Static Electricity
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is the charge of a proton?
1.6 x 10-19 C
What is the charge of an electron?
1.6 x 10-19 C
How are positive ions formed?
losing electrons
How are negative ions formed?
gaining electrons
SI unit of charge
coulomb (C)
The formula for charge is:
Q = ne
Q is charge
e is charge on one electron
n is the number of electrons
State the law of electrostatics.
The law of electrostatics states that like charges repel and unlike charges attract
The force of attraction and repulsion increases as the distance between charges ….
decreases
Only … between a specimen and a charged object is a sure test that allows us to conclude that the specimen is charged.
repulsion
What are electrical conductors?
allow electric charges to flow through them easily.
What are electrical insulators?
do not allow electric charges to flow through them easily.
Why are metals good electrical conductors?
presence of free electrons which can move freely when there is an electric force.
Why can’t insulators conduct electricity?
the electrons are tightly bound to their own atoms and not free to move between atoms.
Difference between the electrons in conductors and insulators
Conductors have ‘free electrons’ or free moving ions that are able to move freely while insulators do not
Why can’t we describe the movement of protons?
because they are found tightly bound within the nucleus of the atom. We can describe movement of positively-charged objects or positive ions (having excess positive charges)
What is an electric field?
a region where an electric charge experiences an electric force.
What is an electric line of force?
the path a positive charge would take if it was free to move.
What is the direction of the electric field?
The direction of how a positive test charge would move.
A stronger electric field = more electric lines of force drawn … to each other
closer
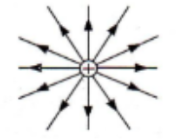
Electric field around positively charged sphere
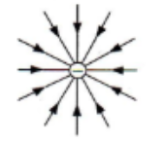
Electric field around a negatively charged sphere
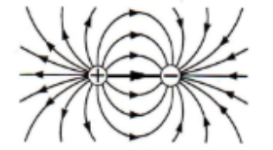
Combined electric field between two opposite charges
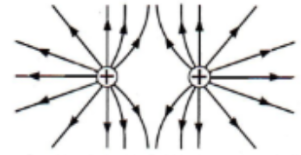
Combined electric field between two similar positive charges
electric field between two opp charged plates; almost uniform
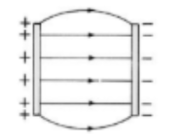
stronger electric field between two opp charged plants; almost uniform +increased density of lines
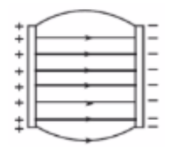
What happens when two different materials (esp. insulating) are rubbed together?
negative charges [electrons] are transferred from one object to another.
The material that loses electrons will become…
positively charged
the material that gains electrons will become…
negatively charged
High electron affinity = … tendency to acquire more electrons
Higher
What is the triboelectric series?
ordering substances according to their affinity

Name some common materials that can be charged by friction to become negatively charged.
Polythene
Ebonite / Amber / Rubber
Name some common materials that can be charged by friction to become positively charged.
Perspex
Glass
What do you rub polythene with to make it negatively-charged?
Wool
What do you rub ebonite / amber / rubber with to make it negatively-charged?
fur
What do you rub perspex with to make it positively-charged?
wool
What do you rub glass with to make it positively-charged?
silk
How do we neutralise electrostatic charges in insulators?
Pass quickly through bunsen flame
How do we neutralise electrostatic charges in conductors?
Touch apparatus to allow excess electrons to flow through our body to the ground (earthing)
When charging via induction, why are the metal spheres placed on insulating stands?
so that excess charges would not flow to or from the Earth to neutralize the metal spheres
What is the advantage of charging by induction?
the net charge of the original charged object remains unchanged, no matter how many times we charge by induction
Can we charge two conductors with friction / by rubbing? (3)
Two conductors cannot be charged with rubbing
because excess charges on the conductor in our hands would flow to the ground/Earth so the conductor would become neutralized.
The excess negative charges would flow from one conductor to another such that both conductors are neutralized.
Can we charge two insulators with induction? (2)
Insulators cannot be charged via induction.
As surface electrons could move only a small distance, an insulator would remain overall neutral as its negative charges cannot leave its surface.
How do we charge two neutral insulated spheres? (7)
Two neutral metal spheres on insulating stands, P and Q are placed touching each other.
