Ch3 - 4 Energy
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Geology
Joint adn Fault Lines: earth curst break and fractures in joints where the fault lines form that split crust
Drilling seeps (instruments)
1920
Torsion balance - measure the gravitational acceleration at the Earth's surface
Seismology - measure earthquakes by their magnitude, energy release and intensity
Vibroseis - Vibration used to create wavetrain.
Gravitometer - measures variations in the Earth's gravitational field
Magnetometer - measuring magnetic forces, especially the earth's magnetism
Wireline log - a continuous measurement of formation properties ran on a wire
Sampling/coring - sample or cylindrical piece of subsurface material
4 crucial characteristics in Resovoir
Source of hydrocarbon, POROUS (void space in rock), PERMEABLE (movement of flow), TRAP
Hydrostatic Pressure
Important aspects are weight of fluid and MD
2 Main Requirements for Rotary Rig
Rotation and Circulation
Derrick Must have these systems
Power system
Hoisting system
Rotary system
Fluid circulating system
Well control system
Data acquisition system and monitoring system
Latest development (Walking ability, developed for PAD Drilling)
Types fo Derrick and Masts
Cantilever
Folding
Telescoping
Bootstrap mast
Substructure
gives space between well floor for well control system/equipment (BOP)
Drill string
The bit is attached at the end of the drill string at the bottom of the well, or hole. The drill string connects the bit to the handling equipment at the surface of the rig (is composed only of the drill pipe and tool joints)
Drill pipe
special pipe with thread and shoulder end connections, called tool joints that is used to connect the drill bit to the surface and transmit drilling fluid to the bit.
Drill collars
thick-walled steel pipes placed at the bottom of the drill string to provide weight for the bit and keep tension in the drill string.
WOB
Weigth on bit
ROP
Rate of Penatration of the formation
TIH
Trip in hole
TOOH
Trip out of hole
BR
Bit Run (when to change bit)
Power system
Gas or Diesel generators
Hoisting System
Kelly Drive
This method is Cheap / Slower limitation is the length of the kelly
and the potential for rotation issues. It involves using a square or hexagonal tool to transmit torque to the drill bit.
Some specs
Top Drive
A drilling system that allows for the rotation of the drill string from the top of the derrick, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of issues associated with traditional rotary systems. Less connections and quicker tripping times.
Components:
• A – Elevator
• B – Bail or Link
• C – IBOP (both manual and pneumatic operated)
• D – Rotating Head
• E – Top drive motor
• F – Dolly Track
• G – Hook
• H – Travelling Block
Other important components
Civil
wireline
Casing
Cementing
The Circulating System
Casing
