QUIZ 4: Modified Diets & Clinical Nutrition
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Types of Modified Diets (6)
Clear Liquid
Full Liquid
Blenderized Liquids (Pureed)
Soft (Bland, Low Fiber) Diet
Mechanical Soft
Dysphagia Diet
Blenderized Liquids (Pureed) Diet
Consistency varies
Purpose: Chewing and swallowing difficulties
Nutritionally adequate
Soft (Bland, low-fiber) Diet
Whole foods, low is fiber, easily digested
Smooth, creamy, non-gas forming
Mechanical Soft Diet
Regular diet that is modified in texture
Minimal chewing
Excludes harder foods
Full Liquid Diet
More variety, still liquid at room temperature
Nutritionally inadequate
Transition from liquids
Ice cream, strained cereal, pureed vegetables
Clear Liquid Diet
No residual and liquid at room temperature
Prevent dehydration
Nutritionally inadequate
Water, tea, broth, juices etc.
Dysphagia Diet
Prescribed when swallowing is impaired (following a stroke)
HOB 90 degrees
Double swallow
Chin to chest
Levels of Liquid Consistencies
Level 0: Thin
Level 4: Extremely Thick
Levels of Solid Textures
Level 3: Liquidized
Level 7: Easy to Chew
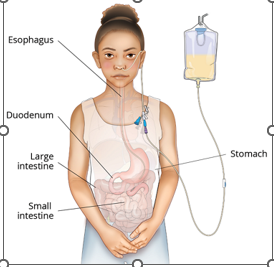
Enteral Feeding (EN)
Used when a client cannot consume adequate nutrients and calories orally but has a gastrointestinal (GI) system that functions at least partially
Contraindication: GI tract nonfunctional
Consists of commercial formula administered through a tube into the stomach
Can be the sole source of nutrition or can be used to augment an oral diet.
Feed whenever possible
Ensure HOB remains 30 degrees for 30-60 mins after
Manifestations of Dysphagia (4)
Drooling
Pocketing food
Choking
Gagging
Nasoenteric tubes (4)
Nasogatric
Nasoduodenal
Nasojujenal (ends in l
Enteric Feedings (4)
Standard (proteins)
Hydrolyzed (proteins)
Disease Specific (proteins)
Modular formulas (proteins
Enteric Delivery Methods (4)
Continuous
Cyclic
Intermittent
Bolus
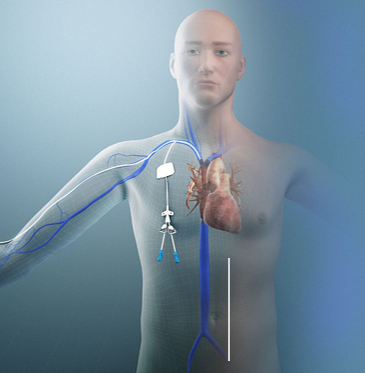
Parenteral Feeding
Used when GI is NOT working
TPN or PPN
Hypervolemia concern: Fluid restriction = Higher concentration (carbs)
Hyperglycemia: Lower concentration (carbs)
Dextrose less than 10% is for short-term use only
Do not feed whenever possible
TPN (Total Parenteral Nutrition)
Nutritionally complete
Located in central vein
Used when hypertonic (>10% dextrose, up to 70%) is needed
PPN (Peiperhal Parenteral Nutrition)
Short-term, incomplete nutrition due to low dextrose (<10%, 2.5-10%)
Fats (Lipids)
Make up 10-30% of parenteral formula
Protein (Amino Acids)
Make up 3-20% of parenteral formula
Determined by requirements + liver and kidney function
Heparin
Added to parenteral formula to prevent fibrin buildup on the catheter tip
IV MEDICATION CONTRAINDICATION
Administering through a PN IV line or port
Enteral Feeding (Preparation)
HOB 30 degrees
Maintain patency
Verify tube placement
Verify bowel sounds
Check residuals Q4-6
Dehydration concern (prepare free water)
Start slow; increase slow
Obtain baseline (height, weight, BMI, labs, GI function, dietician referral for calorie/energy needs)
Enteral Feeding (Ongoing Care)
Flush w/ 15-30mL water before, between and after meds
Monitor gastric residuals and tube site
Discontinue when client consumes 2/3 of protein and calorie needs orally for 3-5 days
When weaning/transitioning, stop EN 1 hour prior to eating
Increase up to 6 small meals/day
Goal: 500-750/day and feed at night before totally discontinuing
