practical 1 a&p 2
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
what CN innervates the lateral rectus?
VI abducens
what CN innervates medical rectus?
III oculomotor
what CN innervates the superior rectus?
III oculomotor
what CN innervates the inferior rectus?
III oculomotor
what CN innervates the inferior oblique?
III oculomotor
what CN innervates the superior oblique?
IV trochlear
action of lateral rectus?
turn eye laterally/ abduction of eye
action of medial rectus?
turn eye medially
action of superior rectus?
elevate and adduct the eye, raise eye superiorly
action of inferior rectus?
depress and adduct eye, move eye inferiorly
action of inferior oblique?
move eye superiorly and laterally, externally rotates eye
action of superior oblique?
move eye inferiorly (depression) and laterally (abduction) , rotate top of eye toward nose (intorsion)
parts of fibrous tunic?
sclera and cornea
parts of vascular tunic?
iris, ciliary body, and choroid
parts of retina?
pigmented layer and neural layer
what are the 3 tunics of the eye?
fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, retina
blind spot test
test to find where blind spot is(optic disc)/if you have one
as you move paper closer to eye and focus on one dot, the other will disappear
near point accommodation test
determine where your near point is
as you move the paper closer, you see to objects or it becomes blurry. measure where you can last see everything clearly
visual acuity test
test your vision using a Snellen chart
astigmatism test
tests for astigmatism and near/far sightedness
none of the lines on the paper should appear blurry or different colors (this indicates astigmatism)
color blindness test
often uses pictures and numbers to differentiate colors, tests if you are colorblind or not
depth perception test
test depth perception by if you can put a pencil in a test tube with one eye closed
photo pupillary reflex
a protective response to prevent damage to photoreceptor cells, constricting of pupil to limit light entry and protect retina and adjust brightness
accommodation pupillary reflex
pupil size changes when viewing distant vs. near objects, allows you to switch between objects yet still maintain focus
convergence reflex
position of eyeballs change when viewing distant vs near objects; simultaneous movement of both eyes inward allowing you to keep the image focused on the fovea centralis
emmetropic
clinical term for “ideal” or normal vision where light rays from distant objects focus directly on resin without needing corrective lenses
myopic
near-sighted (can see close but not far)
hyperopic
farsightedness (can see far but not close)
presbyopic
nature, age related decline in ability to focus on close objects
astigmatism
blurred or distorted vision at all distances caused by irregularly shaped cornea
accommodation
eye’s automatic process of adjusting the Len’s curvature, become more convex for near objects and flatter for distance, to maintain clear focus
chemoreceptor
specialized sensory cells that detect chemical changes in body’s internal and external environments
how many types of taste receptors are there?
5 (sweet, salty, umami, sour, bitter)
what is the organ of smell and where is it located?
olfactory epithelium located in the roof of the nasal cavity
what type of neurons are olfactory receptor cells?
bipolar neurons
where do you find olfactory cilia?
the apical surface of olfactory sensory neurons *which are in olfactory epithelium of upper nasal cavity)
what is the name for the specific receptor for sense of taste? where do you find them?
gustatory cells, they are found in taste buds (which are part of papillae of tongue mucosa, only foliate, valuate, and fungiform) and is soft palate, esophagus, pharynx, and epiglottis
how many types of papillae are there and what are their names?
4 types, fungiform, foliate, vallate, and filiform papillae
which papillae contain receptors for taste?
fungiform, foliate, and vallate contains receptors for taste
filiform don’t contain receptors for taste
how do you test for the important of taste and olfaction in odor identification?
