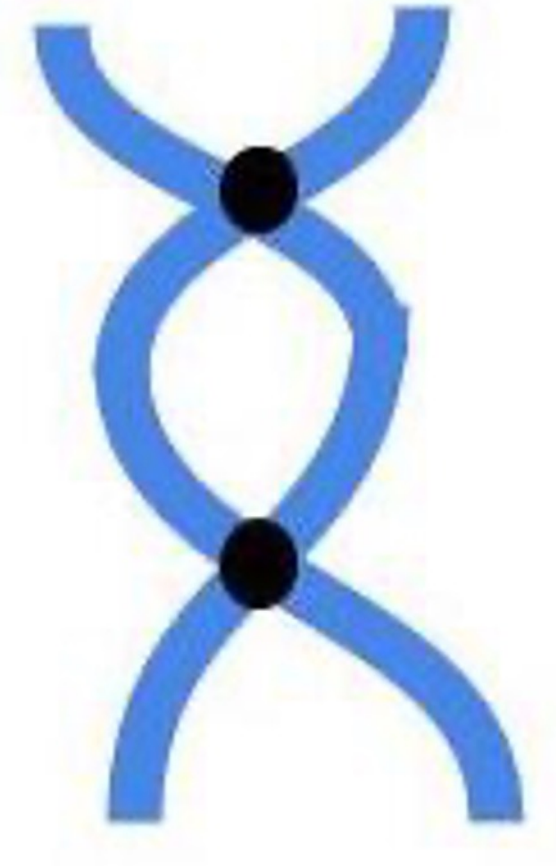
Dicentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Centromere Number*
* **Two** centromeres
* **genetically unstable** because it is __not transmitted in a predictable fashion__
* **Two** centromeres
* **genetically unstable** because it is __not transmitted in a predictable fashion__
46
New cards
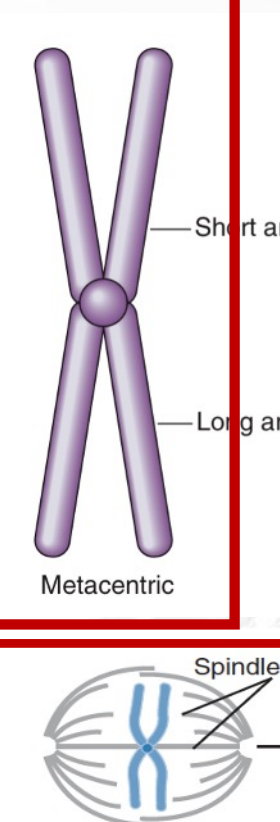
Metacentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Centromere Position*
* **Middle**; yielding arms of roughly equal length
* centrally located
* **5 pairs** in humans
* v-shaped
* **Middle**; yielding arms of roughly equal length
* centrally located
* **5 pairs** in humans
* v-shaped
47
New cards
Submetacentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Centromere Position*
* **Off-center** centromere; “q” arm is longer
* Unequal length
* **13 pairs**
* j-shaped
* **Off-center** centromere; “q” arm is longer
* Unequal length
* **13 pairs**
* j-shaped
48
New cards
Acrocentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Centromere Position*
* means **peak**
* Very **close to one end**; yielding a small short arm
* associated with small pieces of DNA called **satellites**, encoding rRNA
* **5 pairs** in humans
* i-shaped
* means **peak**
* Very **close to one end**; yielding a small short arm
* associated with small pieces of DNA called **satellites**, encoding rRNA
* **5 pairs** in humans
* i-shaped
49
New cards
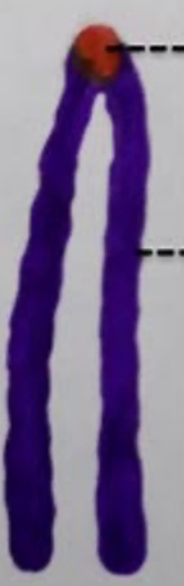
Telocentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Centromere Position*
* Centromere at the **terminal end**
* Not found in humans
* Centromere at the **terminal end**
* Not found in humans
50
New cards
Metacentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Arms Ratio*
* M/m
* 1.0-1.6/1.7
* M/m
* 1.0-1.6/1.7
51
New cards
Submetacentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Arms Ratio*
* Sm
* 3.0
* Sm
* 3.0
52
New cards
Subtelocentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Arms Ratio*
* St
* 3.1-6.9
* St
* 3.1-6.9
53
New cards
Acrocentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Arms Ratio*
* T
* 7.0
* T
* 7.0
54
New cards
Telocentric
**Chromosome Types:** *Arms Ratio*
* T
* none
* T
* none
55
New cards
Telomere
**Morphology of Chromosomes:**
* **Tip** of each chromosome
* **Tip** of each chromosome
56
New cards
TTAGGG
**Morphology of Chromosomes:** *Telomere*
* Tandem repeats of the **hexameric sequence**
* Tandem repeats of the **hexameric sequence**
57
New cards
end-to-end fusion
**Morphology of Chromosomes:** *Telomere Functions*
* Preventing abnormal ___ of chromosomes
* Preventing abnormal ___ of chromosomes
58
New cards
degradation
**Morphology of Chromosomes:** *Telomere Functions*
* Protecting the ends of chromosomes from ___
* Protecting the ends of chromosomes from ___
59
New cards
DNA replication
**Morphology of Chromosomes:** *Telomere Functions*
* Ensuring complete ___
* Ensuring complete ___
60
New cards
chromosome pairing
**Morphology of Chromosomes:** *Telomere Functions*
* Having a role in ___ during meiosis
* Having a role in ___ during meiosis
61
New cards
Individuals with **longer telomeres**
**Morphology of Chromosomes:** *Telomere*
* reported to have a longer subsequent lifespan in some studies of vertebrate species,
* reported to have a longer subsequent lifespan in some studies of vertebrate species,