Prevents formation walld to cave in
Prevents crossflow
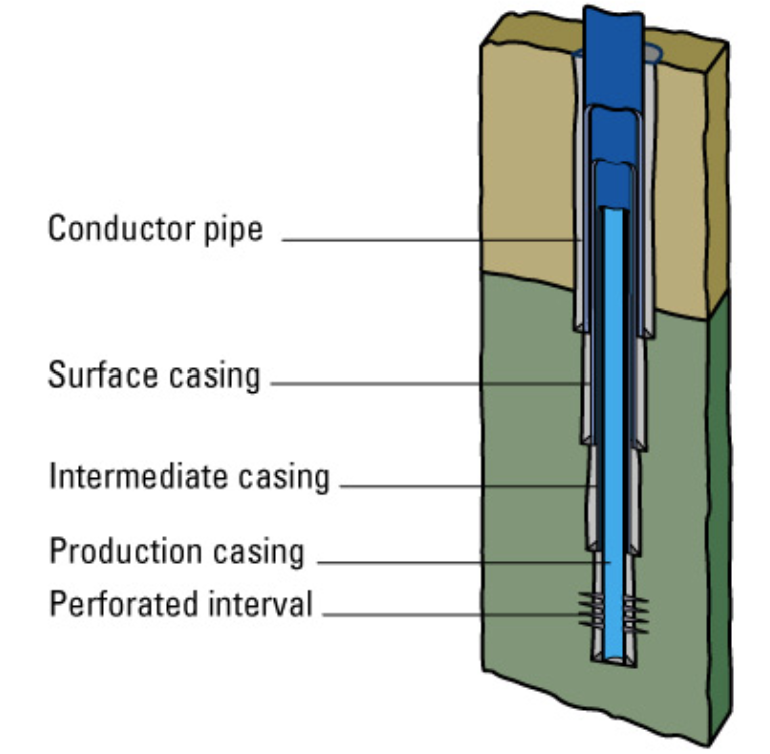
Well Control Systems
BOP: A device used to control the flow of fluids from a well during drilling, completion, and workover operations. (Temporary: have rams and kill/choke lines)
Wellhead: there for the life of well in celluar and monitores anulus
Drill stem
whole drill from swivel to bit
BOP Accumulator 3
Side of the rig use prevent a blow out (hydrolic powered system)
Type of Rams
Blind and Shear Rams
Pipe Failures
Pure fatigue (Cycling loading in the hole)
Notch fatigue (from setting slips)
Corrosion fatigue (Critical for weld section of hte
tool joint on welded pipe vs Forged Pipe)
Drill collars
thicker more weight between drill pipe and bit
Pendulum effect
Defined as the tendency of the drill stem to hang in a vertical position due to the force of gravity. The heavier the pendulum, the stronger is its tendency to remain vertical and the greater the force needed to cause the drill stem to deviate from vertical
BHA
(bottom hole assembly) lower portion of the drill string, from the bit, bit sub, a mud motor, stabilizers, drill collars, heavy-weight DP, crossovers for various thread forms.
MWD
Measure While Drilling (mud telemetry)
LWD
Logging while Drilling (Geosteering near bit)
2 Main category of bits
Rolling cutter bits and Fixed cutter bits
KOP
Kick of point (direction changes)
TVD
True vertical Depth
TD
Target Depth
MD
Measure depth
Inclination
departure from vertical
Azimuth
Depature from magnetic north
Spider Plot
used to survey area
Different Method of deviating the wellbore
Whipstocks
Jetting
Rotary BHA adjustable stabilizer
Traditional Motor
Rotary steerable assy
Positive Displacement Motors
only the bit and rotar can move
Bent Housing
Orient the direction in which the bit is going to travel
Dogleg severity
measure of the amount of change in the inclination, and/or azimuth of a borehole, usually expressed in degrees per 100 feet of course length (low=small)
Rotary Steerable
No more sliding and has an adjustible tool face thru Mud Telemetry
Wireline Operations
Delivery method for tools on a wire through trucks
Run it before you case (survey area)
Case tool wireline (diff)
Perforating guns could work
Cementing
Create Zonal Isolation • Protect Useable Water • Provide Structural
Support for Casing • Protect Casing from Corrosion • Isolate Casing Seat for
Subsequent Drilling
Rig crew
Company man (onsite manager)
Rig manager (rotating schedule)
Derrickman
motorman
Floorman
Prep for stimulation
Tubing head installed, then valve, Clean up, Xmas tree
Stimulation
ensure the hydrocarbon are able to flow in the well bore
Frac
Artifcal lift (pump jack, Electrical submersible pumping (ESP), gas lift, plunger)
Fishing operations
when something falls into pipe (junk) and needs to be fished out
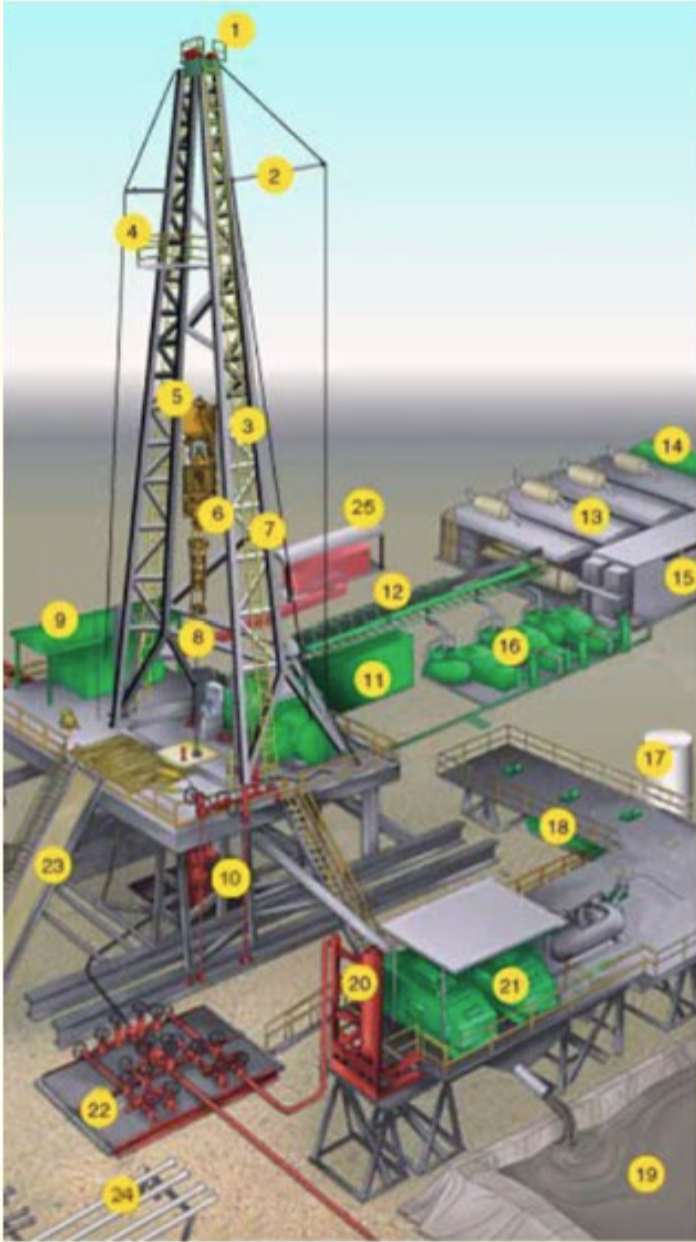

