U1, L5 A&P232
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/34
Last updated 7:38 PM on 1/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
The limbic system is responsible for
emotions, cognition, and memory
2
New cards
the limbic system includes
* amygdala
* hippocampus
* cingulate nucleus
* olfactory bulb
* cortex
* (Avery Henson Called Old Conner)
* hippocampus
* cingulate nucleus
* olfactory bulb
* cortex
* (Avery Henson Called Old Conner)
3
New cards
The limbic system interacts with
the prefrontal lobes, which means that you can react emotionally to conscious understanding.
4
New cards
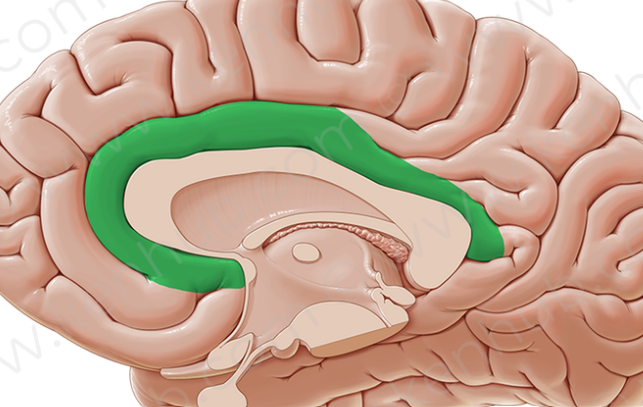
Cingulate gyrus plays a role in
expressing emotions via gestures and resolves mental conflict.
5
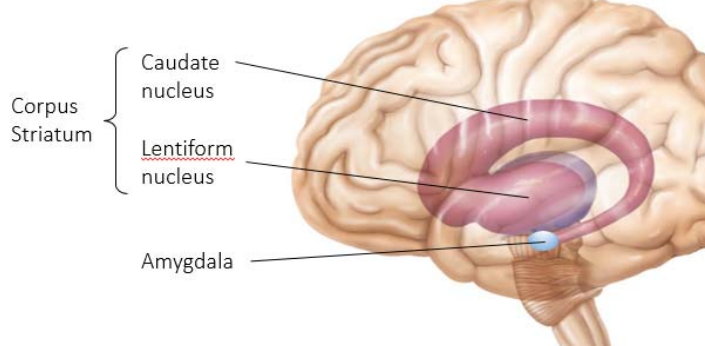
New cards
Amygdala
deals with anger, danger, and fear responses.
6
New cards
Hippocampus converts
new information into long‐term memories
7
New cards
Structures especially important in emotions are the
amygdala and the cingulate gyrus.
8
New cards
The reticular formation consists of
* several nuclei in the brainstem
* well developed connections with the hypothalamus, thalamus, cerebellum, and spinal cord.
* (Help The Crazy Sister)
* well developed connections with the hypothalamus, thalamus, cerebellum, and spinal cord.
* (Help The Crazy Sister)
9
New cards
Functions of reticular formation include
* The RAS (reticular activating system) sends impulses to the cerebral cortex to keep it conscious and alert and filters out repetitive and weak stimuli.
* Motor function: the reticular formation helps control gross motor movements and regulates visceral motor functions (vasomotor, cardiac, and respiratory) centers via autonomic centers.
* Motor function: the reticular formation helps control gross motor movements and regulates visceral motor functions (vasomotor, cardiac, and respiratory) centers via autonomic centers.
10
New cards
Consciousness involves
simultaneous activity of large areas of the cerebral cortex.
