Topic 1 - Atomic structure and the periodic table
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Definition of compound, mixture, element, molecule
Element = A substance containing only one type of atom
Compound = Two or more different elements chemically bonded together
Mixture = Different elements or compounds not chemically bonded together
Molecule = Any element chemically combined, e.g. methane containing carbon and hydrogen, water containing hydrogen and oxygen, ammonia, nitrogen and hydrogen
examples of physical separation techniques and when it can be used
Filtration
Distillation
Crystallisation
Chromatography
Can only be used to separate mixtures
Method of Filtration
Used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid
Equipment:
Filter paper
Filter funnel
Conical flask
Method:
Pour the mixture into the filter paper
This will cause the liquid to pass through the tiny pores in the filter paper
The liquid that passes through the filter paper is known as the filtrate
The solid material cannot pass through the filter paper, so it is trapped
Once all the liquid has passed through the tiny pores of the filter paper we have the liquid separated from the solid
Method of Crystallisation
Used to separate a soluble solid from a liquid but keeping the solid instead of the liquid
Method:
Dissolve the soluble solid into the liquid to form an aqueous solution
Pour the aqueous solution into an evaporating basin
Using a Bunsen burner gently heat the aqueous solution - allow some of the water to evaporate but not all otherwise you won’t form crystals
Place the evaporating basin by a windowsill and leave it overnight for crystals to form
Method of simple distillation
Used to separate a soluble solid from a liquid but keeping the liquid instead of the solid
Apparatus:
Place the solution with the liquid and dissolved solid into the flask
The flask is connected to a glass tube. This glass tube is surrounded by a condenser.
Cold water from the tap continuously runs through the condenser, keeping the internal glass tube cold.
A thermometer is also included
Method:
Heat solution using a Burner
As the solution is heated the liquid evaporates turning into a vapour
The vapour rises up the glass tube
As the vapour passes over the thermometer the thermometer reading increases
The solution is usually heated until it boils
The vapour then passes into the condenser
The vapour then condenses when it is in the glass tube surrounded by the condenser because cold tap water is circulating around the condenser
The vapour therefore turns into a liquid as it passes through the condenser
The solid is in the flask while the liquid is collected in the beaker
Pros and cons with simple distillation
Simple distillation can be used to produce drinking water from sea water. However a lot of energy is required for simple distillation so generally it is not used to produce drinking water
What is fractional distillation
In fractional distillation we separate a mixture of different liquids. However, these different liquids must have different boiling points.
Apparatus used in fractional distillation
Apparatus:
A mixture of two different liquids in a flask
The flask containing the mixture is attached to a fractionating column containing hundreds of glass beads
At the top of the fractionating column we have a thermometer
Then there is a condenser which cold tap water circulates around
Method for fractional distillation
Method:
Gently heat the mixture ensuring that in the mixture the different liquids have different boiling points
All of the liquids will start to evaporate but the one with the lower boiling point will evaporate more easily.
Now there is a mixture of two different vapours entering the fractionating column.
When the vapours reach the fractionating column they condense and drip back into the flask where the liquids evaporate again.
This repeated evaporation and condensation increases the amount of the lower boiling point chemical in the fractionating column.
The temperature on the thermometer will rise meaning that a mixture of the different vapours is passing over the thermometer. However, the mixture will contain more of the chemical with the lower boiling point.
These vapours now pass into the condenser and turn back to a liquid. However, this liquid is still a mixture of the different chemicals
Eventually the temperature on the thermometer stops rising this will be the reading of the lower of the two boiling points.
Now we have mainly one chemical passing into the condenser. As this chemical condenses we can collect it in a fresh beaker.
This is our first proper fraction in other words the chemical which has the lowest boiling.
Eventually the temperature on the thermometer begins to rise again meaning that a mixture of vapours are passing into the condenser. However, this mixture mainly contains the chemical with the higher boiling point.
When the thermometer reaches a constant temperature we are now collecting a relatively pure sample of the second chemical.