First Offshore
Socali in late 1800s
FP
Fixed platforms

CT
Compliant Tower

TLP
Tension Leg Platform
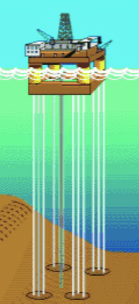
Mini-TLP
Mini-tension Leg Platform

SP
SPAR Platform

FPS
Foating Production systems

FPSO
Floathing Production storage and offloading
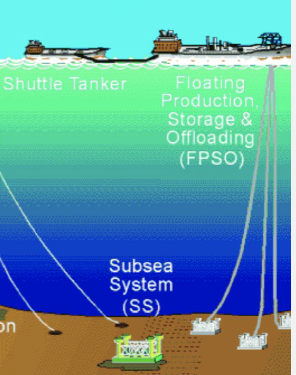
SS
Subsea system
Barges
brings well to surface for a dry well
Submersible
leveraging large bottles but same concept of a parge
Jack up
Have legs sumerge in sea floor for about 500ft
Semi Sub
Floating units > 500
column-stabilized
Subsea Wellhead
LMRP
Lower Marine riser package allows for quick disconnect of the marine rise
Heave Compensation
helps with sea movements and keeps the drill and piping sationary (passive, active, and both)
SubSea BOP
Same concept but bigger/heavery and has LMRP and lower stack with valve controls
Marine Riser
cylindrical pipe connecting a subsea wellhead
Biggest diff from Onshore and Offshore
Econmics, Time fram, Tech diff, Storage and transport
FEED
Front end Enngineering design
EPC
Engineering Procrment Construction
Green Field
Conceptulize what to do in new terretory (first one)
Brown Field
Planning in prexisting area (been drilled at)
FID
Final Investment Deciscions
ROV
Remote operated vehicle
Flow Assurance
Ensures mesaures in case there is issues like frozen methane in piping due to extreme temp changes in sea
Mudmar, suction pile
Prevent offshore structures from sinking into seabed
subsea equipment

Vertical Subsea Tree
valves in a vertical bore
Advantages:
• Vertical trees require only one time BOP nipple down.
• No wireline plug to be removed from a tree for a well intervention program.
• Better for fields that don’t expect to do workover or have small chance of doing the workover
• Simpler and cheaper to change a vertical tree when compared to a horizontal tree
• Disadvantages:
• If the workover operations such as recompletion, changing tubing, installing extra downhole tools, etc. are required, a vertical tree must be removed in order to install BOP on top of the well.
Horizontal Subsea tree
valves in a horizontal configuration
Advantages:
• Better for fields that expect to do workover quite often because a tree does not need to be removed.
• Can have a larger bore tubing
• Lower total height of a tree
• Disadvantages:
• Less flexibility for operation if the delivery of a tree is delayed.
• Two runs for subsea BOP and riser are required
• Completion string must be removed if replacement of a tree is needed.
• Two wireline plugs (crown plugs) must be removed before starting any well intervention program. There have been several cases when people have faced a lot of difficulty for removing the plugs. This can lead to extra time and cost forthe operation
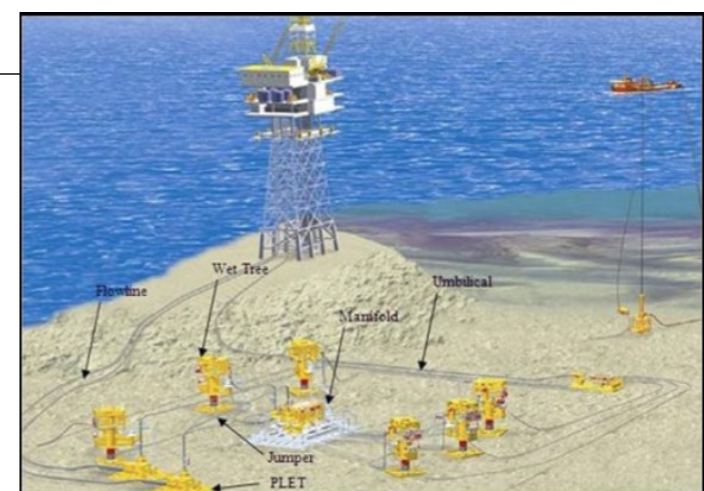
Manifold
Structure w/ valves and pipework designed to commingle and direct produced fluids from multiple wells into one or more flowlines
Jumpers
short pipe connector that is used to transport production fluid between two subsea components
Umbilical Systems (UTA)
bundled arrangement of tubing, piping, and/or electrical conductors in an armored sheath that is installed from the host (umbilical termination assembly)
Subsea Flowlines
pipelines used to connect a subsea wellhead with a manifold or the surface facility
FLNG
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas
FSRU
FLoating Storage Regasification Unit (stores LNG)
Production Riser
portion of the flowline that resides between the host facility and the seabed adjacent to a host facility
PLET
Pipline ends and In line termination: subsea structures designed to attach the pipeline end and then lowered to the seabed in the desired orientation
PLEM
Pipeline end manifold
HIPPS
High integrity presuure protection system
CIU
Chemical injection unit
SDU
Subsea Distribution unit (hydrolic and electircal control system)
Riser Tensioner
type of heave compensator