use different containers with different odors in each to test if you can identify the smell
Pen light test
tests Pupillary Reflex and pupil constriction when light is shined in eye
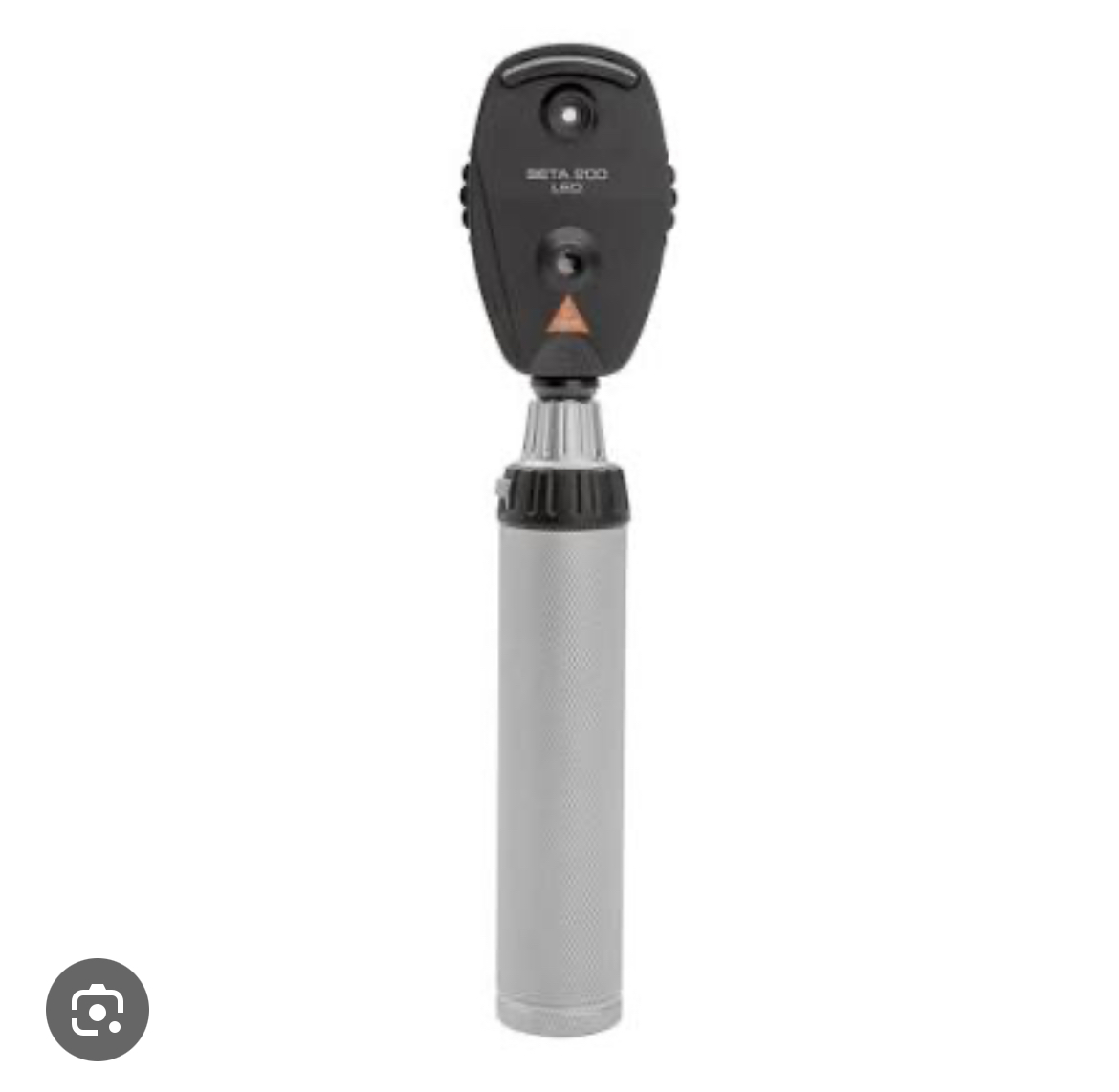

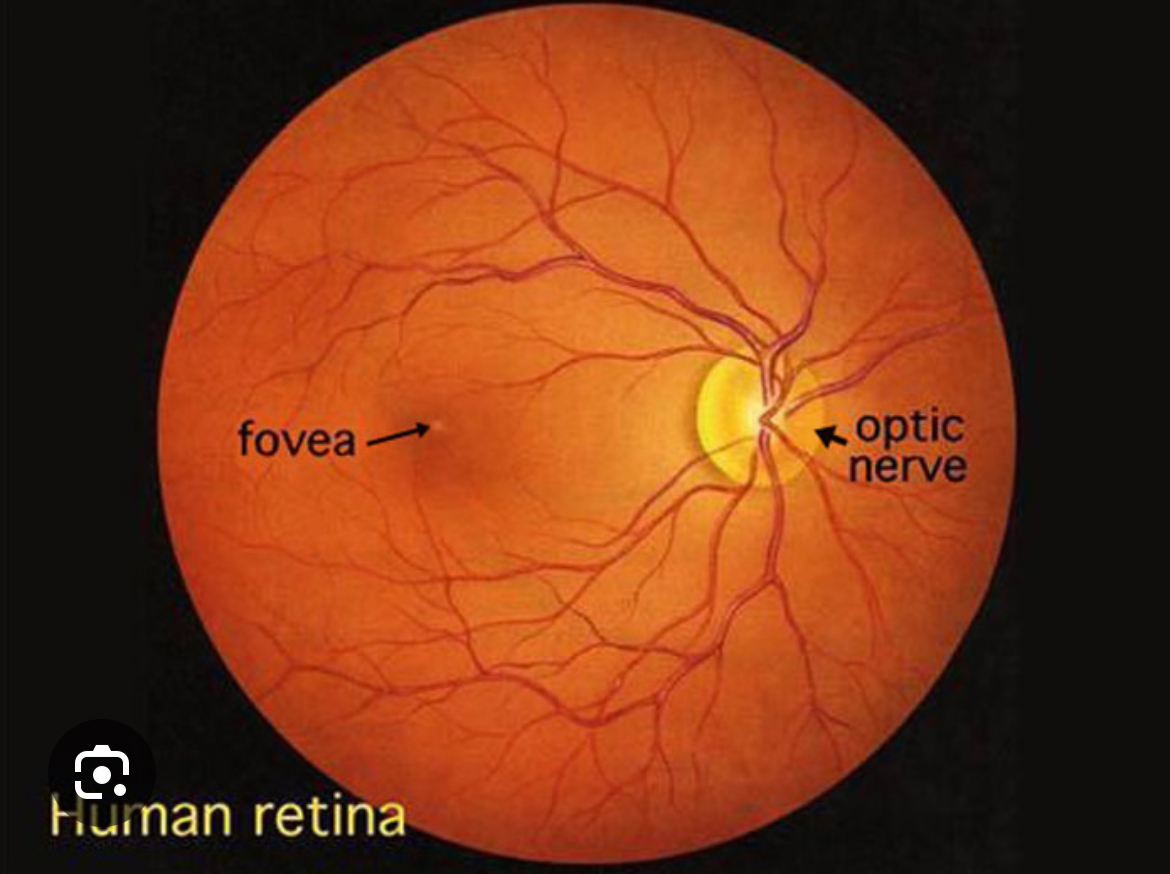
what is this instrument and what does it do?