We have now separated the different chemicals based on their boiling points.
Pros and cons of fractional distillation
If the two liquids have very similar boiling points then it is much harder to separate them so we many need to carry out several rounds of fractional distillation.
The equipment is not really useful for separating a very large volume of liquid. e.g. refining crude oil
What is Paper chromatography
Paper chromatography allows us to separate substances based on their different solubilities.
Method for Paper chromatography
Take a piece of chromatography paper.
draw a pencil line near the bottom of the paper.
Then put a dot of our first colour onto the pencil line
Then put a dot of our second colour next to the first colour. It is possible to do this for several colours ensuring there is enough space on the paper
Then place the bottom of the paper into the solvent. Ensuring that the solvent doesn’t go above the pencil line to prevent the colour dissolving to the solvent
As the solvent moves up the paper it dissolves the ink in the two coloured dots which causes the ink to be carried up the paper dissolved in the solvent
What are the two phases in Paper chromatography
The paper is called the stationary phase because the paper does not move.
The solvent is called the mobile phase because the solvent moves.
paper chromatography results and what they mean
If only one spot of colour forms on the paper this means that the original spot placed on the pencil line is a single pure colour.
However, if there are two different spots of colour forming on the paper this tells us that the original colour placed on the pencil line was a mixture of two different colours.
This tells us that a pure compound will produce a single spot in all solvents. Whereas the compounds in a mixture may separate into different spots depending on the solvent.
Why does paper chromatography work
paper chromatography works because different substances have different solubilities.
A more soluble substance is more attracted to the mobile phase.
Why is the starting line drawn in pencil
If we drew the line in pen, the pen ink could dissolve in the solvent and move up the paper
What was the first discovery of atoms
The ancient Greeks believed that everything is made of atoms. They believed that atoms are tiny spheres which cannot be divided. This idea was accepted for hundreds of years.
When was the negative particle discovered?
In 1897, scientists discovered that atoms contained tiny negative particles which are now called electrons.
What did the discovery of negative particles mean for the ancient Greeks?
This proved the ancient Greeks wrong as scientists discovered that atoms are not tiny spheres that cannot be divided and instead have an internal structure.
What was the first model of the atom
Plum pudding model
Describe the plum pudding model
In the plum pudding model, an atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded in it.

What experiment was carried out to prove if the plum pudding model was correct?
alpha scattering experiment
Describe the alpha scattering experiment method
Scientists took a piece of gold foil (used gold because we can hammer gold into very thin foil, just a few atoms thick)
Then they fired tiny positive particles(alpha) at the gold foil
Results from the alpha particle scattering experiment
They found that many alpha particles passed straight through the foil without changing direction. Sometimes particles were deflected and sometimes they bounced straight back off the gold foil.
From the results of the alpha particle scattering experiment was was concluded?
Because most of the particles went straight through the gold foil, it was concluded that atoms were mainly empty space. This already proved the plum pudding model wrong.
Because some were deflected, they concluded that the centre of the atom must have a positive charge. (alpha particles are positive, so if it gets close to the positive centre then it will repel and change direction)
Because some bounced straight back, it was concluded that the centre of an atom must contain a great deal of mass.
What replaced the plum pudding model?
Nuclear model
Describe the nuclear model
Most of the atom is simply empty space. In the centre of the atom there is a tiny positive nucleus - containing most of the mass of the atom. Around the edge of the atom, there are negative electrons
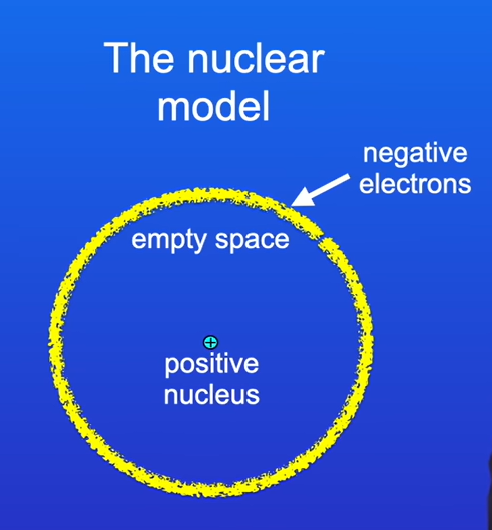
Why was the nuclear model modified?