11
New cards
Consciousness encompasses
perception of sensation, voluntary initiation, control of movement, and higher mental processing
12
New cards
Degrees of clinical consciousness are
* alertness
* drowsiness
* stupor
* coma
* (Can Anthony Draw Shakira)
* drowsiness
* stupor
* coma
* (Can Anthony Draw Shakira)
13
New cards
Normal brain function involves
continuous electrical activity
14
New cards
what tracks electrical activity in the brain
* electroencephalogram (EEG)
* measures with action potentials
* measures with action potentials
15
New cards
Recorded patterns of neuronal electrical activity are called
brain waves
16
New cards
Brain waves change with
* age
* sensory stimuli
* brain disease
* chemical state of the body
* (And So Ben Cried)
* sensory stimuli
* brain disease
* chemical state of the body
* (And So Ben Cried)
17
New cards
EEGs can be used to
diagnose and localize brain lesions, tumors, infarctions, infections, abscesses, and epileptic lesions.
18
New cards
Memory is
the storage and retrieval of information
19
New cards
The two categories of memory are
* declarative (fact)
* non‐declarative (skill, motor and emotional) memory.
* non‐declarative (skill, motor and emotional) memory.
20
New cards
Fact memory (declarative) (what does it do?)
* entails learning explicit information (dates, facts, etc.).
* related to our conscious thoughts and our language ability
* stored with the context in which it was learned.
* related to our conscious thoughts and our language ability
* stored with the context in which it was learned.
21
New cards
two stages to the declarative memory
* short term memory
* long term memory
* long term memory
22
New cards
short term memory (STM, or working memory)
* a fleeting memory of the events that continually happen.
* It lasts seconds to hours and is limited to 7 or 8 pieces of information.
* It lasts seconds to hours and is limited to 7 or 8 pieces of information.
23
New cards
long term memory (LTM)
* has a limitless capacity.
* Although the mechanisms are not fully understood, Long‐term potentiation is involved
* Although the mechanisms are not fully understood, Long‐term potentiation is involved
24
New cards
Working memory is
* temporary “register” for information while it is being used.
* a memory (could be STM or LTM) that is retrieved to complete an ongoing task.
* a memory (could be STM or LTM) that is retrieved to complete an ongoing task.
25
New cards
STM are converted into LTM by
hippocampus
26
New cards
Factors that affect transfer of memory from STM to LTM include
* Emotional state
* Rehearsal
* Association
* Automatic memory
* (Eat Regularly Alright Anna)
* Rehearsal
* Association
* Automatic memory
* (Eat Regularly Alright Anna)
27
New cards
Non‐ declarative memory (what is it)
* is less conscious and does not retain the context in which it was learned
* Instead it is best remembered by doing
* Instead it is best remembered by doing
28
New cards
Categories of non‐ declarative memory include
* Procedural (skill) – play piano (corpus striatum)
* Motor – ride a bike (cerebellum)
* Emotional (amygdala)
* (Please ME)
* Motor – ride a bike (cerebellum)
* Emotional (amygdala)
* (Please ME)
29
New cards
There are two major types of sleep
* Non‐Rapid Eye Movement (NREM)
* Rapid Eye Movement (REM).
* Rapid Eye Movement (REM).
30
New cards
A person passes through four stages of NREM during the first
* 30‐45 minutes of sleep.
31
New cards
A typical sleep pattern alternates between
* REM and NREM sleep with cycles being more REM dependent
32
New cards
REM sleep occurs after
* the fourth NREM stage has been achieved
33
New cards
Non‐REM sleep is
* a quiet sleep time
* muscles relax, but maintain some tone
* breathing and heart rate is slow and regular
* consumption of energy by the brain is minimal.
* EEG shows high voltage (synchronized) waves are generated
* muscles relax, but maintain some tone
* breathing and heart rate is slow and regular
* consumption of energy by the brain is minimal.
* EEG shows high voltage (synchronized) waves are generated
34
New cards
In REM (rapid eye movement) phase
* postural muscles relaxed,
* breathing and heart rate are irregular
* Brain metabolism exceeds levels seen when the subject is awake.
* EEG shows low voltage fast irregular waves similar to awake state
* breathing and heart rate are irregular
* Brain metabolism exceeds levels seen when the subject is awake.
* EEG shows low voltage fast irregular waves similar to awake state
35
New cards
Dreaming mostly occurs during
REM and last stages of Non‐REM sleep