ophthalmoscope, allows you to see there is blow flow to retina (blood vessels) and that retina is still intact
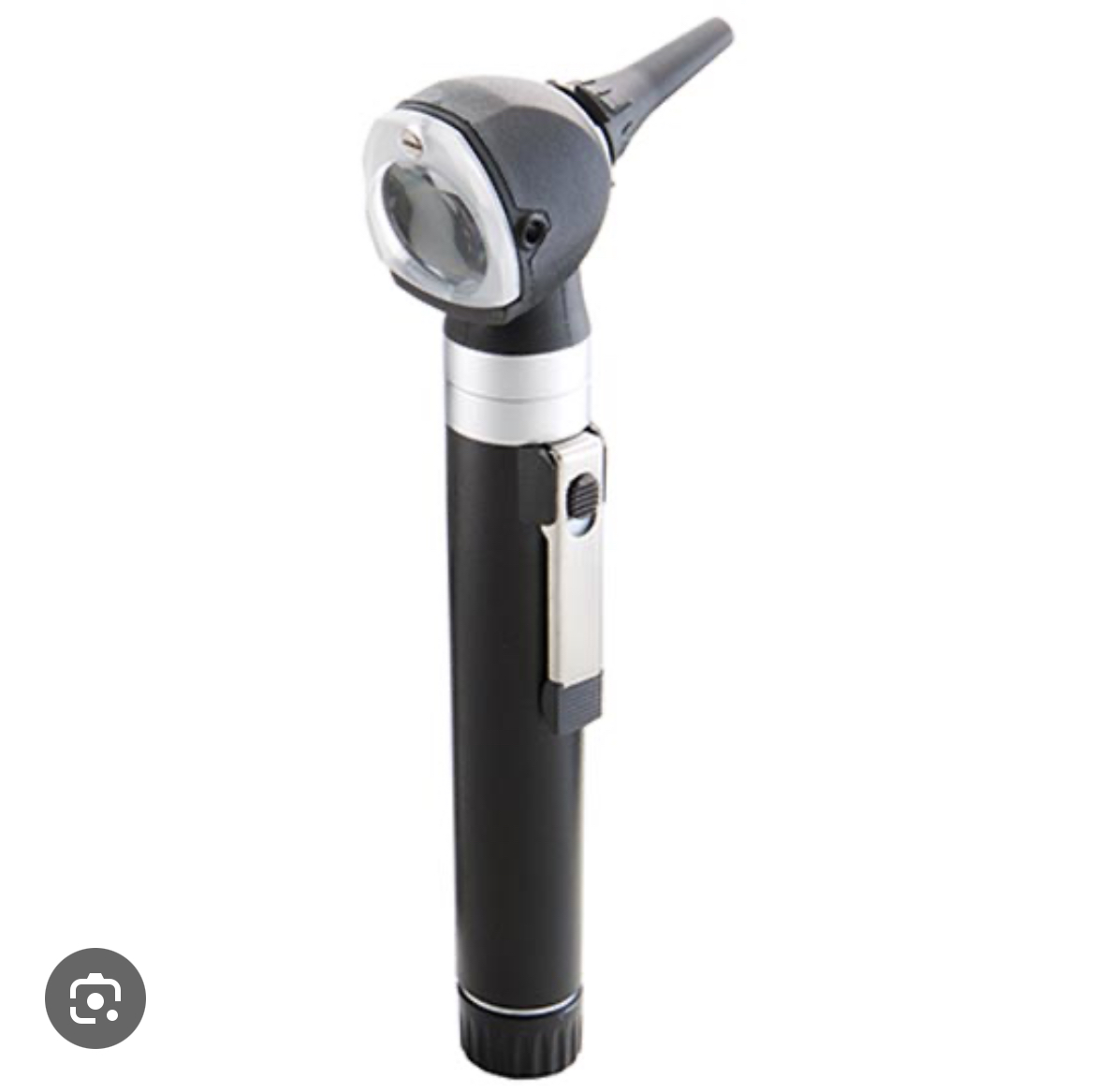

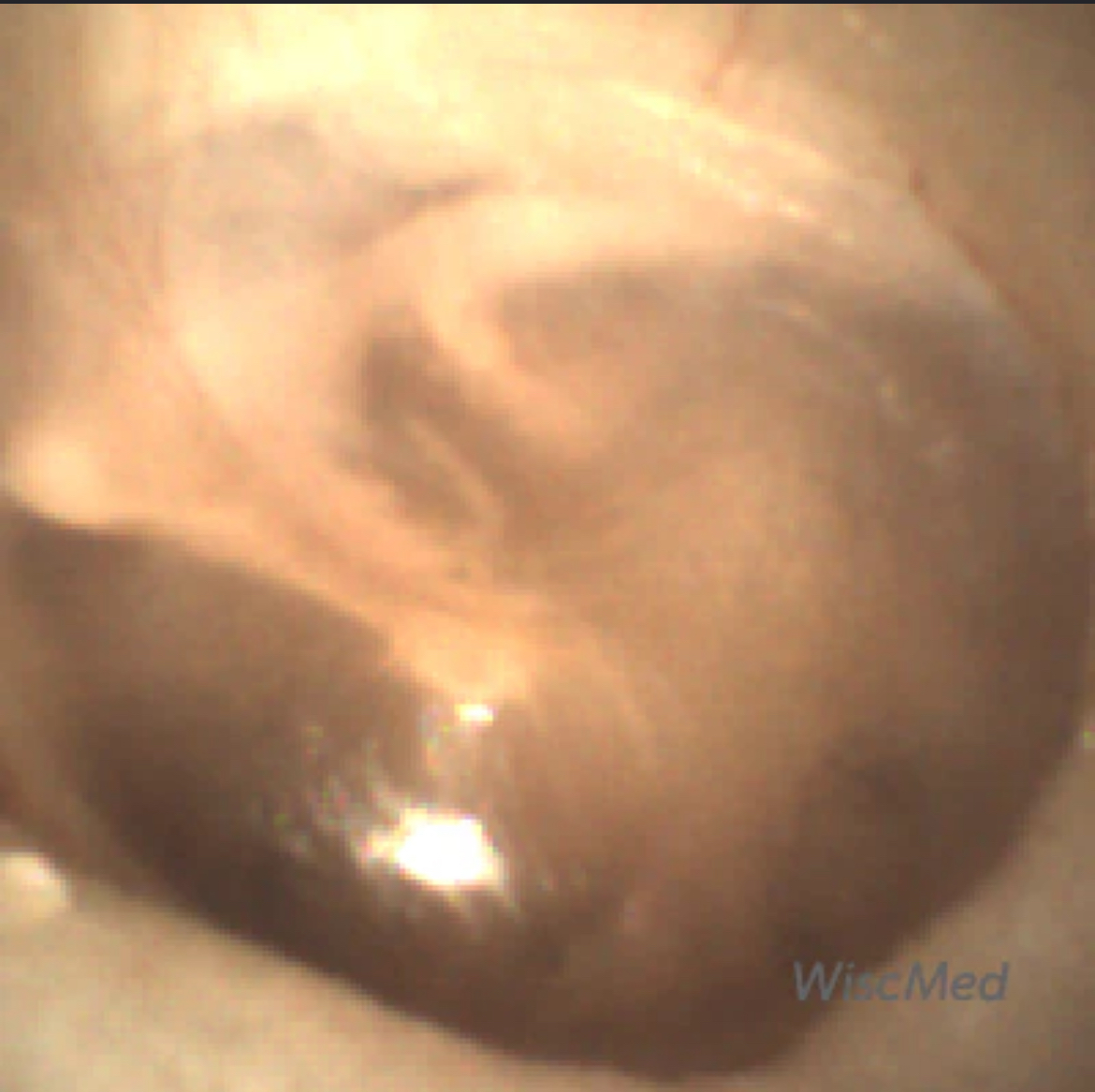
what is this instrument and what does it do?
otoscope, allows you to visualize tympanic membrane and make sure it is still intact
what is the measurement of binocular visual field test?
determine with a protractor your visual field, record when you first see an object in periphery to when you can’t see it anymore in other periphery
how did you demonstrate olfactory adaptation?
smell something for a long period of time and gradually you smell it less
what is an otoscope used for?
used to visualize the tympanic membrane and make sure it is still intact
what is an ophthalmoscope used for?
to visualize back of eye and make sure their is blood flow to retina dn that retina is still intact
is the cochlea for hearing or equilibrium?
hearing
is spiral organ for hearing or equilibrium?
hearing
is crista ampullaris for hearing or equilibrium?