It was proved by the alpha particle scattering experiment that the nuclear model was correct however in the following years, further discoveries were made.
What did Niels Bohr do?
He proposed the idea that electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances, rather than just in a general area. This was based on calculations that Bohr carried out.
What happened to Bohr’s idea?
It was accepted because it agreed with the results of experiments by other scientists. The orbits of electrons are now called shells.
Why was there a positive charge in the centre of the atom?
It was because of tiny positive particles which they called protons.
What does the amount of protons mean?
It determines the amount of positive charge in the nucleus.
What did James Chadwick discover?
He discovered that the nucleus also contains neutral particles which he called neutrons.
What is the radius of an atom?
around 0.1 nanometers (1×10^-10m)
What is the radius of the nucleus?
approximately 1×10^-14 m
Relative charge of protons, neurons and electrons?
Proton = +1
Neutron = 0
Electron = -1
overall charge of atoms
0, because the number of protons is the same as the number of electrons. (cancellation)
What is the relative mass?
It means the mass of one particle compared the another
Relative mass of protons, neutrons, electrons
Protons = 1
Neutron = 1
This means that protons and neutrons have the same mass
Electrons = negligible
what is the atomic number?
It is the smaller number (bottom) and it tells us the number of protons in atoms of that element.
what is the mass number?
tells us the total number of protons and neutrons added together. it is the larger number (top).
How to calculate the number of neutrons in an atom?
subtract the atomic number from the mass number
What is an isotope?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. They have the same number of protons and electrons different number of neutrons.
What are ions?
Ions are atoms which have an overall charge because they have either lost or gained electrons.
Difference between positive and negative ions?
Positive ions have lost electrons
Negative ions have gained electrons
Why does chlorine have a mass number of 35.5 and what is relative atomic mass?
Because it is an average of the mas numbers for each isotope (chlorine 35 and chlorine 37). However, the average is weighted for the abundance of each isotope. This is the relative atomic mass.
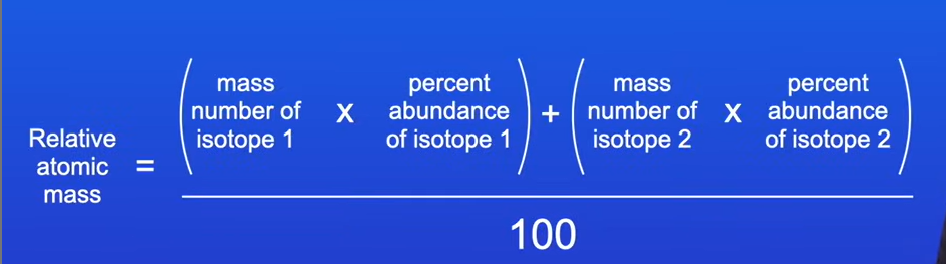
How to calculate relative atomic mass for an element based on its isotopes?
We use this equation:
mass number of isotope 1 x percent abundance of isotope 1
+ mass number of isotope 2 x percent abundance of isotope 2
answer/100
What does the number of electrons in the outer shell tell us?
It tells us the group number of that element in the periodic table
Where are elements with a full outer shell put on the periodic table?
Group 0 - noble gases
Origin of the name ‘periodic table’
The word periodic means occurring at regular intervals and in the table the elements with similar properties occur at regular intervals.
Why are elements organised in groups?
All the elements in a group have similar chemical properties, so they react in a similar way because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shell.
What was Döbereiner’s Triads?
Johann Döbereiner noticed that elements with similar chemical properties often occurred in threes.