Enteral: GI Complications
Constipation, diarrhea, cramping, pain, N/V
Dumping syndrome (dizziness, rapid pulse, diaphoresis, pallor)
Enteral: GI Complications (Nursing Action)
Consider changing the formula
Decrease formula, Increase free-water
Formula at room temperature
Enteral: Mechanical Complications
Tube misplacmeent, dislodgment, aspiration, irritation, clogging
Parenteral: Mechanical Complications
Catheter misplacement, pneumothorax, air embolus, obstruction, bolus infusion
Parenteral: Infection & Sepsis
Fever and elevated WBC’s
Result from contamination
Refeeding syndrome
Resulting from the body quickly changing from a catabolic to anabolic state. Results in fluid and electrolyte imbalance.
Enteral: Mechanical Complications (Nursing Action)
Confirm placement prior to feeding
Elevate HOB 30 degrees or higher
Bolus over 15 min.
Flush tube with 30mL water every 4 hours
Check residuals every 4-6 hours
Do not mix formula with meds
Enteral: Metabolic Complications
Dehydration, hyperglycemia, electrolyte imbalance, Fluid overload, Refeeding syndrome (starvation state to feeding- can be fatal)
Parenteral: Metabolic Complications
Hyper/hypoglycemia, Electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, fluid overload
Enteral: Metabolic Complications (Nursing Action)
Consider changing the formula to Isotonic
Increase or decrease free-water
Monitor Electrolytes, Glucose and daily weight
Treat symptoms
Enteral: Foodborne Contamination
Bacterial contamination of formula
Enteral: Foodborne Contamination (Nursing Action)
Wash hands before
Clean equipment
Use closed feeding systems.
Cover and label open cansReplace the feeding bag, tubing, and any equipment every 24 hr.
Fill generic bags with only 4 hr worth of formula.
Parenteral Feeding (Ongoing Care)
Fluid balance, flow
Examine solution, verify solution with second RN
Aseptic and sterile technique (changing central line)
Change bag and tubing Q24H
Parenteral Feeding (Nursing Actions)
Introduce enteral substances to prevent GI atrophy
Should be discontinued as soon as possible to avoid potential complications.
Discontinuation should be done gradually to avoid rebound hypoglycemia.
Gradual transition, once discontinued.
Educate the client and family home administration
Specific Pareneteral Nursing Actions
•Monitor for manifestations of infection.
•Use strict aseptic technique when setting up the IV tubing, changing the site dressing, and accessing or deaccessing the IV access.
•Change the PN bag and tubing set at least every 24 hr
•Monitor blood glucose .
•Administer sliding scale insulin or add to the TPN
Dextrose for hypoglycemia
•Monitor daily weights, I&O, and oral intake of nutrients.
•Notify the provider of weight gain greater than 1 kg/day.
•Titrate lipids to weight changes
Nutritionally inadequate
Liquid diet
Clear liquid diet
Duodenal and jejunal feedings tubed are used for clients with risk for what underlying concern?
Risk of aspiration
Risk of respiratory depression
Risk of kidney disease
Risk of aspiration
Cyclic
A continuous rate of a block of time
No more than 4 hours if exposed to air
Intermittent
Administered every 4 to 6 hours in equal portions
Continuous
Administered at a continuous rate over a 24hr period
No formula poured inside bag (closed system; no air exposure)
Residuals
If more than half the total administered, call the provider to slow or hold the feeding. GI tract cannot digest the total within expected parameters