equilibrium
hearing acuity test
tests hearing; patient puts headphones on and determines when they hear sounds (used to determine if there is hearing loss), test bone conduction
sound localization test
tests patients hearing at different areas to see if you have trouble hearing from one specific location
frequency range
measures the lowest to highest pitches a human can detect using a frequency response analyzer
weber test
tests conduction hearing and sensorineural deafness; sound should be the same and not louder of one side one tuning fork is placed on chin and forehead
rinne test
tests bone and air conduction hearing, as well as damage to tympanic membrane or ear ossicles; after sound from tuning fork can’t be heard on mastoid process it should be able to by heard by pinna of ear
bing test
tests for conductive hearing loss, when tuning fork is placed on mastoid process and finger is stuck in auditory canal should should be amplified
sound location test
tests hearing at different areas, should be able to correctly identify where sound is coming from
postural reflex test
tests for body’s ability to compensate for changes to static equilibrium; when pushed to left, left foot moves to compensate for change, **no swaying when walking in a straight line
barany’s test
test for nystagmus (rapid eye movement); after spinning, eyes should equalize and stop
Romberg test
determines integrity of the dorsal white column of spinal cord; when standing there should be no lateral sway
balance test
assess postural stability, see if you can balance on one leg
nystagmus
involuntary, rhythmic oscillation of one or both eyes
vertigo
false sensation of spinning or movement (often from inner ear problems)
hormone and effect of anterior pituitary
prolactin stimulates the mammary glands for milk synthesis
hormone and effect of posterior pituitary gland
antidiuretic hormone stimulates water retention in kidneys
hormone and effect of thyroid gland
calcitonin to lower blood calcium levels by stimulating bone deposition (especially in kids)
parathyroid gland hormone and effect
parathyroid hormone raises blood Ca +2 levels by stimulating bone resorption and inhibiting deposition, reducing urinary Ca +2 output from kidneys, and enchanting calictriol synthesis in small intestine
adrenal glands- cortex hormone and effect
aldosterone promotes Na+ and water retention and K+ excretion from kidneys, maintains blood pressure and volume
adrenal glands -medulla hormone and effect
epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine promote alertness, mobilize organic fuels, raise metabolic rate, and stimulate circulation and repiraiton
pancreas hormone and effect
insulin stimulates glucose and amino acid uptake, lowers blood glucose level, promotes glycogen, fat, and protein synthesis
thymus hormone and effect
thymosin stimulates T lymphocyte development and acuity
pineal gland hormone and effect
melatonin, affects the brain and controls circadian rhythm
ovaries hormone and effect
progesterone regulates menstrual cycle and pregnancy in uterus and prepares mammary glands for lactation
testes hormone and effect
testosterone stimulates fetal and adolescent reproductive development, musculoskeletal growth, sperm production and libido
pathway of blood to and from heart
blood enters through right atrium from superior and inferior venae cavae → blood in right atrium flows through tricuspid valve into right ventricle → contraction of right ventricle forces pulmonary valve open → blood flows thru pulmonary valve into pulmonary trunk → blood is distributed by right and left pulmonary arteries to the lungs where it unloads CO2 and loads O2 → blood returns from lungs via pulmonary veins to left atrium → blood in left atrium flows through bicuspid valve into left ventricle → contraction of left ventricle forces aortic valve open → blood flows through aortic valve into ascending aorta → blood in aorta is distributed to every organ in the body where it unloads O2 and loads CO2 → blood returns to right atrium via venae cave
simplified pathway of blood
venae cavae → right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary valve → pulmonary trunk → pulmonary arteries → lungs where co2 replaced by o2→ pulmonary veins → left atrium→ bicuspid valve → left ventricle → aortic valve → aorta→ blood flows through body
what heart chamber is oxygen rich?
left atrium and left ventricle
what heart chambers are oxygen poor?
right atrium and right ventricle
path of intrinsic conduction
sinuatrial node fires → excitation spreads through atrial myocardium → atrioventricular node fires → excitation spreads down atrioventricular bundle → subendocardial branches distribute excitation through ventricular myocardium
what is an ECG and what does it measure?
electrocardiograph- graphic recording of the electrical changes (repolarization and depolarization) occurring during the cardiac cycle
P wave
atria depolarizing
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
T wave
ventricular repolarization
heart rate formula
mm /beat x 0.04 sec/min x 60 sec/min
normal heart rate and normal range
60-100 bpm
bradycardia
excessively low HR below 60 BPM
tachycardia
excessively high HR above 100 BPM
fibrillation
heart upper chambers quiver instead of contracting m
myocardial infarction
heart attack, lack of blood flow to heart causes tissues to die
pulse points and arteries?
wrist = radial artery
neck= carotid artery
auscultation
involves listening to body sounds using a stethoscope
systole
phase of cardiac cycle where heart muscle contracts
diastole
phase of heartbeat when the heart muscle relaxes and allows the chambers to fill with blood
how do you calculate heart rate from an ECG?
count number of big or little squares between tops of waves
1500/# of little squares
300/ # of big squares
rhythmic throbbing of an arterial wall as blood is being pumped thru the vessel
pulse
where are the 2 most common pulse points?