Examples of the triads
Lithium, Sodium, and Potassium which are three metals that all react rapidly in water.
Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine which are all reactive non-metals
What was John Newland’s law of octaves
He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic weight, and he saw that every eighth element reacted in a similar way.
Problems with the law of octaves
By always sticking to the exact order of atomic weight, sometimes elements were grouped together when they had totally different properties. So, his octaves were not taken seriously by others.
What did Dmitri Mendeleev do?
He developed the first modern periodic table.
How did Mendeleev develop the first modern periodic table?
He started by arranging all the elements in order of increasing atomic weight.
However, if needed he would switch the order of specific elements, so that they would fit the patterns of other elements in the same group.
He also realised that some elements hadn’t been discovered yet, so he left gaps when he thought an element was missing.
He was very confident with this, that he even predicted the properties of the undiscovered elements based on other elements in the same group.
Why did others deem Mendeleev’s periodic table correct?
Many years later, new elements were discovered and their properties matched his predictions.
Difference between Mendeleev’s periodic table to the modern one
In the modern periodic table, the elements are arranged in order of atomic number. However, when Mendeleev developed his table, protons hadn’t been discovered so he ordered the elements by atomic weight.
However, this made it seem like his table was in the wrong order because of isotopes.
Modern periodic table has group 0 (noble gases), these hadn’t been fully discovered when Mendeleev published his table
What did ordering in atomic weight mean for Tellurium and Iodine
When ordered by atomic weight they were in the wrong groups, but when ordered by atomic number they are in the right groups. However, Mendeleev addressed this problem when he swapped them around. This is ‘pair reversal’
Properties of noble gases
Very unreactive because they have a full over shell of electrons making them stable
All of the noble gases have boiling points lower than room temperature.
Boiling points of the noble gases increases as the relative atomic mass increases (as we move down group 0)
Where are metals on the periodic table?
Left
Where are non-metals on the periodic table?
Right
Where are the highly reactive metals on the table?
On the far left, in groups 1 and 2
What is in the centre of the periodic table?
Transition metals - they are generally less reactive than those in groups 1 and 2
What happens when metals react and why?
When they react, they lose electrons to achieve a full outer shell which gives them the stable electronic structure of a group 0 noble gas. This is true for all metals.
When they react they always for positive ions because they always lose electrons meaning that the protons and electrons no longer cancel each other out, leaving the metal with a positive charge.
How to show that a metal has become a positive ion?
By drawing square brackets around the ion and writing the overall charge in the top right corner.
What are group 1 metals called?
Alkali metals
Properties of alkali metals
Soft metals (can be cut with a scalpel)
relatively low melting points
Low density - they have a relatively low mass for their volume
React rapidly with oxygen, chlorine and water
When they react they all form ions with a 1+ charge.
How do alkali metals react with oxygen?
Reacts rapidly with oxygen in the air.
As we move down group 1, the metals react more rapidly
Formula for balancing the reacting alkali metals with oxygen
4M(s) + O2(g) → 2M2O(s)
M = metal
() = state
Alkali metals all react with oxygen in the same way because they all have one outer electron.
How do alkali metals react with chlorine?
Also react rapidly with chlorine (group 7)
Formula for balancing the reacting alkali metals with chlorine
2M(s) + Cl2(g) → 2MCl(s)
M = metal
() = state symbol
Alkali metals all react with chlorine in the same way because they all have one outer electron.
How does lithium react with water
Lithium reacts rapidly with water, we can also see fizzing which means a gas is being produced. Universal indicator turns purple telling us that we’ve make an alkaline solution.
How does sodium react with water?
We see a gas being produced because of fizzing and an alkaline solution forms. Sodium reacts more rapidly than lithium as the reaction is more aggressive
How does potassium react with water?
Reaction is extremely rapid, A gas is being produced and an alkaline solution forming. Lithium glows and moves around faster in the water than sodium.
