Unit 1-B
1/24
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Competitive Market
Many buyers, none of whom can control the price, or prevent others from entering/ exiting the market.
Quantity Demand
Quantity of goods or services consumers are willingly able to purchase at a specific price.
Demand
Quantity of goods/services consumers are willingly able to purchase at various prices.
Demand Schedule
A way to see demand in a table.
Demand Curve
A way to see demand in a graph format.
Law of Demand
When price goes up, quantity demand goes down. When price goes up, QD goes down.
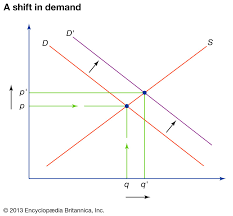
Does this show increase or decrease in demand
Increase in Demand
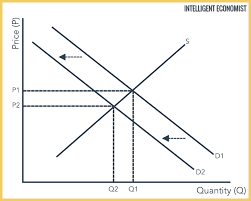
Does this show increase or decrease in demand?
Decrease in demand.
What is the M in Merit?
Market Size
If the number of consumers goes up: The Market demand goes up.
What is the E in Merit stand for?
Expectations by Consumers
If the expectations are up to par in the future: Demand goes up.
What does the R stand for in MERIT?
Related Prices (Substitutes & Complements)
If A and B are substitutes: and the price goes up, Demand Quantity goes up.
If A and B are compliments: and the price goes up, Demand goes down.
What does the I stand for in MERIT
Income of Consumers (Normal and Inferior)
If good A is a normal good, and income goes up: Demand goes up
If good A is a normal good and
What does the T stand for in MERIT
Tastes and Preferences.
Substitute in Consumption
Consumers will typically either buy one or the other.
Complements in Consumption
Two goods that are jointly produced given the same resources.
Quantity Supplied
The amount of a good or service people are willing to sell at some specific price.
Supply Schedule
Shows how much a good or service producers would supply at different prices.
Supply Curve
Shows the relationship between the quantity supplied and the price.
Law of Supply
Other things being equal, the price and quantity supplied of a good are positively related.
Change in Supply
Shift of the supply curve, in which indicates a change in the quantity supplied at any given price.
Movement along the supply curve
A change in the quantity supplied of a good arising from a change in the good’s price.
Input
A good or service that is used to produce another good or service.
Substitutes in Production
Two goods that producers can use the same inputs to make either one good or the other.
Complements in Production
Two goods are __________ if increased production of either good creates more of the other.
Equilibrium
Quantity where buyers are willing to purchase and sellers will want to provide.