Airframe 8083 - CH 8: Aircraft Painting and Finishing
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Solvents
A chemical that is added into other liquids in order to thin the liquid, making it sprayable. Solvents must be volatile, and will cool the surface that it is applied onto once it evaporates. Think about sweating and how it cools your body. Due to their volatility, these are one of the many chemicals you want to avoid inhaling.

Acetone
A highly flammable, volatile, clear solvent, used for removing grease from fabric before doping, and most often used for paint thinning. It can also be used for varnish removal. Ideally this would be used for thinning fiberglass resin, polyester resins, vinyl, and adhesives.

Methyl Ethyl Ketone (MEK)
A highly flammable, volatile, clear solvent, that is ideal for varnish removal, paint and primer thinning, in surface coatings, adhesives, printing inks, polyester wax catalyst, and resins. MEK is effective at reducing emissions during coating operations due to its volatility. Wear gloves while applying. Overall, a really versatile solvent.

Methylene Chloride
An extremely effective paint stripping solvent. This is the more dangerous, not so environmentally friendly stripper. Also great for degreasing/cleaning metal parts. Despite its danger, its flash point is actually very low under normal use conditions, so it can be used to reduce the flammability of other substances.

Toluene
A clear, water insoluble liquid with a distinct benzine-like odor. Commonly used in paints, paint thinners, lacquers, and adhesives. Acceptable thinner for zinc chromate primer. Toluene is likely linked to brain damage, so respirators and PPE is priority.

Linseed Oil
The most common liquid carrier in oil paint. It makes the paint more fluid, transparent, and glossy. Makes brushing easier, and provides a better final product. Linseed oil is more subject to spontaneous combustion, so disposal of soaked rags must be done carefully and diligently.

Thinners
A plethora of solvents used to reduce the viscosity of any primers, subcoats, and topcoats.

Varnish
A transparent protective finish for wood. Viable for interior and exterior grades, however the exterior grade will not dry as hard as the interior to allow for thermal expansion without damaging the finish. Commonly is a combination of a drying oil, a resin, and a thinner or solvent. Polyurethane and epoxy varnishes will remain liquid after the solvent evaporates, while resin varnishes will harden once it evaporates.

Primers
A primer is the foundation for the final topcoat finish. Its bonds to the surface, inhibits corrosion of metal, and provides an anchor point for the finish coats. The primer pigments must be either anodic to the metal surface or passivate the surface (should moisture be present). The binder MUST be compatible with the finish coats or else the finish could peel/be unsatisfactory.

Wash Primer
Water-thin coatings of phosphoric acid in solutions of vinyl butyral resin, alcohol, and other ingredients. This primer has almost no filling qualities, meaning it doesn’t contain much solids. These passivate the surface, temporarily provides corrosion resistance, and provide an adhesive base for next coating such as urethane or epoxy primer. Wash primers will not require sanding. Some wash primers have a very small recoat time, so following manufacturer’s instructions is imperative.

Gray Enamel Undercoat
A good primer for composite substrates, since it can fill minor imperfections and will dry fast without shrinkage. It also provides high corrosion resistance.

Urethane
Urethane primer is a two part product that uses a chemical activator to cure. It has good filling properties, and can be sanded easy. Film thickness is important to observe to avoid shrinkage. Should be applied over wash primer for best results. Urethanes contain ISOCYANATES, which you should avoid inhaling or coming in contact with. WEAR PROPER PPE.

Epoxy
A synthetic, thermosetting resin that produces tough, hard, chemical resistant coatings and adhesives. You need to use a catalyst to initiate the curing process, however it is not classified as harmful since no isocyanates are present in the product. Epoxy can be used as a nonsanding primer/sealer over bare metal and it is softer than urethane. Great for steel tube frame aircraft prior to installing fabric covering.

Zinc Chromate
A corrosion resistant pigment that can be added to primers of many resin types. Older zinc chromate will have a distinctive yellow color, while the newer zinc PHOSPHATE will have a green color. This primer uses the moisture in the air to chemically react with the bare metal, creating a corrosion resistant layer. Zinc chromate is almost entirely unavailable now as it has major environmental and health concerns.

Dope
The main finish for fabric covered planes. It could give the fabric properties such as increased tensile strength, airtightness, weather-proofing, UV protection, and tautness to the fabric cover. This finish however has mostly been superseded by a better, more effective vinyl finish.

Synthetic Enamel
An oil based, no clear coat paint that provides durability and protection. It can also be mixed with hardener to increase the durability and shine while decreasing the drying time. A very economical choice of finish.