Formula for balancing the reacting alkali metals with water
2M(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2MOH(aq) + H2(g)
M = metal
(aq) = aqueous
What is aqueous
When something is dissolved in water it is called aqueous
Why do group 1 metals get more reactive as we move down the group?
As we move down metals lose an electron more easily than the other making them more reactive. This is because as we more down group 1, the radius of the atoms increases which means there is a greater distance between the positive nucleus and the negative outer electron. As this distance increases, the outer electron is less attracted to the positive nucleus. Secondly, the outer electron is repelled by electrons in the internal shells, this is called shielding. Shielding decreases the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electron. As we move down group 1, the elements have more electrons in their internal shells which means that shielding increases as we move down group 1.
These two reasons make the outer electron less attracted to the nucleus as we move down group one making it easier to lose electrons - this makes elements more reactive as we move down in group 1.
What is group 7 called?
Halogens
What are halogens and what is their electron structre?
non-metals that have 7 electrons in their outer energy level
How do halogens react?
They covalently bond with each other.
What is a covalent bond?
When elements bond when sharing electrons
What do every group 7 element form?
A molecule consisting of two atoms joined by a covalent bond with itself.
How to show a halogen has covalently bonded without electrons?
Use a stick (long dash) between the two elements like this:
F — F
I — I
Cl — Cl
Br — Br
When do the melting and boiling points of halogen change?
They change when we more down the group
How to work out the physical state of each halogen at room temperature (20oC)
By using the melting and boiling points.
How do melting and boiling points change in group 7?
The melting and boiling points increase as we move down group 7
State of Fluorine and Chlorine at room temperature (20 degrees)
Gas because their boiling points are lower than 20 degrees.
Why is Bromine a liquid at room temperature, and Iodine solid?
Bromine is a liquid at room temperature because the melting point of bromine is lower than 20 degrees but the boiling point of bromine is higher than 20 degrees.
Iodine is a solid at room temperature because both the melting and boiling point of iodine is higher than 20 degrees.
What is the relative molecular mass?
It gives us an idea of the size of a molecule
What is the trend in relative molecular mass in halogens?
As we move down group 7, the relative molecular mass increases. So the molecules get bigger as you move down group 7.
What do halogens form when they react with non-metals?
Group 7 elements form covalent compounds when they react with other non-metal elements.
What happens when halogens react with metals?
When halogens react with metals, they form ionic compounds. When a halogen reacts with a metal atom the halogen gains one electron from the metal atom, this gives the halogen an overall charge of -1.
What happens to the name of the halogen when it forms an ion with a metal?
When halogens form ions with a -1 charge the name of the halogen now ends with “ide”.
e.g.
fluoride ions
chloride ions
bromide ions
iodide ions
What happens to the negative electron that the halogen gains?
The negative electron is attracted to the positive charge in the nucleus of the halogen atom.
Trend in reactivity in halogens
Fluorine is most reactive, and halogens get less reactive as we move down group 7. This makes Iodine the least reactive.
Why does reactivity decrease as you move down group 7?
Elements that are less reactive gain electrons less easily, this is because of two reasons.
As you move down group 7, the distance between the outer shell and the nucleus increases. This means that the outer electrons are less attracted to the positive nucleus as you move down group 7.
There are more electrons in the internal shells as you move down group 7. Electrons in internal energy levels repel the outer electrons. This is shielding. As you move down group 7, the level of shielding increases.
So, both the increased distance and increased shielding mean that the attraction between the outer electrons and the nucleus is lower as you move down, making it harder for atoms at the bottom to attract an electron in its outer shell than it is for atoms at the top. This makes atoms at the bottom less reactive than those at the top.
What can a more reactive halogen do to a less reactive halogen?
A more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive halogen from an aqueous solution of its salt.
Formula for a balanced displacement equation
2MX + X2 → 2MX + X2
M = metal
X = halogen
MX = metal compound
X = different halogen (one that is more reactive and displaces the other)