tuberculosis
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Mycobacterium
-does not gram stain
-rod shaped bacilli, nonmotile, no spores, no capsule, cord formation
-complex, waxy, layered
-aerobic, slow growth
-acid fast staining: red, fluorescent
TB etiology
-mycobacterium tuberculosis
-acid fast bacilli, aerobic, slow growing
-mycolic acid
-ziehl-neelsen staining
TB pathophysiology
-airborne droplet nuclei
-passed from people with active pulmonary TB
active TB
-caused by mycobacterium
-actively replicating and causing disease
-sx: cough, fever, weigh loss, fatigue
-contagious
latent TB
-bacteria are present but not causing illness
-TB present but not causing issues
-no sx
-NOT contagious
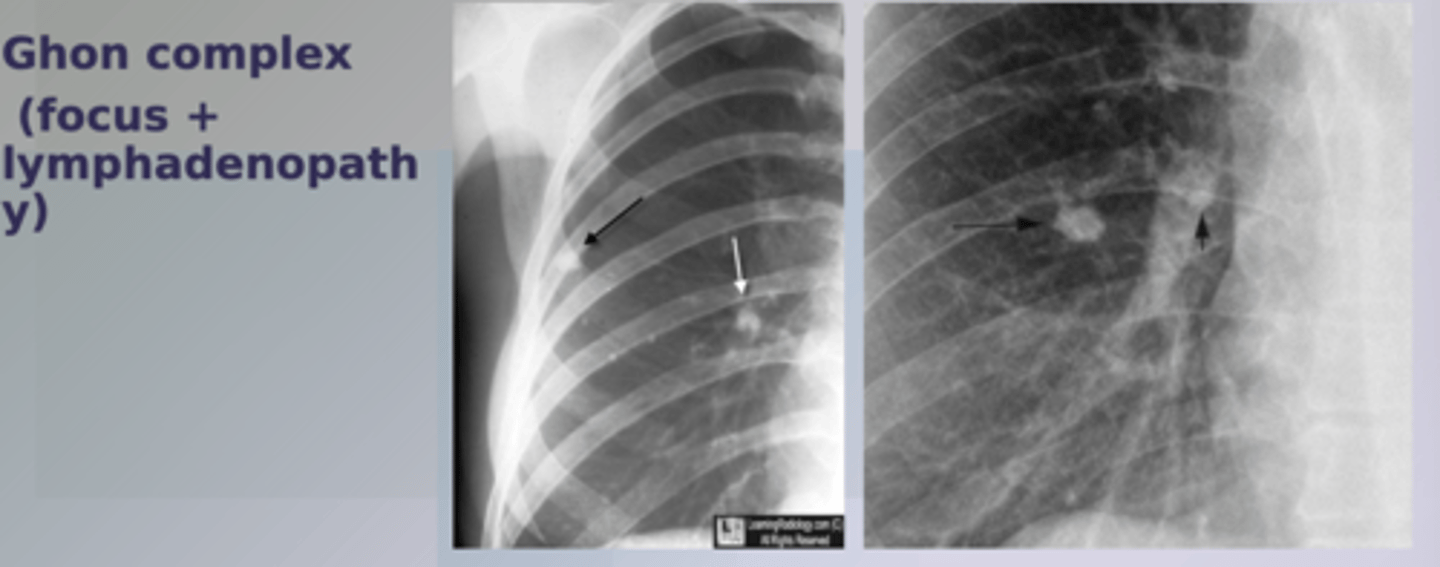
primary TB
-initial infection
-patho: inhaled > deposition in alveoli > forms Ghon focus> spread to hilar lymph nodes via drainage > go away(5%), latent infection(90%), or primary disease(5%)
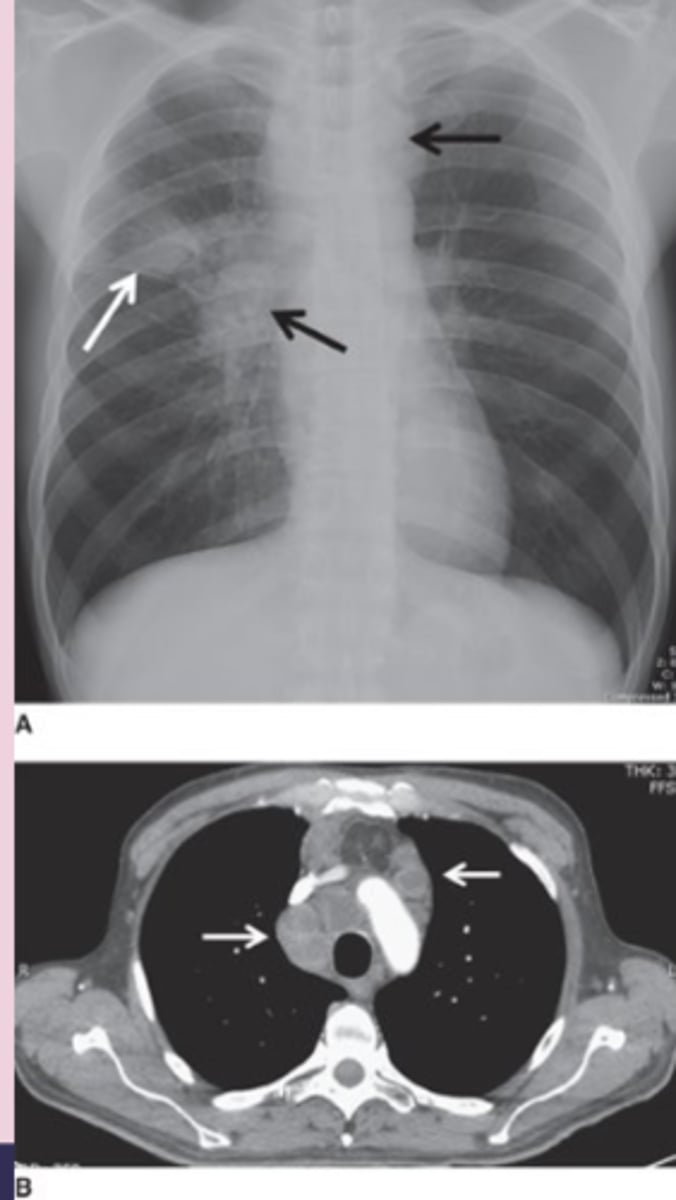
secondary TB
-when infection becomes active again after period of being latent
-patho: in previously infected > reactivates or new infection > cavitation (abnormal thick wall, air filled space), fibrosis, local spread
TB risk factors
-HIV/AIDS
-healthcare workers
-homeless
-incarcerated
-foreign born/ endemic areas
-native american
-DM
-CKD
-immunosuppression
-cancer
TB pulmonary sx
-fever, night sweats, weight loss, fatigue
-chronic dry cough >3 weeks
-hemoptysis (cough blood)
-chest pain
-dyspnea