Lacquers
A finish that is known best for how easy it is to spray, because it dries quickly and can be applied in thin coats. However, its strength lacks, being vulnerable to things like gasoline, acid rain, and bird droppings. Lacquers are currently almost never used for exterior final coats on aircraft due to its durability, and environmental concerns. Upwards of 85% of the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the spray gun will end up in the atmosphere, leading some states to ban its use.

Polyurethane
These finishes are at the top of the list as far as abrasion, stain, and chemical resistance. It also introduced that nice wet, glossy look. It also provides plenty of UV protection on its own. All of this leads to it being the main choice for commercial and corporate aircraft.
What are the 3 methods of applying finish?
Dipping, generally used for smaller components or in a factory setting.
Brushing, ideal for small repair work.
Spraying, the preferred method for most aircraft finish operations.

Siphon-Feed Gun
The conventional paint spraying tool, which uses a venturi in the nozzle that allows the compressed air to draw paint from the supply cup and deliver it through the nozzle.

Gravity-Feed Gun
Provides the same quality as a siphon-feed gun, however the paint cup is mounted on the top allowing gravity to do the job of delivery.

HVLP
the “High Volume Low Pressure” spray is an internally mixed spray gun, meaning the paint is mixed inside the air cap. Because of the low pressure used in the application of the paint, it transfers about 65% to 80% of the finish material to the surface. These are available in either the siphon or gravity fed variety, as well as a model that can be connected to an external paint container.

Zahn Cup
A device used to measure the viscosity of a liquid. It is found by observing the rate at which the liquid drains out of the cup (efflux time). The exact viscosity you want for your choice of product should be included in the product’s technical data sheet. These zahn cups come in a couple of sizes, and which one to use will also be listed by the manufacturer. #2 and #3 size is most often recommended.

What causes Pinholes in a finish?
Trapped solvents, air, or moisture. This can happen if you use the wrong thinner or reducer, poor spraying technique resulting in uneven application, or contaminants in the paint or air lines.

What causes Blushing in a finish?
Blushing is cause by moisture being trapped in the paint, which is result of the rapid evaporation of the solvent that then cools the surface enough to condense the moisture in the air. This will usually happen when the humidity is higher than 80%, but can also be caused by an incorrect temperature (60 F < x < 95 F), an incorrect reducer (fast drying) being used, or too much air pressure.

What cause sags & runs in a finish?
Too much paint application in one area, applying to close to the surface, or moving too slowly across the surface.

What causes orange peeling in a finish?
A variety of reasons that include improper spray gun adjustment, not enough reducer (too thick) or the wrong reducer, material not mixed enough, forced drying method such as fans or heat causing it too dry too quickly, too little flash time between coats, and spray painting when the ambient or substrate temperature is either too hot or too cold.

What causes fisheyes in a finish?
The surface not being completely cleaned of all traces of silicone wax.

What causes sanding scratches in a finish?
The surface not being properly sanded and/or sealer prior to spraying the finish coats. This will usually only appear on nonmetal surfaces.

What causes wrinkling in a finish?
Trapped solvents and unequal drying of the paint finish due to excessively thick or solvent heavy paint coats. Rapid temperature changes will promote uneven release of the solvents.

What causes spray dust?
The spray particles drying before it reaches the surface.

Airless Spray Gun
A spray gun that uses delivers paint to an orifice using high hydraulic pressure through a pump to atomize the fluid, without the use of air. Provides better transfer efficiency and production speed with less overspray than a conventional air atomized system. Better used for production work, since air atomized systems will provided a better finish.

Fresh Air Breathing Systems
A fully air supplied paint mask that should be used while using ANY polyurethane coatings. It uses a small electrically powered turbine that is constantly delivering a fresh filtered air supply to your mask.
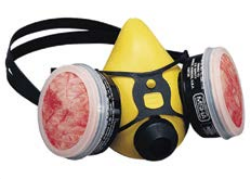
Charcoal Respirator
A charcoal filtered respirator that uses disposable, replaceable filters that can be detached and reattached. These are better for all other spraying and sanding operations to protect your lungs.
what are the key points of application of paper decals?
Immerse the paper decal in clean water for 1 to 3 minutes, do not exceed 3 minutes or else the decal will lose its backing WHILE immersed. Anything less than 1 minute won’t allow enough time for the decal to separate from its backing once YOU take it out of the water.
Place one edge on the receiving surface and press lightly, then slide the paper backing from beneath the decal.
Make minor adjustments with fingers, remove water drops from decal, and press out all bubbles to the nearest edge.
what are the key points of application of metal decals with cellophane backing?
Immerse in clean water for 1 to 3 minutes
Remove and dry carefully with clean cloth
Remove cellophane backing, do not touch adhesive
On smaller decals, place corner of decal first. On larger foil decals, place center than work outwards.
Remove all air pockets by rolling for good adhesion.