radial artery (wrist)an and carotid artery (neck)
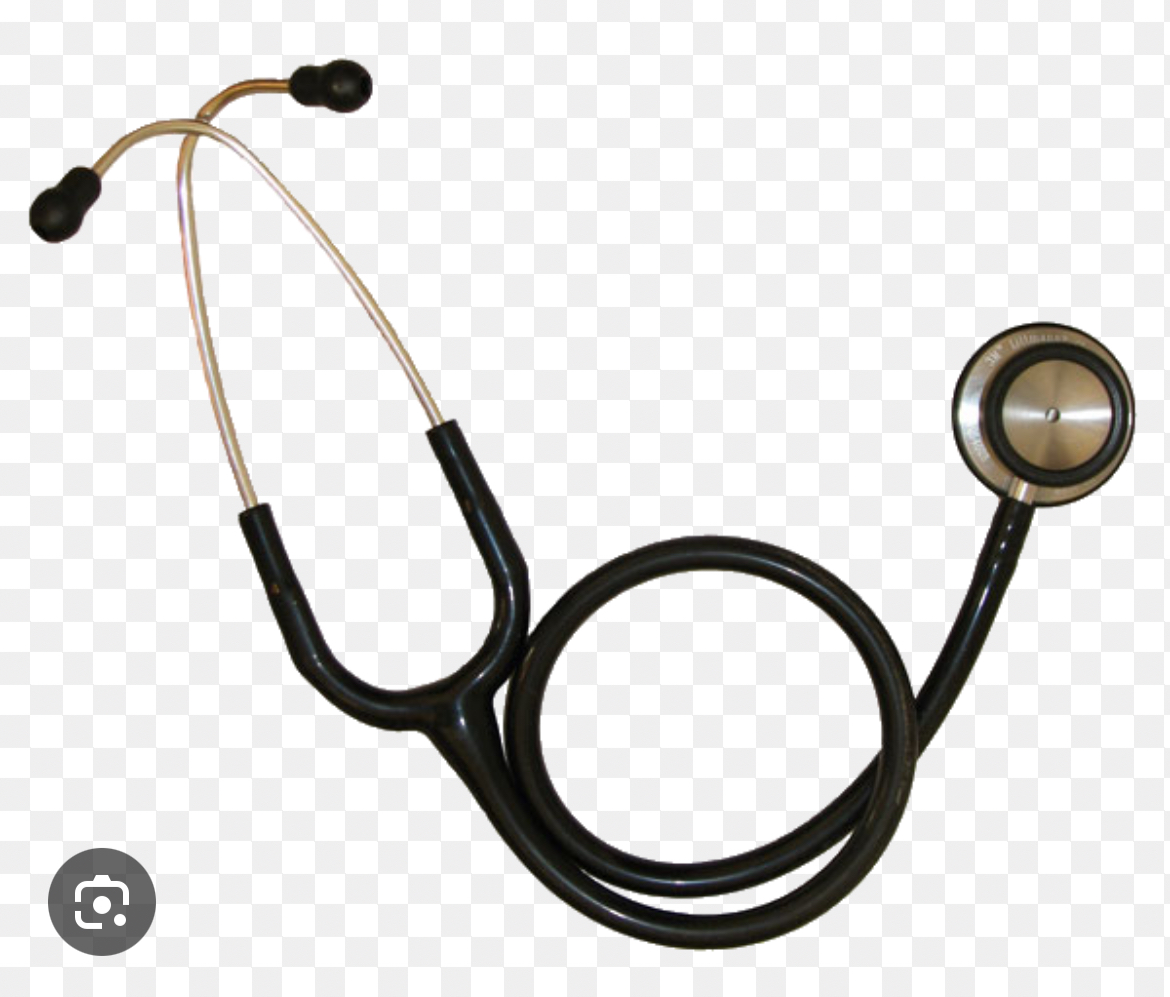
an instrument used for auscultation, listening to the internal sounds of the body
stethoscope
a hollow cup for low frequency sounds
bell of stethoscope
a flat solid disc for high frequency sounds (drum)
diaphragm of stethoscope
S1 = lubb sound
closing of atrioventricular valves