-lymphadenitis, joint pain, headache, dysuria, hematuria, abdominal pain
TB dx
1. tuberculin skin test (TST/PPD/mantoux)
-positive = >5 HIV+ recent contact/immunocomp, >10 high risk, >15 low risk
-according to diameter of induration
2. interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA): more specific, BCG vaccine
-1. confirmatory: CXR
-primary= hilar lymphadenopathy, lower/mid lobe
-reactivation= upper lobe, cavitation
-2. confirmatory: sputum study= ABF smear, culture(gold standard), PCR
-3. confirmatory: tissue biopsy= caseating granulomas (necrotizing)
Rifampin
-MOA: bind to bacterial RNA polymerase > inhibit RNA synthesis
-SE: turn all body fluids orange, hepatitis, flu syndrome
-strong CYP inducer
-empty stomach
-hepatotoxicity
Isoniazid
-MOA: inhibits mycolic acid synthesis by KatG
-SE: peripheral neuropathy > reversible vit B, hepatitis
Pyrazinamide
-MOA: inhibits cell membrane metabolism > accumulation of toxins in mycobacterial cell
-caution in pregnancy
-SE: hyperuricemia, hepatotoxicity
ethambutol
-MOA: inhibit mycobacterium arabinosyl transferase II > disrupt mycobacterial cell wall
-SE: optic neuritis: red and green color loss
active TB tx
-RIPE therapy for 2 months
-reduce to isoniazid and rifampin for 4 months
-isolation for 2-4 weeks
latent TB tx
only choose one method
1. isoniazid 9 months
2. rifampin 4 months
3. isoniazid + rifapentine 3 months
pregnancy TB tx
-active: RIP for 9 months, monitor LFT, vit B6 supplement
-latent: isoniazid for 9 months, vit B6 supplement