A negative polythene strip is brought near P.
Electrons on P are repelled away from the strip and move into Q, leaving behind excess positive charges on the end of P nearer to the negatively-charged strip.
Sphere Q is then separated from P while the negatively-charged polythene strip is kept in position.
Polythene strip is removed.
Sphere P becomes positively-charged while Sphere Q becomes negatively-charged.
Since spheres P and Q are conductors, they have equal amounts of opposite charges which are redistributed throughout spheres P and Q when far apart.
How do we charge a single insulated sphere → negative? (6)
Positively-charged acetate strip is brought near a neutral conductor (metal sphere) mounted on an insulating stand.
Electrons of the conducting sphere are attracted to the positively-charged strip at end P, leaving behind positive charges at the other side, Q of the conductor.
The conductor is then earthed by touching it with a finger.
As the negative charges at P are attracted to the positive charges of the strip, this allows electrons to flow up from the Earth to neutralize the positive charges at Q.
Finger is then removed from the conductor.
Acetate strip is removed and there is a redistribution of the excess negative charges on the sphere due to the law of electrostatics and the sphere is left negatively-charged.
How do we charge a single insulated sphere → positive? (6)
Negatively-charged polythene strip is brought near a neutral conductor (metal sphere) mounted on an insulating stand.
Electrons of the conducting sphere are repelled away from the negatively-charged strip and move to end Q, leaving behind positive charges at the other side, P of the conductor.
The conductor is then earthed by touching it with a finger.
As the positive charges at P are attracted to the negative charges of the strip, this allows electrons at Q to flow down to Earth.
Finger is then removed from the conductor.
Polythene strip is removed and there is a redistribution of the charges on the sphere due to the law of electrostatics and the sphere is left positively-charged.
What are some electrostatic hazards?
Lightning
Fires due to sparks caused by electrostatic discharge
Damage to electronic equipment
How does lightning happen?
Thunderclouds are charged by friction between water molecules in the thunderclouds and air molecules.
Ionises the air → ionised air provides a conducting path for electric charge to be discharged to the nearest or sharpest object on the ground
How do overcome the hazard brought by lightning?
Lighting conductors on buildings → provide conducting path for electrons in air to discharge safely to the ground
What are some ways we overcome the hazard of fires due to sparks caused by sudden electrostatic discharge?
Excess charges on a petrol tanker flow safely through a metal chain to the ground
Synthetic rubber types containing graphite aid in electric discharge to the ground
What are some ways we overcome the hazard of damage to electronic equipment?
Electrical components are stored in antistatic packaging (metallised film)
What are some applications of electrostatics?
Electrostatic paint spraying
Photocopier
Electrostatic precipitator
How does electrostatic paint spraying work? (3)
Paint droplets from an aerosol become charged from rubbing against the nozzle of the spray
Droplets attracted to the metal body of the car which is earthed
Since droplets have the same charge, they repel each other in the spray and spread out evenly → even coat of paint
How does a photocopier work? (8)
Makes use of a metal selenium (photoconductor) which conducts when in light, insulator in the dark
Whole surface of drum is charged positively by rotating it near highly charged metal wire
When a printed page is photocopied, light is reflected off the page and projected onto the drum
White parts of page reflect light to some parts of the drum → these areas become conducting and lose charge
Other parts of the drum correspond to black parts of the page → areas on drum receive no light and remain insulating/charges remain
Fine particles of carbon powder (toner) are attracted to the charged areas of drum and presses against the copy paper
Toner is transferred onto photocopy as drum rotates and presses against the copy paper
Heat is supplied to melt toner power and fix it onto paper surface
How does an electrostatic precipitator work?
Consists of metal plates that are positively charged and a number of negatively charged metal rods running through them
Air molecules around rods are ionized
Positive ions are attracted back to rods
Negative ions picked up by tiny particles of ash and dust
Negatively charged particles are attracted to the metal plates where they are collected
What is an electrostatic precipitator used for?
to remove fine ash and dust from chimneys
What is an electrostatic paint spray used for?
to ensure an even coat of paint
What is field strength?
Field strength is a region of space where an object experiences a force.
How can a charged conductor that is insulated from the ground be neutralized?
By providing a path to the ground (earthing the conductor) such as a conducting wire.
Ionising the air around it by heating it up.